Dell PowerVault MD3000i Dell PowerVault MD3000/MD3000i Array Tuning Best Pract - Page 24
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices, Sharing Bandwidth with Multiple SAS
 |
View all Dell PowerVault MD3000i manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
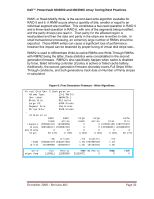
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices Figure 11: MD3000i Advanced IPv4 Settings: VLAN, QOS, Jumbo Frames Support 5.1.3 Sharing Bandwidth with Multiple SAS HBAs Each SAS wide port includes four full duplex serial links within a single connector. The individual SAS 1.1 links run a maximum speed of 3Gb/s. A single path is used as the primary path to a connected device - the second, third, and fourth paths are used as overflow, when concurrent I/Os overload the primary channel. For example, if the first link is transmitting data at 3Gb/s, SAS uses 10-bit encoding versus 8-bit for byte transmission, which makes a single 3Gb/s capped at 300MiB/s. If another block of data then needs to be written to disk, for example, and link 1 is still busy, link 2 will manage the overflow of data that cannot be transmitted by link 1. If link 1 finishes its transmission of data, the next block of data will be transmitted on link 1 again, otherwise another link will be used. In this way, for heavy I/O workloads, it is possible that all links are being December 2008 - Revision A01 Page 24