Dell PowerVault MD3000i Dell PowerVault MD3000/MD3000i Array Tuning Best Pract - Page 15
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices, 7.3 I/O Distribution
 |
View all Dell PowerVault MD3000i manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
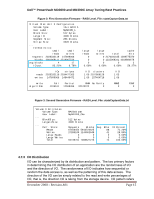
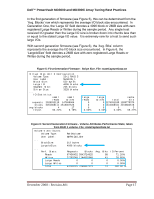
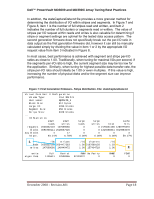
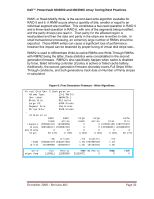
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices Figure 2: First Generation Firmware - RAID Level. File: stateCaptureData.txt Virtual Disk Unit 0 Configuration Volume Type: 13+1 RAID 5 User Label: MyRAID5_1 Block Size: 512 bytes Large IO: 4096 blocks Segment Size: 256 blocks Stripe Size: 3328 blocks ... IO Statistics: small small reads writes requests 2028332119 147699066 blocks 3091968111 2518067526 avg blocks 4 17 IO pct. 93.21% 6.78% large reads 0 0 0 0.00% large cache writes total hits 0 2176031185 1289775370 0 1315068341 4019884678 0 0 3 0.00% 0.00% 59.27% IOs stripes reads 2028332119 2034477363 writes 147699066 148449472 /IO clusters 1.00 2107869128 1.00 157404718 /IO 1.03 1.06 write algorithms Full Partial RMW No Parity 1105611 12598366 32120072 0 RMW2 0 FSWT 0 Figure 3: Second Generation Firmware - RAID Level. File: stateCaptureData.txt Volume 0 Attributes: Volume Type: User Label: ... BlockSize: LargeIoSize: ... Perf. Stats: Reads Writes Large Reads Large Writes Total RAIDVolume MyRAID10_One 512 bytes 4096 blocks Requests Blocks 67456452 5943724625 27283249 1144902648 0 0 0 0 94739701 7088627273 Avg. Blks 88 41 0 0 74 IO Percent 71.20% 28.80% 0.00% 0.00% 100.00% 4.7.3 I/O Distribution I/O can be characterized by its distribution and pattern. The two primary factors in determining the I/O distribution of an application are the randomness of I/O and the direction of I/O. The randomness of I/O indicates how sequential or random the data access is, as well as the patterning of this data access. The direction of the I/O can be simply related to the read and write percentages of I/O, that is, the direction I/O is taking from the storage device. I/O pattern refers December 2008 - Revision A01 Page 15