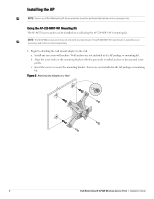
Dell W-Series 228 W-AP228 Access Point Installation Guide - Page 5
Identifying Known RF Absorbers/Reflectors/Interference Sources
 |
View all Dell W-Series 228 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
Pre-Installation Checklist Before installing your AP, be sure that you have the items listed below: Gigabit Ethernet cable of required length IEEE 802.3at compliant PoE source Dell controller configured and installed on the network Layer 2/3 network connectivity to your AP One of the following network services: Aruba Discovery Protocol (ADP) DNS server with an "A" record DHCP Server with vendor specific options NOTE: Dell in compliance with governmental requirements, has designed the W-AP228 access point such that only authorized network administrators can change configuration settings. For AP configuration information, refer to the Dell Networking W-Series ArubaOS Quick Start Guide and Dell Networking W-Series ArubaOS User Guide. CAUTION: Access points are radio transmission devices and as such are subject to governmental regulation. Network administrators responsible for the configuration and operation of access points must comply with local broadcast regulations. Specifically, access points must use channel assignments appropriate to the location in which the access point will be used. Verifying Pre-Installation Connectivity Before you install APs in a network environment, make sure that the APs will be able to locate and connect to the controller when they are powered on. Specifically, you must verify the following conditions: When connected to the network, each AP is assigned a valid IP address. APs can locate the controller. Refer to the Dell Networking W-Series ArubaOS Quick Start Guide for instructions on locating and connecting to the controller. Identifying Specific Installation Locations Use the AP placement map generated by Dell's RF Plan software application to determine the proper installation location(s). Each location should be as close as possible to the center of the intended coverage area and should be free from obstructions or obvious sources of interference. These RF absorbers/reflectors/interference sources will impact RF propagation and should have been accounted for during the planning phase and adjusted for in RF plan. Identifying Known RF Absorbers/Reflectors/Interference Sources Identifying known RF absorbers, reflectors, and interference sources while in the field during the installation phase is critical. Make sure that these sources are taken into consideration when you attach an AP to its fixed location. Examples of sources that degrade RF performance include: Cement and brick Objects that contain water Metal Microwave ovens Wireless phones and headsets Dell Networking W-AP228 Wireless Access Point | Installation Guide 5