Dynex DX-BUSB User Manual (English) - Page 13
Wireless Equivalent Privacy WEP, Wi-Fi Protected Access WPA, Currently, there are four encryption
 |
View all Dynex DX-BUSB manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
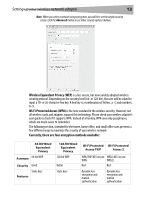
Setting up your wireless network adapter 13 Note: When you select a network using encryption, you will first see the simple security screen. Click the Advanced button to see other security options (below). Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a less secure, but more widely adopted wireless security protocol. Depending on the security level (64- or 128-bit), the user will be asked to input a 10- or 26-character hex key. A hex key is a combination of letters, a-f, and numbers, 0-9. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is the new standard in the wireless security. However, not all wireless cards and adapters support this technology. Please check your wireless adapter's user guide to check if it supports WPA. Instead of a hex key, WPA uses only passphrases, which are much easier to remember. The following section, intended for the home, home office, and small office user, presents a few different ways to maximize the security of your wireless network. Currently, there are four encryption methods available: 64-Bit Wired Equivalent Privacy Acronym 64-bit WEP Security Good Static keys Features 128-Bit Wired Equivalent Privacy Wi-Fi Protected Wi-Fi Protected Access-TKIP Access 2 128-bit WEP Better WPA-TKIP/AES (or just WPA2-AES (or just WPA) WPA2) Best Best Static keys Dynamic key encryption and mutual authentication Dynamic key encryption and mutual authentication