HP 800 ACSE/Presentation and ROSE Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 38
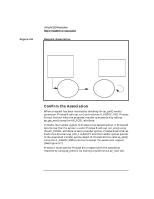
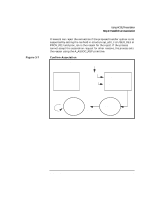
Confirm the Association
 |
View all HP 800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
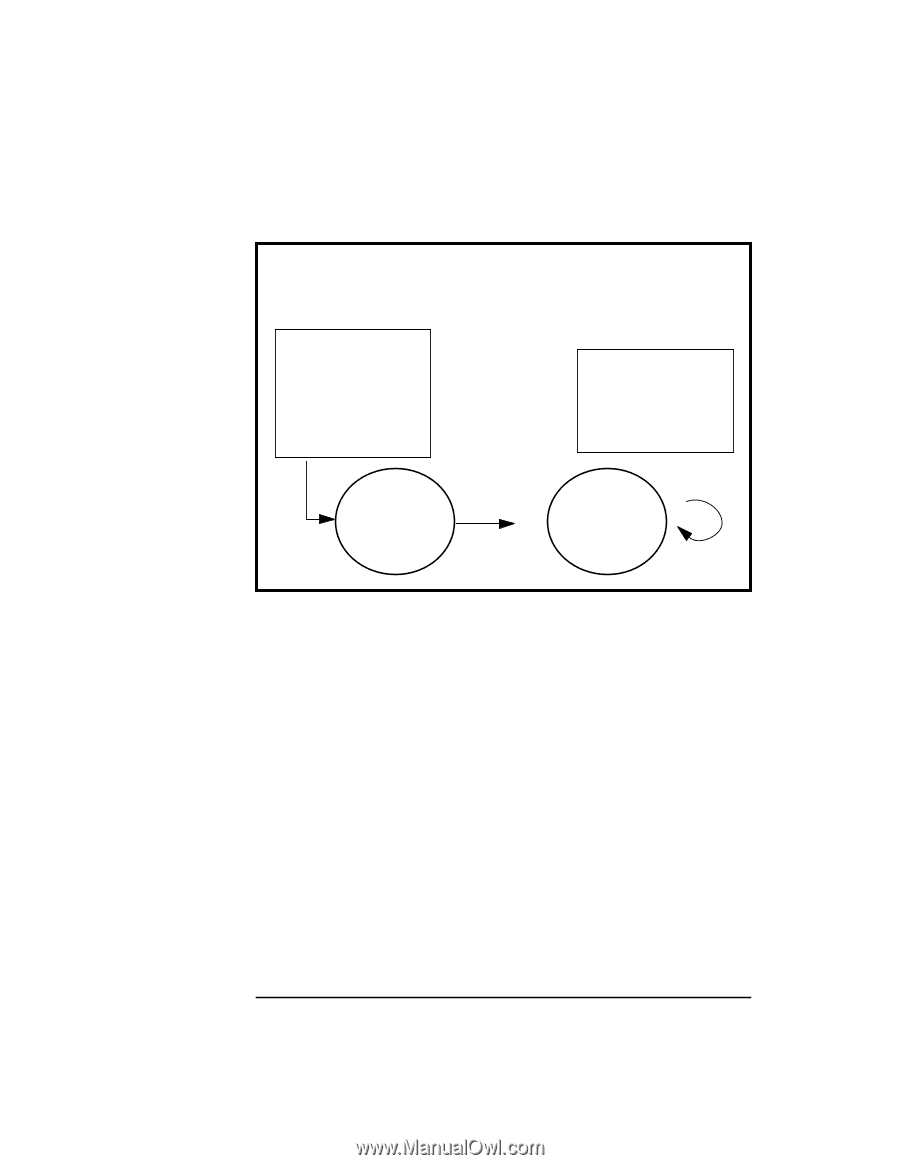
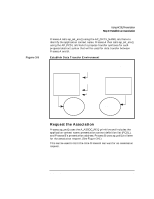
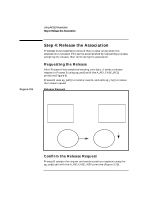
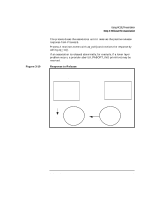
Figure 3-6 Using ACSE/Presentation Step 2: Establish an Association Request Association Process A AP Environment A remote p-address, appl. context name pres. context def. list Process B AP Environment B Initiator Communication Endpoint A ap_snd() request assoc. Responder Communication Endpoint B (listening) ap_poll() Confirm the Association When a request has been received by checking the ap_poll() events parameter, Process B calls ap_rcv() and receives A_ASSOC_IND. Process B must find out what the proposed transfer syntaxes are by calling ap_get_env() using the AP_PCDL attribute. It checks the transfer syntax to Process A's proposed syntax. If Process B determines that the syntax is valid, Process B calls ap_set_env() using the AP_PCDRL attribute to set its transfer syntax. Process B sets the res field in the structure ap_cdrl_t to ACCPT and the transfer syntax pointer to the supported transfer syntax object id. Process B then calls ap_snd() using the A_ASSOC_RSP primitive to accept the association request. (See Figure 3-7.) Process A must wait for Process B to respond with the connection response by using ap_poll() or by making a synchronous ap_rcv() call. 38 Chapter 3