HP 8100 Technical Reference Guide: HP Compaq 8100 Elite Series Business Deskto - Page 68
Functional Description, DirectX DX10 support
 |
View all HP 8100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 68 highlights
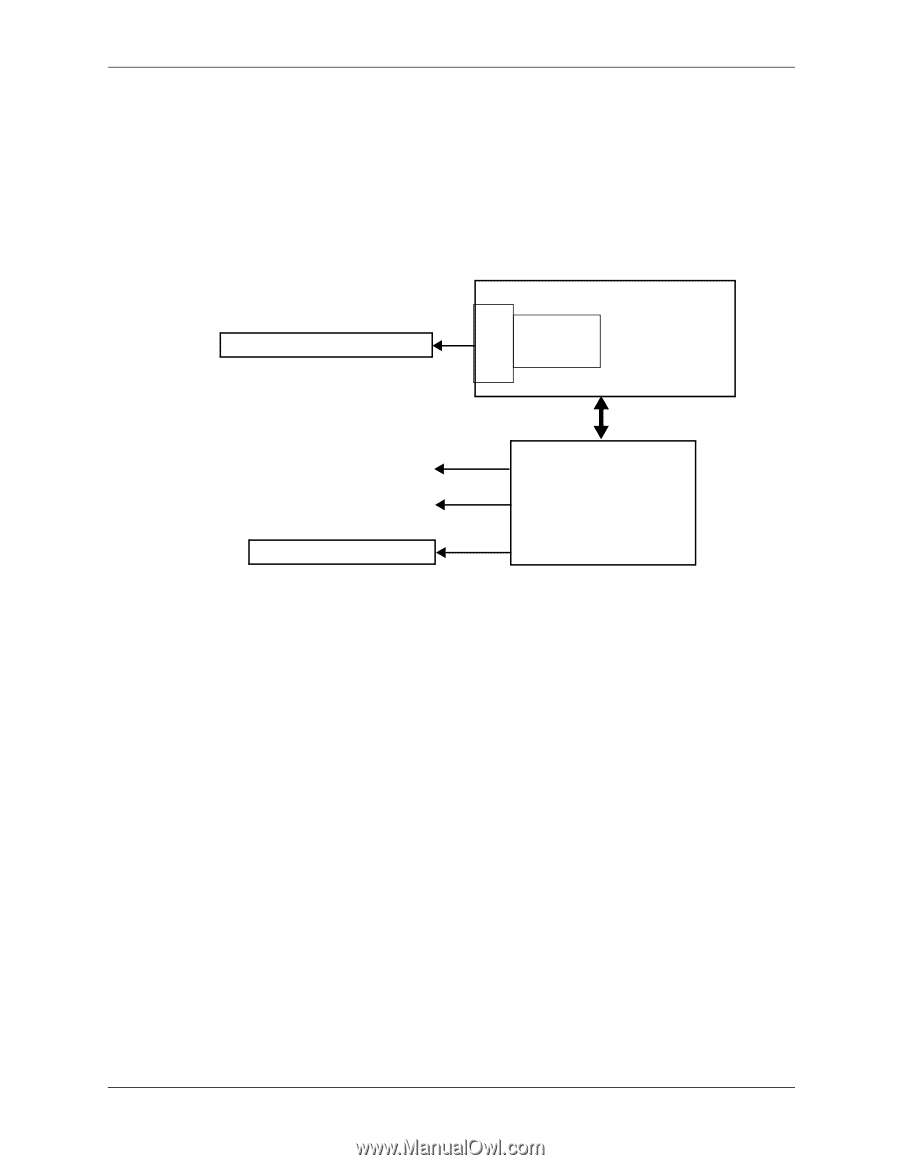
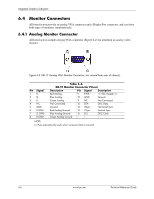
Integrated Graphics Subsystem 6.2 Functional Description The integrated HD Graphics controller (hereafter referred to as an internal graphics controller) featured in select Intel processors supported by these systems operates off the internal PCIe x16 bus of the processor and, through the Flexible Display Interface (FDI) and the Q57 PCH component, can drive an external analog multi-scan monitor and/or a DisplayPort-compatible digital monitor. The integrated graphics controller includes a memory management feature that allocates portions of system memory for use as the frame buffer and for storing textures and 3D effects. Intel Processor PCIe 2.0 x16 Graphics slot PCIe HD Graphics I/F Controller Analog RGB Monitor Digital DisplayPort Monitor PCIe 2.0 x4 slot (x16 conn.) FDI Q57 PCH-D0 Figure 6-1. Integrated Graphics Subsystem, Block diagram The integrated graphic controller of the Intel i5-661 provides the following features: ■ DirectX DX10 support ■ OpenGL 2.1 support ■ Dynamic video memory allocation, where the amount of memory required by the application is acquired (or released) by the controller ■ Intelligent memory management allowing tiled memory addressing, deep display buffering, and dynamic data management ■ Core engine operating up to 900 MHz ■ 2560 x 1600 maximum resolution The integrated graphics controller uses a portion of system memory for instructions, textures, and frame (display) buffering. At boot time, 32 megabytes of system memory is pre-allocated for the graphics controller whether using Windows XP, Windows Vista, or Windows 7. Using a process called Dynamic Video Memory Technology (DVMT), the integrated graphics controller dynamically allocates display and texture memory amounts according to the needs of the application running on the system. 6-2 www.hp.com Technical Reference Guide