HP DL320 HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide - Page 66
Boot options, BIOS Serial Console, Config, uring AMP modes
 |
UPC - 829160513218
View all HP DL320 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 66 highlights
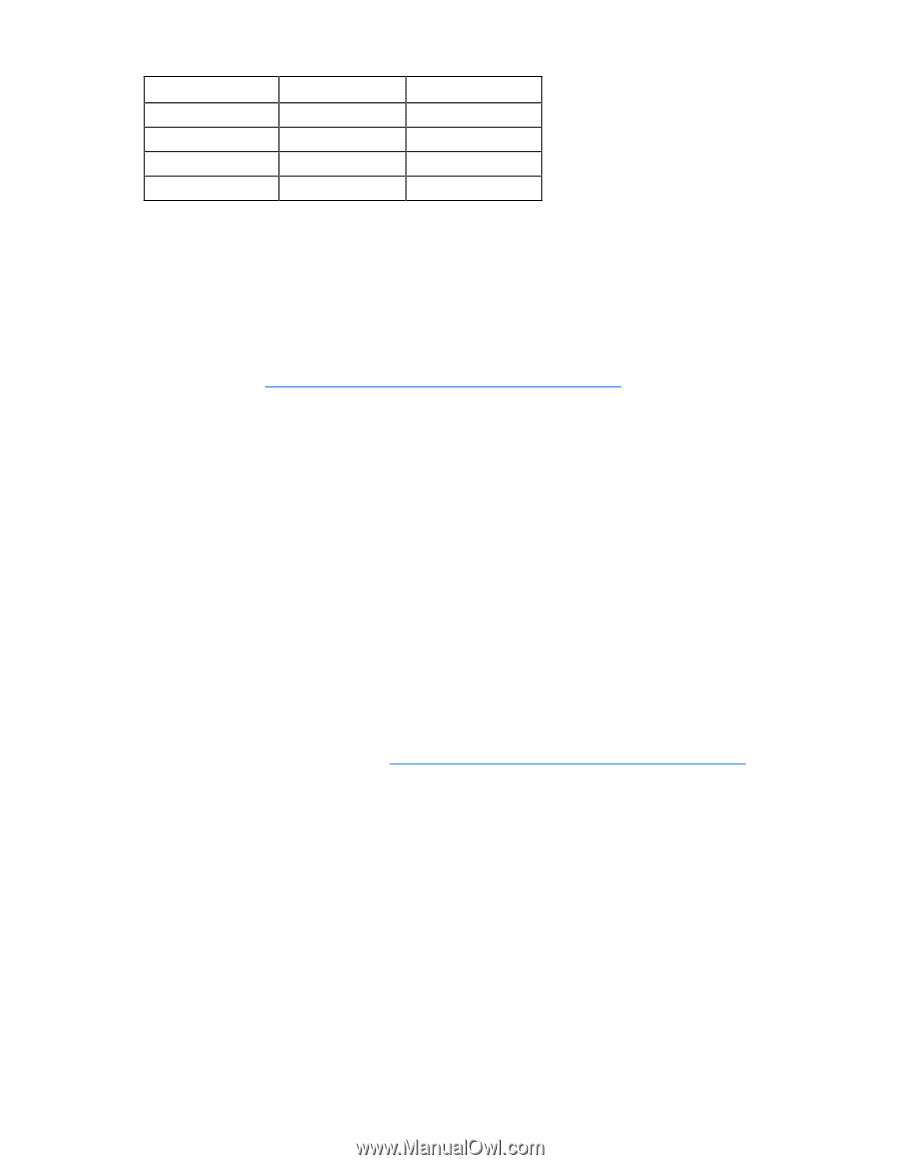
Drives installed 1 2 3, 4, 5, or 6 More than 6 Drives used 1 2 3, 4, 5, or 6 0 RAID level RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 5 None To change any ORCA default settings and override the auto-configuration process, press the F8 key when prompted. By default, the auto-configuration process configures the system for the English language. To change any default settings in the auto-configuration process (such as the settings for language, operating system, and primary boot controller), execute RBSU by pressing the F9 key when prompted. After the settings are selected, exit RBSU and allow the server to reboot automatically. For more information on RBSU, see the HP ROM-Based Setup Utility User Guide on the Documentation CD or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support/smartstart/documentation). Boot options Near the end of the boot process, the boot options screen is displayed. This screen is visible for several seconds before the system attempts to boot from a supported boot device. During this time, you can do the following: • Access RBSU by pressing the F9 key. • Access the System Maintenance Menu (which enables you to launch ROM-based Diagnostics or Inspect) by pressing the F10 key. • Force a PXE Network boot by pressing the F12 key. BIOS Serial Console BIOS Serial Console allows you to configure the serial port to view POST error messages and run RBSU remotely through a serial connection to the server COM port. The server that you are remotely configuring does not require a keyboard and mouse. For more information about BIOS Serial Console, see the BIOS Serial Console User Guide on the Documentation CD or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support/smartstart/documentation). Configuring AMP modes Not all ProLiant servers support all AMP modes. RBSU provides menu options only for the modes supported by the server. Advanced memory protection within RBSU enables the following advanced memory. • Advanced ECC Mode-Provides memory protection beyond Standard ECC. All single-bit failures and some multi-bit failures can be corrected without resulting in system downtime. • Online Spare Mode-Provides protection against failing or degraded DIMMs. Certain memory is set aside as spare, and automatic failover to spare memory occurs when the system detects a degraded DIMM. DIMMs that are likely to receive a fatal/uncorrectable memory error are removed from operation automatically, resulting in less system downtime. See the server-specific user guide for DIMM population requirements. Software tools and solutions 66
-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188
 |
 |