HP DL740 HP F8 Architecture Technology Brief - Page 11
I/O Subsystem, PCI Mode
 |
UPC - 808736765770
View all HP DL740 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
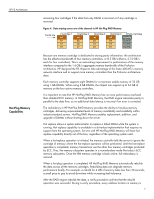
HP F8 Architecture I/O Subsystem PCI Mode PCI-X Mode The F8 chipset optimizes cross-bus traffic by incorporating a patent-pending Guaranteed Snoop Access algorithm. The algorithm defers fewer requests than Profusion does, thus reducing the amount of traffic on the processor bus. The F8 chipset defers cycles only when necessary to prevent a livelock situation5, yet maintains the order and coherency of the requests. Through the Guaranteed Snoop Access algorithm, HP designers have significantly optimized the flow of cross-bus traffic and thus enhanced the scalability of the F8 architecture. HP is a leading technology innovator of industry-standard I/O subsystems, as evidenced by its development of PCI Hot-Plug technology, the I/O controller for the Profusion chipset, and co-development of the latest enhancement to the PCI bus: PCI-X technology. HP has used this expertise to help a chipset vendor develop an industry-standard PCI-X bridge that provides a high-performance data path between the F8 chipset and peripheral devices. HP designed the F8 chipset to support up to four of these industry-standard PCI-X bridges using a 200-MHz, double-pumped, point-to-point connection that results in an effective data transfer of 400 MT/s. The point-to-point connection is source synchronous, which means that the clock signal travels with the data signal. Because the clock signal and the data travel together, the risks of signal degradation are minimized and the source signal is always synchronized with the receiver to provide more effective data transmission. Each PCI-X bridge supports two 64-bit PCI-X bus segments. Each of the eight bus segments can be independently configured to run either in PCI mode operating at 33 or 66 MHz or in PCI-X mode operating at 66 or 100 MHz. Both modes support PCI Hot Plug using an integrated controller developed and licensed by HP. The PCI-X bridge supports delayed PCI transactions, an important feature that improves bus performance. All reads to main memory are completed as delayed transactions when the PCI-X bridge operates in PCI mode. The device that initiates the transaction polls the PCI-X bridge to determine if the requested data is cached there, rather than holding the bus while waiting for the data. This polling allows other devices to use the bus while the transaction is completed. The PCI-X bridge includes prefetch buffers to make it a caching device. Each buffer can hold multiple cache lines. These buffers have been sized to provide optimal performance at a reasonable and cost-effective silicon die size. Because of the delayed transaction support, the PCI-X bridge can get data for multiple PCI devices concurrently. The F8 architecture incorporates PCI-X technology to significantly expand the I/O performance. PCI-X technology, developed by Compaq, Hewlett-Packard, and IBM, is an evolutionary I/O upgrade to conventional PCI technology. PCI-X enables the design of I/O subsystems and peripheral devices that can operate at bus frequencies greater than 66 MHz using a 64-bit bus width. The PCI-X bridge designed for the F8 architecture will run at 66 or 100 MHz, allowing flexibility for system architects and supporting multiple devices for end users. 5 Livelock: When two processes continuously change their state in response to changes in the other process without doing any useful work. (The Free On-line Dictionary of Computing, http://foldoc.doc.ic.ac.uk/, Editor Denis Howe) 11