HP DL740 HP F8 Architecture Technology Brief - Page 7
Benefits of Data Protection With RAID, Error Detection and Correction, error condition, parity
 |
UPC - 808736765770
View all HP DL740 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
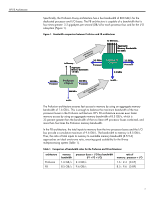
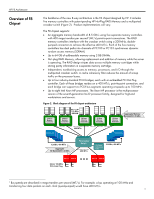
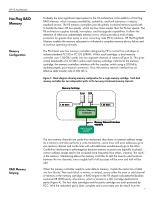
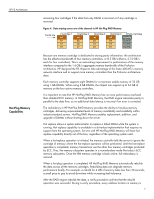
HP F8 Architecture Benefits of Data Protection With RAID Error Detection and Correction read. Errors found will be reported to the system. If the verify fails, the system continues to operate in non-redundant mode and the new memory will not be brought online until the problem is corrected. Hot-add and hot-upgrade capabilities allow a user to scale up a computer system as needed by adding or exchanging DIMMs in a memory cartridge while the system is operating. Hotadd and hot-upgrade capabilities require support from the operating system to recognize the additional memory that is available. HP is working with leading operating system suppliers to ensure that these capabilities will be supported in their future releases. Some suppliers of industry-standard servers, including HP, use an alternative data protection method known as distributed ECC to guard against memory device failures. Distributed ECC provides better data protection than standard ECC by distributing bits across multiple DRAM devices. However, if a DRAM device fails, the DIMM must be replaced. Without the redundancy of Hot-Plug RAID Memory, a failed DRAM device results in the need for immediate, unplanned downtime to replace the bad memory DIMM. With HP Hot-Plug RAID Memory, the RAID engine provides redundancy to ensure data protection, and the hot-plug abilities allow a DIMM to be replaced without any downtime. The F8 chipset uses ECC logic in each memory controller to maintain data integrity throughout the memory subsystem. HP has developed an advanced 8-bit ECC algorithm that can reliably detect single-bit, multi-bit, and 4-bit or 8-bit DRAM failures in memory devices. The RAID engine developed by HP corrects these errors (Table 2). Table 2. Comparison of protection provided by parity checking, ECC, and HP Hot Plug RAID Memory error condition single-bit double-bit DRAM failure ECC detection fault parity detect X X X standard ECC correct detect detect X Hot Plug RAID Memory correct correct correct detect In a memory read transaction, every block of data simultaneously travels through the ECC logic and the RAID parity engine. The ECC logic determines whether the data is good or bad. If the data is bad, the chipset uses the regenerated data from the RAID engine. Thus, the error detected by the ECC is eliminated and only good data is transmitted. If the ECC logic sends a signal that the data is good, then this data is compared with the regenerated data from the RAID engine. If the two blocks of data are not identical, an error undetectable by ECC has occurred. While such an occurrence would be rare, an ECC-only system would be unable to detect such failures and could pass along corrupt data as if it were good. With HP Hot-Plug RAID Memory, when an error undetectable by ECC occurs, the data comparison fails and the memory controller initiates an nonmaskable interrupt (NMI), preventing transmission of corrupt data. This feature makes HP Hot-Plug RAID Memory virtually immune to data corruption. 7