| Section |
Page |
| Service Handbook |
1 |
| Service Handbook |
1 |
| Service Handbook |
1 |
| HP Visualize B1000/C3000 UNIX® Workstations |
1 |
| Manufacturing Part Number:� n.a. |
1 |
| Printed in USA ��May 2001 |
1 |
| Edition E0501 |
1 |
| Notice |
2 |
| Notice |
2 |
| The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. Hewlett-Packard a... |
2 |
| Hewlett-Packard Warranty Statement |
2 |
| Hewlett-Packard Warranty Statement |
2 |
| HP PRODUCT������������������������������� ���DURATION OF WARRANTY ������HP Visualize Wo... |
2 |
| Model B1000/C3000��� |
2 |
| 1. HP warrants HP hardware, accessories and supplies against defects in materials and workmanship... |
2 |
| 1. HP warrants HP hardware, accessories and supplies against defects in materials and workmanship... |
2 |
| 1. HP warrants HP hardware, accessories and supplies against defects in materials and workmanship... |
2 |
| 2. HP warrants that HP software will not fail to execute its programming instructions, for the pe... |
2 |
| 2. HP warrants that HP software will not fail to execute its programming instructions, for the pe... |
2 |
| 3. HP does not warrant that the operation of HP products will be uninterrupted or error free. If ... |
2 |
| 3. HP does not warrant that the operation of HP products will be uninterrupted or error free. If ... |
2 |
| 4. HP products may contain remanufactured parts equivalent to new in performance or may have been... |
2 |
| 4. HP products may contain remanufactured parts equivalent to new in performance or may have been... |
2 |
| 5. The warranty period begins on the date of delivery or on the date of installation if installed... |
2 |
| 5. The warranty period begins on the date of delivery or on the date of installation if installed... |
2 |
| 6. Warranty does not apply to defects resulting from (a) improper or inadequate maintenance or ca... |
2 |
| 6. Warranty does not apply to defects resulting from (a) improper or inadequate maintenance or ca... |
2 |
| 7. TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THE ABOVE WARRANTIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND NO OTHER WARRANTY O... |
3 |
| 7. TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THE ABOVE WARRANTIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND NO OTHER WARRANTY O... |
3 |
| 8. HP will be liable for damage to tangible property per incident up to the greater of $300,000 o... |
3 |
| 8. HP will be liable for damage to tangible property per incident up to the greater of $300,000 o... |
3 |
| 9. TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THE REMEDIES IN THIS WARRANTY STATEMENT ARE CUSTOMER’S SOL... |
3 |
| 9. TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THE REMEDIES IN THIS WARRANTY STATEMENT ARE CUSTOMER’S SOL... |
3 |
| Restricted Rights Legend |
3 |
| Restricted Rights Legend |
3 |
| Use, duplication, or disclosure by the U.S. Government Department of Defense is subject to restri... |
3 |
| © Copyright 2001 Hewlett-Packard Company. All Rights Reserved. |
3 |
| This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. All rights are res... |
3 |
| UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively thr... |
3 |
| © Copyright 1980, 1984 AT&T, Inc. |
3 |
| © Copyright 1979, 1980, 1983 The Regents of the University of California. |
3 |
| This software and documentation is based in part on the Fourth Berkeley Software Distribution und... |
3 |
| Printing History |
4 |
| Printing History |
4 |
| New editions of this manual incorporate all material updated since the previous edition. Update p... |
4 |
| The manual part number and printing date indicate its current edition. The manual part number cha... |
4 |
| HP Part Number ��������������Printing Date ������������Edition |
4 |
| Non-Applicable ��������������������May 2001 �������������� First |
4 |
| 1� Product Information |
17 |
| 1� Product Information |
17 |
| This chapter introduces the HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstations, including their controls and i... |
17 |
| This chapter introduces the HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstations, including their controls and i... |
17 |
| Included in this chapter are the following topics: |
18 |
| • Product description |
18 |
| • Product description |
18 |
| • Product description |
18 |
| • Product description |
18 |
| • System unit front panel controls |
18 |
| • System unit front panel controls |
18 |
| • System unit rear panel connectors |
18 |
| • System unit rear panel connectors |
18 |
| • Monitor information |
18 |
| • Monitor information |
18 |
| • Keyboard and Mouse information |
18 |
| • Keyboard and Mouse information |
18 |
| • Operating System Overview |
18 |
| • Operating System Overview |
18 |
| B1000/C3000:product description, |
19 |
| B1000/C3000:product description, |
19 |
| B1000/C3000:product description, |
19 |
| The HP Visualize B1000 and C3000 workstations contain the following key features: |
19 |
| The HP Visualize B1000 and C3000 workstations contain the following key features: |
19 |
| • Processor: |
19 |
| • Processor: |
19 |
| • Processor: |
19 |
| — One 300MHz PA8500 processor in the B1000 or one 400MHz PA8500 processor in �����the C3000 |
19 |
| — One 750MHz PA8700 processor in the C3700 |
19 |
| — The PA8500 processor has a 0.5MByte instruction cache and a 1.0MByte data cache |
19 |
| — The PA8700 processor has a 0.75MByte instruction cache and a 1.5MByte data cache |
19 |
| • Operating System: |
19 |
| • Operating System: |
19 |
| The B1000/C3000 requires the HP-UX 10.20 and Workstation Additional Core Enhancements (ACE) for H... |
19 |
| • User Interface: |
19 |
| • User Interface: |
19 |
| HP CDE graphical user interface |
19 |
| • Compatibility: Source and binary code compatible with the Series 700 product family |
19 |
| • Compatibility: Source and binary code compatible with the Series 700 product family |
19 |
| • Monitors: |
19 |
| • Monitors: |
19 |
| — 21-inch 1280¥1024 (stereo capability) and 1600¥1200 color, 75Hz |
19 |
| • Optional Graphics: |
19 |
| • Optional Graphics: |
19 |
| HP Visualize-EG and Visualize fx2 Pro (for B1000) |
19 |
| HP Visualize-EG, Visualize fx2 Pro and Visualize fx4 Pro (for C3000) |
19 |
| • Main Memory: |
19 |
| • Main Memory: |
19 |
| — 128MByte and 256MByte DIMMs for B1000 and C3000 workstations |
19 |
| — Eight memory slots available per each B1000 and C3000 workstations � ����� |
19 |
| — Minimum of 128MBytes and a maximum of 2GBytes of memory (B1000 and C3000) |
19 |
| • Internal Storage Devices: |
19 |
| • Internal Storage Devices: |
19 |
| – Wide Ultra2 Low-Voltage Differential SCSI – up to two: |
19 |
| 9.0 GB Hard Disk Drive |
19 |
| 18.0 GB Hard Disk Drive |
19 |
| – Removable Media (one of each maximum) |
19 |
| CD-ROM Drive |
19 |
| Floppy Disk Drive |
20 |
| • Standard Network: |
20 |
| • Standard Network: |
20 |
| – RJ45, Twisted Pair 10 BaseT/100 BaseT |
20 |
| • Standard I/O Ports: |
20 |
| • Standard I/O Ports: |
20 |
| — Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential (LVD) SCSI, one |
20 |
| — Ultra Narrow Single-Ended (NSE) SCSI, one |
20 |
| — Parallel port (IEEE 1284), one |
20 |
| — Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports, two |
20 |
| — Serial Interface ports (RS-232C), two |
20 |
| — Audio ports (Line-in, Line-out, headset, and microphone-in) |
20 |
| • Optional I/O: |
20 |
| • Optional I/O: |
20 |
| Six PCI slots are available for the B1000/C3000 workstations. |
20 |
| – 1 PCI 4X:64 bit, 66 MHz, primary graphics (full size, 3.3V) |
20 |
| – 2 PCI 1X:32 bit, 33 MHz, (half size, 5V) |
20 |
| – 3 PCI 2X:64 bit, 33 MHz, (full size, 5V) |
20 |
| • Keyboard: |
20 |
| • Keyboard: |
20 |
| – Universal Serial Bus (USB) keyboard, one |
20 |
| • Mouse: |
20 |
| • Mouse: |
20 |
| – Universal Serial Bus (USB) mouse, one |
20 |
| System Unit Front Panel Controls |
21 |
| System Unit Front Panel Controls |
21 |
| Figure 1-1 shows the location of the system unit front panel controls. |
21 |
| Figure 1-1 shows the location of the system unit front panel controls. |
21 |
| Figure�1�1.� System Unit Front Panel Controls |
21 |
| Figure�1�1.� System Unit Front Panel Controls |
21 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
21 |
| LCD:location, |
21 |
| LCD:location, |
21 |
| The Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is located on the left side of the front panel. The LCD displays... |
21 |
| LCD:symbols, |
22 |
| LCD:symbols, |
22 |
| LCD:symbols, |
22 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
22 |
| Power switch:soft power down procedure, |
22 |
| Power switch:soft power down procedure, |
22 |
| Use the Power switch to power the system unit on and off. When you use the soft power down proced... |
22 |
| Storage Device:controls and features, |
22 |
| Storage Device:controls and features, |
22 |
| Storage Device:controls and features, |
22 |
| This workstation allows either or both of the following internal storage devices: CD drive or flo... |
22 |
| NOTE You cannot have two internal storage devices of the same type. For example, you cannot have ... |
22 |
| NOTE You cannot have two internal storage devices of the same type. For example, you cannot have ... |
22 |
| Figure 1�3. |
22 |
| Figure 1�3. |
22 |
| Storage device:CD drive, |
23 |
| Storage device:CD drive, |
23 |
| Storage device:CD drive, |
23 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
23 |
| Table�1�1.� CD Drive Controls |
23 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
23 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
23 |
| Control/Feature |
23 |
| Control/Feature |
23 |
| Purpose |
23 |
| Purpose |
23 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
23 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
23 |
| Eject Button |
23 |
| Press to open the Disc Tray and insert or remove a disc. When the drive is in use, press the ejec... |
23 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
23 |
| Emergency Eject |
23 |
| Emergency Eject |
23 |
| If the workstation does no have power, you can insert the end of a paper clip into this small hol... |
23 |
| If the workstation does no have power, you can insert the end of a paper clip into this small hol... |
23 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
23 |
| Disk Tray |
23 |
| Disk Tray |
23 |
| The Disk Tray holds the CD. This style of CD drive does not use a disk caddy. |
23 |
| The Disk Tray holds the CD. This style of CD drive does not use a disk caddy. |
23 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
23 |
| Busy Indicator |
23 |
| Busy Indicator |
23 |
| Lights during a data access operation and blinks during a data transfer. The indicator blinks ini... |
23 |
| Lights during a data access operation and blinks during a data transfer. The indicator blinks ini... |
23 |
| • A defective disc |
23 |
| • A defective disc |
23 |
| • A defective disc |
23 |
| • A disc insertion error (for example, an upside down disc) |
23 |
| • A disc insertion error (for example, an upside down disc) |
23 |
| • No disc present |
23 |
| • No disc present |
23 |
| NOTE The audio features of the CD drive are supported through applications only. One such applica... |
23 |
| NOTE The audio features of the CD drive are supported through applications only. One such applica... |
23 |
| The optional |
24 |
| Figure 1�4. |
24 |
| Figure 1�4. |
24 |
| Figure�1�4.� Floppy Drive Controls and Features |
24 |
| Figure�1�4.� Floppy Drive Controls and Features |
24 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
24 |
| Table�1�2.� Floppy Drive Controls and Features |
24 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
24 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
24 |
| Control/Feature |
24 |
| Purpose |
24 |
| Purpose |
24 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
24 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
24 |
| Floppy Drive Eject Button |
24 |
| Floppy Drive Eject Button |
24 |
| Push the eject button to remove floppy diskettes from the drive. |
24 |
| Push the eject button to remove floppy diskettes from the drive. |
24 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
24 |
| Floppy Drive Activity LED |
24 |
| Floppy Drive Activity LED |
24 |
| The floppy drive LED flashes to indicate the drive is in use. |
24 |
| The floppy drive LED flashes to indicate the drive is in use. |
24 |
| Security Lock |
24 |
| Security Lock |
24 |
| Access to the mass storage devices is controlled by a security lock on the front panel. Locking t... |
24 |
| To prevent access to internal components requires the use of the security loop on the rear panel ... |
24 |
| Rear Panel Connectors: |
25 |
| Rear Panel Connectors: |
25 |
| Rear Panel Connectors: |
25 |
| This section describes the following connectors on the system unit’s rear panel: |
25 |
| This section describes the following connectors on the system unit’s rear panel: |
25 |
| • Two serial ports (RS-232) |
25 |
| • Two serial ports (RS-232) |
25 |
| • Two serial ports (RS-232) |
25 |
| • Two serial ports (RS-232) |
25 |
| • Two Universal Serial Bus ports (USB) |
25 |
| • LAN connector, 10 BaseT/100 BaseT |
25 |
| • LAN connector, 10 BaseT/100 BaseT |
25 |
| • HP parallel IEEE 1284 (printer) connector |
25 |
| • Audio connectors (PCI based, line in, line out, headset, and microphone in) |
25 |
| • Audio connectors (PCI based, line in, line out, headset, and microphone in) |
25 |
| • Ultra2 Wide LVD (Low Voltage Differential) SCSI |
25 |
| • Ultra2 Wide LVD (Low Voltage Differential) SCSI |
25 |
| • Ultra Narrow Single-Ended (NSE) SCSI |
25 |
| • Ultra Narrow Single-Ended (NSE) SCSI |
25 |
| • TOC (transfer of control) button |
25 |
| • TOC (transfer of control) button |
25 |
| • AC power cord connector |
25 |
| • AC power cord connector |
25 |
| • Security loop |
25 |
| • Security loop |
25 |
| NOTE To maintain FCC/EMI compliance, verify that all cables are fully seated and properly fastened. |
25 |
| NOTE To maintain FCC/EMI compliance, verify that all cables are fully seated and properly fastened. |
25 |
| Figure�1�5.� System Unit Rear Panel Connectors |
25 |
| Figure�1�5.� System Unit Rear Panel Connectors |
25 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
26 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:audio connectors, |
26 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:audio connectors, |
26 |
| The Model B1000 and C3000 workstations have audio-input and -output capabilities through external... |
26 |
| The rear panel contains the Audio IN (Stereo line-in) and Microphone (Mic-in), and Audio OUT (Ste... |
26 |
| The audio connectors are standard stereo audio mini-jacks (see Figure 1-6). |
26 |
| NOTE Hewlett-Packard recommends using gold-plated plugs available through audio retailers for bes... |
26 |
| NOTE Hewlett-Packard recommends using gold-plated plugs available through audio retailers for bes... |
26 |
| Figure�1�6.� Audio Connectors |
26 |
| Figure�1�6.� Audio Connectors |
26 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
26 |
| Table 1�3. |
26 |
| <TABLE> |
27 |
| Table�1�3.� Audio Electrical Specifications |
27 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Frequency Response |
27 |
| Frequency Response |
27 |
| 25 to 20KHz |
27 |
| 25 to 20KHz |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Input Sensitivity/Impedance |
27 |
| Input Sensitivity/Impedance |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Line in |
27 |
| Line in |
27 |
| 2.0V pk/47kohm |
27 |
| 2.0V pk/47kohm |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Microphone in |
27 |
| Microphone in |
27 |
| 22mVpk/1kohm |
27 |
| 22mVpk/1kohm |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Max Output Level/Impedance |
27 |
| Max Output Level/Impedance |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Line Out |
27 |
| Line Out |
27 |
| 2.8Vpp/47kohm |
27 |
| 2.8Vpp/47kohm |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Headphone |
27 |
| Headphone |
27 |
| 2.75Vpp/50ohm |
27 |
| 2.75Vpp/50ohm |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Speaker (internal) |
27 |
| Speaker (internal) |
27 |
| 5.88Vpp/48ohm |
27 |
| 5.88Vpp/48ohm |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Output Impedance |
27 |
| Output Impedance |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Line Out |
27 |
| Line Out |
27 |
| 619ohm |
27 |
| 619ohm |
27 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
27 |
| Headphone |
27 |
| Headphone |
27 |
| 118ohm |
27 |
| 118ohm |
27 |
| USB:, |
27 |
| USB:, |
27 |
| USB:, |
27 |
| The USB connectors located on the rear panel of the workstation provide an interface for the keyb... |
27 |
| The USB connectors located on the rear panel of the workstation provide an interface for the keyb... |
27 |
| For more information on the Universal Serial Bus, refer to the following URL: |
27 |
|
27 |
| CAUTION Usage of devices other than USB specification may result in unpredictable functionality a... |
27 |
| CAUTION Usage of devices other than USB specification may result in unpredictable functionality a... |
27 |
| NOTE The USB clip on the rear of the chassis provides strain relief for the USB cables. |
27 |
| NOTE The USB clip on the rear of the chassis provides strain relief for the USB cables. |
27 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:parallel, |
27 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:parallel, |
27 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:parallel, |
27 |
| The 25-pin HP Parallel I/O interface uses IEEE 1284 I/O interface protocols to support peripheral... |
27 |
| The 25-pin HP Parallel I/O interface uses IEEE 1284 I/O interface protocols to support peripheral... |
27 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:network, |
27 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:network, |
27 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:network, |
27 |
| The B1000/C3000 workstations have a built-in Twisted Pair (TP) connector for the 802.3 (ETHERNET)... |
27 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:serial, |
28 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:serial, |
28 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:serial, |
28 |
| There are a variety of peripheral devices that can attach to the RS-232 Serial Input/Output (SIO)... |
28 |
| The SIO ports are programmable, allowing functions such as bit rate, character length, parity, an... |
28 |
| Table 1�4. |
28 |
| Table 1�4. |
28 |
| <TABLE> |
28 |
| Table�1�4.� Serial I/O Pins |
28 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| Pin No. |
28 |
| Pin No. |
28 |
| Signal |
28 |
| Signal |
28 |
| Description |
28 |
| Description |
28 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 1 |
28 |
| 1 |
28 |
| DCD |
28 |
| DCD |
28 |
| Data Carrier Detect |
28 |
| Data Carrier Detect |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 2 |
28 |
| 2 |
28 |
| RXD |
28 |
| RXD |
28 |
| Receive Data |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 3 |
28 |
| 3 |
28 |
| TXD |
28 |
| TXD |
28 |
| Transmit Data |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 4 |
28 |
| 4 |
28 |
| DTR |
28 |
| DTR |
28 |
| Data Terminal Ready |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 5 |
28 |
| 5 |
28 |
| GND |
28 |
| GND |
28 |
| Ground |
28 |
| Ground |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 6 |
28 |
| 6 |
28 |
| DSR |
28 |
| DSR |
28 |
| Data Set Ready |
28 |
| Data Set Ready |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 7 |
28 |
| 7 |
28 |
| RTS |
28 |
| RTS |
28 |
| Request To Send |
28 |
| Request To Send |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 8 |
28 |
| 8 |
28 |
| CTS |
28 |
| CTS |
28 |
| Clear To Send |
28 |
| Clear To Send |
28 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
28 |
| 9 |
28 |
| 9 |
28 |
| RI |
28 |
| RI |
28 |
| Ring Indicator |
28 |
| Ring Indicator |
28 |
| SCSI:connectors, |
28 |
| SCSI:connectors, |
28 |
| SCSI:connectors, |
28 |
| The B1000/C3000 workstations have built in SCSI connectors for Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differenti... |
28 |
| NOTE There must ALWAYS be a terminator at both ends of a SCSI bus. This means one internal termin... |
28 |
| NOTE There must ALWAYS be a terminator at both ends of a SCSI bus. This means one internal termin... |
28 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:TOC, |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:TOC, |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:TOC, |
29 |
| The TOC (transfer of control) button interrupts the system and transfers control from the default... |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:power cord |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:power cord |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:power cord |
29 |
| Plug the workstation’s power cord into the power cord connector to provide AC power to the system. |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:security loop, |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:security loop, |
29 |
| Rear Panel Connectors:security loop, |
29 |
| The security loop provides a means of locking the left side panel with a padlock or other locking... |
29 |
| 1. Inspect left side panel for proper seating in the mainframe chassis. |
29 |
| 1. Inspect left side panel for proper seating in the mainframe chassis. |
29 |
| 2. Push in the retractable pin on the spring loaded square fastener. |
29 |
| 2. Push in the retractable pin on the spring loaded square fastener. |
29 |
| 3. Insert the locking device through the top and bottom holes of the square fastener. |
29 |
| 3. Insert the locking device through the top and bottom holes of the square fastener. |
29 |
| 4. Inspect after locking device is in place to assure that the retractable pin is captured in the... |
29 |
| 4. Inspect after locking device is in place to assure that the retractable pin is captured in the... |
29 |
| The internal components of the workstation is now secured. See |
29 |
| NOTE A locking device is not supplied with the workstation; the customer must supply a lock to us... |
29 |
| NOTE A locking device is not supplied with the workstation; the customer must supply a lock to us... |
29 |
| Figure�1�7.� Security Loop Operation |
30 |
| Figure�1�7.� Security Loop Operation |
30 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
31 |
| Monitor:, |
31 |
| Monitor:, |
31 |
| The B1000/C3000 workstations support the following monitors: |
31 |
| The B1000/C3000 workstations support the following monitors: |
31 |
| • 19-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor (A4575A) |
31 |
| • 19-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor (A4575A) |
31 |
| • 19-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor (A4575A) |
31 |
| • 19-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor (A4575A) |
31 |
| • 19-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor (A4575A) |
31 |
| • 21-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor (A4576A) |
31 |
| • 21-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor (A4576A) |
31 |
| • 21-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor (A4576A) |
31 |
| • 21-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor (A4576A) |
31 |
| For information on the A4575A monitors, see: |
31 |
| • HP A4575A Color Monitor CE Handbook |
31 |
| • HP A4575A Color Monitor CE Handbook |
31 |
| • HP A4575A Color Monitor CE Handbook |
31 |
| The A4575A is a 19\ |
31 |
| For information on the A4576A monitor, see: |
31 |
| The A4576A is a 21\ |
31 |
| NOTE Note that the word “multi-sync” is used as a common word to refer to “multi-frequency” and/o... |
31 |
| NOTE Note that the word “multi-sync” is used as a common word to refer to “multi-frequency” and/o... |
31 |
| NOTE The connection to earlier HP monitors with 15-pin mini-DSub cables can be made using the A41... |
31 |
| NOTE The connection to earlier HP monitors with 15-pin mini-DSub cables can be made using the A41... |
31 |
| USB:support, |
32 |
| USB:support, |
32 |
| USB:support, |
32 |
| USB Keyboard |
32 |
| USB Keyboard |
32 |
| The HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstations support USB keyboards. The keyboard shipped with the wo... |
32 |
| The HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstations support USB keyboards. The keyboard shipped with the wo... |
32 |
| The USB keyboard is designed specifically for use with HP workstations. All keyboard models with ... |
32 |
| Some applications may expect to use keycodes generated by keys existing on other types of keyboar... |
32 |
| NOTE HIL and PS/2 devices are not supported by the B1000/C3000 workstations. |
32 |
| NOTE HIL and PS/2 devices are not supported by the B1000/C3000 workstations. |
32 |
| USB HP Scroll Mouse |
32 |
| USB HP Scroll Mouse |
32 |
| The HP scroll mouse (USB) has a left and right button that function the same as most mice. Howeve... |
32 |
| The HP scroll mouse (USB) has a left and right button that function the same as most mice. Howeve... |
32 |
| For general information on the various cursor shapes associated with different areas of HP CDE wh... |
32 |
| HP Hub for USB Devices |
32 |
| HP Hub for USB Devices |
32 |
| The HP USB hub (part number D6804) provides the ability to connect more than one USB device to th... |
32 |
| The HP USB hub (part number D6804) provides the ability to connect more than one USB device to th... |
32 |
| Operating System:overview, |
33 |
| Operating System:overview, |
33 |
| Operating System:overview, |
33 |
| The B1000/C3000 workstation uses the HP-UX operating system, version 10.20 and the Workstation Ad... |
33 |
| If you’re running HP-UX 11.0, the result from this command will be similar to this: |
33 |
| Instant Ignition systems (systems with preloaded software) have X-Windows, Hewlett-Packard’s grap... |
33 |
| If the Instant Ignition system does not have the kernel preconfigured with all of the device driv... |
33 |
| For problems or questions with Instant Ignition, refer to |
33 |
| Note that both of the documents mentioned in the previous paragraphs can be found at the followin... |
33 |
| http://www.docs.hp.com/ |
33 |
| http://www.docs.hp.com/ |
33 |
| Memory:, |
34 |
| Memory:, |
34 |
| Memory:, |
34 |
| DIMM:memory, |
34 |
| The main memory for an HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstation can vary from a minimum of 128 MBytes... |
34 |
| The main memory for an HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstation can vary from a minimum of 128 MBytes... |
34 |
| To install DIMM cards in the B1000/C3000 workstation reference |
34 |
| Memory:failures, |
34 |
| Memory:failures, |
34 |
| Memory:failures, |
34 |
| DIMM:memory failures, |
34 |
| The HP Visualize B1000/C3000 system (with HP-UX 10.20 and later) uses Memory Page Deallocation, a... |
34 |
| You can use the command |
34 |
| The PDT can also be checked using the |
34 |
| 2� Configuration |
35 |
| 2� Configuration |
35 |
| This chapter provides details about setting up and changing the system configuration for the HP V... |
35 |
| This chapter provides details about setting up and changing the system configuration for the HP V... |
35 |
| Chapter Overview |
36 |
| Chapter Overview |
36 |
| This chapter contains the following sections: |
36 |
| This chapter contains the following sections: |
36 |
| • Workstation Configurations |
36 |
| • Workstation Configurations |
36 |
| • Workstation Configurations |
36 |
| • Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) Configurations |
36 |
| • Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) Configurations |
36 |
| — Internal Storage Devices |
36 |
| — Memory |
36 |
| — I/O Cards |
36 |
| — Monitor-Type Selection |
36 |
| Configuration:workstation, |
37 |
| Configuration:workstation, |
37 |
| Configuration:workstation, |
37 |
| Refer to the HP Workstations Website for a complete list of supported accessories, peripherals, a... |
37 |
| http://www.hp.com/workstations/support/ |
37 |
| http://www.hp.com/workstations/support/ |
37 |
| Configuration:FRU, |
38 |
| Configuration:FRU, |
38 |
| Configuration:FRU, |
38 |
| This section provides information for setting up or changing the configuration of the system Fiel... |
38 |
| This section provides information for setting up or changing the configuration of the system Fiel... |
38 |
| Internal Storage Configurations |
38 |
| Internal Storage Configurations |
38 |
| Configuration:hard disk drive, |
38 |
| Configuration:hard disk drive, |
38 |
| Configuration:hard disk drive, |
38 |
| The SCSI IDs for hard disk drives are hard-wired into the SCA Ultra2 Wide LVD SCSI interfaces in ... |
38 |
| The SCSI IDs for hard disk drives are hard-wired into the SCA Ultra2 Wide LVD SCSI interfaces in ... |
38 |
| Similarly, no jumpers are installed at the factory, nor is any jumper installation required at th... |
38 |
| NOTE There must ALWAYS be a terminator at both ends of a SCSI bus. This means one internal termin... |
38 |
| NOTE There must ALWAYS be a terminator at both ends of a SCSI bus. This means one internal termin... |
38 |
| Table 2-1 lists the default device IDs for internal storage devices. These IDs are the default ID... |
38 |
| <TABLE> |
38 |
| Table�2�1.� Default Device IDs TABLE |
38 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
38 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
38 |
| Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI |
38 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
38 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
38 |
| 1st Hard Disk Drive |
38 |
| ID6 |
38 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
38 |
| 2nd Hard Disk Drive |
38 |
| ID5 |
38 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
38 |
| DDS Drive, external optional device |
38 |
| ID3 |
38 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
38 |
| ** Do not assign SCSI ID7 to any internal storage device. |
38 |
| Figures 2-1 and 2-2 show the two types of hard disk drives supported for the B1000/C3000 workstat... |
38 |
| Figure�2�1.� Hard Drive, 9Gbyte/18Gbyte Ultra2 Low Voltage Differential |
39 |
| Figure�2�1.� Hard Drive, 9Gbyte/18Gbyte Ultra2 Low Voltage Differential |
39 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
39 |
| Figure�2�2.� 9Gbyte, 7200 RPM, Hard Disk Drive |
39 |
| Figure�2�2.� 9Gbyte, 7200 RPM, Hard Disk Drive |
39 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
40 |
| Configuration:hard disk drive:SAM, |
40 |
| Configuration:hard disk drive:SAM, |
40 |
| This section describes how to add a hard drive to your system as a file system using SAM. For mor... |
40 |
| 1. Log in as |
40 |
| 1. Log in as |
40 |
| 1. Log in as |
40 |
| 2. Move the mouse pointer to the Application Manager control for tools and click the left mouse b... |
40 |
| 2. Move the mouse pointer to the Application Manager control for tools and click the left mouse b... |
40 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
40 |
| 3. Click twice on the |
40 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
40 |
| 4. Click twice on the |
40 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
40 |
| 5. Double click on the |
40 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
41 |
| 6. Double click on the |
41 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
41 |
| The following screen message is displayed: �����Scanning the system’s hardware... The Disk and Fi... |
41 |
| 7. Click on |
41 |
| 7. Click on |
41 |
| 8. Enter the mount directory name in the Mount Directory field of the Add Disk window and click o... |
41 |
| 8. Enter the mount directory name in the Mount Directory field of the Add Disk window and click o... |
41 |
| Configuration:CD Drive, |
42 |
| Configuration:CD Drive, |
42 |
| Configuration:CD Drive, |
42 |
| The optional CD drive connects to the ATAPI (IDE) interface in the CD drive bay backplane within ... |
42 |
| However, as shown in |
42 |
| CAUTION CD-ROM drives are susceptible to mechanical and electrostatic shock. When handling the dr... |
42 |
| CAUTION CD-ROM drives are susceptible to mechanical and electrostatic shock. When handling the dr... |
42 |
| Figure�2�3.� CD Drive Jumper Setting (Rear View) |
42 |
| Figure�2�3.� CD Drive Jumper Setting (Rear View) |
42 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
42 |
| Configuration:floppy disk drive, |
42 |
| Configuration:floppy disk drive, |
42 |
| Configuration:floppy disk drive, |
42 |
| The optional 3.5-inch floppy disk drive requires no ID, switch, or jumper settings. See the secti... |
42 |
| The optional 3.5-inch floppy disk drive requires no ID, switch, or jumper settings. See the secti... |
42 |
| CAUTION Floppy disk drives are susceptible to mechanical and electrostatic shock. When handling t... |
42 |
| CAUTION Floppy disk drives are susceptible to mechanical and electrostatic shock. When handling t... |
42 |
| Configuration:memory, |
43 |
| Configuration:memory, |
43 |
| Configuration:memory, |
43 |
| This workstation has 8 memory slots, labeled 0 through 7. Memory can be configured from 128MB to ... |
43 |
| Figure�2�4.� Memory Connectors |
43 |
| Figure�2�4.� Memory Connectors |
43 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
43 |
| CAUTION The memory cards must be installed in the correct order, else the system will not boot pr... |
43 |
| The B1000/C3000 workstation supports the 128 MByte DIMMs or the 256 MByte DIMMs. If users install... |
44 |
| NOTE Users who wish to achieve both maximum performance and maximum future capacity are advised t... |
44 |
| NOTE Users who wish to achieve both maximum performance and maximum future capacity are advised t... |
44 |
| See the section titled |
44 |
| Use the Boot Console Handler to verify that the workstation recognizes the installed memory. See |
44 |
| Configuration:I/O cards, |
45 |
| Configuration:I/O cards, |
45 |
| Configuration:I/O cards, |
45 |
| There are six I/O slots located on the rear panel of the B1000 and C3000 workstations. Slots 1 th... |
45 |
| There are six I/O slots located on the rear panel of the B1000 and C3000 workstations. Slots 1 th... |
45 |
| Figure�2�5.� PCI Card Slot Numbering and Capabilities |
45 |
| Figure�2�5.� PCI Card Slot Numbering and Capabilities |
45 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
45 |
| NOTE If you connect your monitor to a different graphics card slot, you will need to change the g... |
45 |
| NOTE If you connect your monitor to a different graphics card slot, you will need to change the g... |
45 |
| See the section titled |
45 |
| Monitor: |
46 |
| Monitor: |
46 |
| Monitor: |
46 |
| The B1000/C3000 supports the following monitors: |
46 |
| The B1000/C3000 supports the following monitors: |
46 |
| • 19-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor, 75 Hz (A4575A) |
46 |
| • 19-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor, 75 Hz (A4575A) |
46 |
| • 19-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor, 75 Hz (A4575A) |
46 |
| • 19-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor, 75 Hz (A4575A) |
46 |
| • 19-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor, 75 Hz (A4575A) |
46 |
| • 21-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor (stereo capability), 75 Hz (A4576A) |
46 |
| • 21-inch, 1280¥1024 color monitor (stereo capability), 75 Hz (A4576A) |
46 |
| • 21-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor, 75 Hz (A4576A) |
46 |
| • 21-inch, 1600¥1200 color monitor, 75 Hz (A4576A) |
46 |
| The |
46 |
| Note that connection to earlier HP monitors with 15-pin mini-DSub cables can be made using the A4... |
46 |
| Monitor:unsupported, |
46 |
| Monitor:unsupported, |
46 |
| Monitor:unsupported, |
46 |
| NOTE The B1000/C3000 workstations support a maximum of four Visualize-EG graphics cards with four... |
46 |
| NOTE The B1000/C3000 workstations support a maximum of four Visualize-EG graphics cards with four... |
46 |
| 3� Troubleshooting |
47 |
| 3� Troubleshooting |
47 |
| This chapter provides information about isolating a failing component, known as a Field Replaceab... |
47 |
| This chapter provides information about isolating a failing component, known as a Field Replaceab... |
47 |
| To troubleshoot a HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstation, you must be familiar with the HP-UX opera... |
48 |
| As a super-user who is troubleshooting a HP-UX system, you should be able to shutdown and reboot ... |
48 |
| Note any error or status messages, then run the power-up boot ROM diagnostics, known as Self Test... |
48 |
| For a complete description of using |
48 |
| http://wojo.rose.hp.com/ |
48 |
| http://wojo.rose.hp.com/ |
48 |
| troubleshooting: |
49 |
| troubleshooting: |
49 |
| troubleshooting: |
49 |
| The following four figures contain troubleshooting flowcharts you can follow to isolate a failing... |
49 |
| The following four figures contain troubleshooting flowcharts you can follow to isolate a failing... |
49 |
| NOTE For the system to power up, the left side panel must be properly seated in the mainframe cha... |
49 |
| NOTE For the system to power up, the left side panel must be properly seated in the mainframe cha... |
49 |
| Figure�3�1.� Power On LCD, Troubleshooting Flow |
50 |
| Figure�3�1.� Power On LCD, Troubleshooting Flow |
50 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
51 |
| troubleshooting:console, |
51 |
| troubleshooting:console, |
51 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
52 |
| troubleshooting:bootable device, |
52 |
| troubleshooting:bootable device, |
52 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
53 |
| troubleshooting:HP-UX Boot, |
53 |
| troubleshooting:HP-UX Boot, |
53 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
54 |
| troubleshooting:LCD, |
54 |
| troubleshooting:LCD, |
54 |
| This workstation uses an LCD panel to display firmware/OS progress codes. the codes, referred to ... |
54 |
| This workstation uses an LCD panel to display firmware/OS progress codes. the codes, referred to ... |
54 |
| FLT ����A hardware error has been detected |
54 |
| FLT ����A hardware error has been detected |
54 |
| TST ����Hardware being tested |
54 |
| TST ����Hardware being tested |
54 |
| SHU ����System being shutdown |
54 |
| SHU ����System being shutdown |
54 |
| INI ����Hardware being initialized |
54 |
| INI ����Hardware being initialized |
54 |
| WRN ����A non-optimal operating condition exists |
54 |
| WRN ����A non-optimal operating condition exists |
54 |
| RUN ����Computer is running operating system |
54 |
| RUN ����Computer is running operating system |
54 |
| In general, the LCD display has the following format: |
54 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
54 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
54 |
| ZZZ ������������ Three character chassis code |
54 |
| YYYY ������� ��� Four digit hexadecimal code |
54 |
| YYYY ������� ��� Four digit hexadecimal code |
54 |
| FFFFFF ����� ��� Six character field replaceable unit description��� |
54 |
| FFFFFF ����� ��� Six character field replaceable unit description��� |
54 |
| WWWWWWWWWWWWWWWW Description of the chassis code |
54 |
| WWWWWWWWWWWWWWWW Description of the chassis code |
54 |
| If the system encounters an |
54 |
| FLT |
54 |
| FLT |
54 |
| 30FC |
54 |
| 30FC |
54 |
| SYS BD |
54 |
| SYS BD |
54 |
| bad sys bd id |
54 |
| bad sys bd id |
54 |
| troubleshooting:fan failures and warnings, |
55 |
| troubleshooting:fan failures and warnings, |
55 |
| troubleshooting:fan failures and warnings, |
55 |
| This section provides the failure and warning messages you will see in the LCD if there is a prob... |
55 |
| This section provides the failure and warning messages you will see in the LCD if there is a prob... |
55 |
| A chassis code which indicates that a fan has failed ( |
55 |
| <TABLE> |
55 |
| Table�3�1.� Fan Numbers and Corresponding Name |
55 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| Fan Number |
55 |
| Fan Number |
55 |
| Name of the Fan |
55 |
| Name of the Fan |
55 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| 1 |
55 |
| 1 |
55 |
| (not used) |
55 |
| (not used) |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| 2 |
55 |
| 2 |
55 |
| Lower System Fan |
55 |
| Lower System Fan |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| 3 |
55 |
| 3 |
55 |
| Upper System Fan |
55 |
| Upper System Fan |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| 4 |
55 |
| 4 |
55 |
| PCI Card Fan |
55 |
| PCI Card Fan |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| 5 |
55 |
| 5 |
55 |
| Turbo Cooler Fan, CPU |
55 |
| Turbo Cooler Fan, CPU |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| 6 |
55 |
| 6 |
55 |
| Disk/Memory Fan |
55 |
| Disk/Memory Fan |
55 |
| Here is an example of a failure message for the I/O (PCI card) fan:���������� |
55 |
| <TABLE> |
55 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| WRN D014 SYS BD |
55 |
| WRN D014 SYS BD |
55 |
| WRN D014 SYS BD |
55 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
55 |
| fan 4: failure! |
55 |
| fan 4: failure! |
55 |
| fan 4: failure! |
55 |
| Here is an example of a warning message for the Turbo Cooler Fan, CPU: |
55 |
| To locate the correct fan, see |
55 |
| Figure�3�5.� Fan Locations |
56 |
| Figure�3�5.� Fan Locations |
56 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
56 |
| • The fan itself, if it is either a system board cooling fan, PCI (I/O) fan, or a memory fan. |
56 |
| • The fan itself, if it is either a system board cooling fan, PCI (I/O) fan, or a memory fan. |
56 |
| • The fan itself, if it is either a system board cooling fan, PCI (I/O) fan, or a memory fan. |
56 |
| • The entire system board tray assembly, if it is a turbo cooler fan (that is, a fan mounted on a... |
56 |
| • The entire system board tray assembly, if it is a turbo cooler fan (that is, a fan mounted on a... |
56 |
| See |
56 |
| troubleshooting:boot failure, |
57 |
| troubleshooting:boot failure, |
57 |
| troubleshooting:boot failure, |
57 |
| To start this workstation from an operating system stored on a device different from the usual bo... |
57 |
| To start this workstation from an operating system stored on a device different from the usual bo... |
57 |
| troubleshooting:bootable media, |
58 |
| troubleshooting:bootable media, |
58 |
| troubleshooting:bootable media, |
58 |
| To list all devices that may contain bootable media, go to the Main Menu of the Boot Console Inte... |
58 |
| To list all devices that may contain bootable media, go to the Main Menu of the Boot Console Inte... |
58 |
| Main Menu: Enter a command or a menu > search ipl |
58 |
| Main Menu: Enter a command or a menu > search ipl |
58 |
| The search may turn up more devices than there are lines on the display. If using a text terminal... |
58 |
| • To hold the display temporarily, press�� |
58 |
| • To hold the display temporarily, press�� |
58 |
| • To hold the display temporarily, press�� |
58 |
| • To continue the display, press �� |
58 |
| • To continue the display, press �� |
58 |
| • To halt the search, press � |
58 |
| • To halt the search, press � |
58 |
| These flow-control commands do not work with a bitmapped display, but such a display can show mor... |
58 |
| To search for devices of just one type that actually contain bootable media, go to the Main Menu ... |
58 |
| Main Menu: Enter a command > search ipl device_type |
58 |
| Main Menu: Enter a command > search ipl device_type |
58 |
| where |
58 |
| • fwscsi |
58 |
| • fwscsi |
58 |
| • fwscsi |
58 |
| • fwscsi |
58 |
| • scsi |
58 |
| • scsi |
58 |
| • scsi |
58 |
| • lan |
58 |
| • lan |
58 |
| • lan |
58 |
| • ide |
58 |
| • ide |
58 |
| • ide |
58 |
| • pcin |
58 |
| • pcin |
58 |
| • pcin |
58 |
| Stable Storage |
58 |
| Stable Storage |
58 |
| Stable Storage is non-volatile memory associated with each PA-RISC processor module. Stable stora... |
58 |
| Stable Storage is non-volatile memory associated with each PA-RISC processor module. Stable stora... |
58 |
| boot command:notations, |
59 |
| boot command:notations, |
59 |
| boot command:notations, |
59 |
| The |
59 |
| The |
59 |
| • Mnemonic |
59 |
| • Mnemonic |
59 |
| • Mnemonic |
59 |
| • Path number |
59 |
| • Path number |
59 |
| Type |
59 |
| Here are examples of mnemonic notation: |
59 |
| • boot |
59 |
| • boot |
59 |
| • boot |
59 |
| • boot |
59 |
| • boot |
59 |
| • boot |
59 |
| • boot |
59 |
| Here is an example of path number notation: |
59 |
| • boot p1 |
59 |
| • boot p1 |
59 |
| • boot p1 |
59 |
| • boot p1 |
59 |
| Supported Boot Paths |
59 |
| Supported Boot Paths |
59 |
| SCSI devices are bootable when connected to the SCSI port on the system. Diskless workstations ca... |
59 |
| SCSI devices are bootable when connected to the SCSI port on the system. Diskless workstations ca... |
59 |
| ISL:environment, |
59 |
| ISL:environment, |
59 |
| ISL:environment, |
59 |
| The ISL environment provides the means to load the operating system (HP-UX) environment. The ISL ... |
59 |
| The ISL environment provides the means to load the operating system (HP-UX) environment. The ISL ... |
59 |
| The ISL program is the first program loaded into main memory from an external media (LAN, disk, o... |
59 |
| The ISL environment provides the following capabilities: |
59 |
| • Execute user-entered commands to modify boot device paths and boot options in stable storage. |
59 |
| • Execute user-entered commands to modify boot device paths and boot options in stable storage. |
59 |
| • Execute user-entered commands to modify boot device paths and boot options in stable storage. |
59 |
| • Run off-line diagnostic programs and utilities. |
59 |
| • Run off-line diagnostic programs and utilities. |
59 |
| • Provide automatic booting of the HP-UX operating system after power-on or reset. |
59 |
| • Provide automatic booting of the HP-UX operating system after power-on or reset. |
59 |
| The ISL program provides a stand-alone environment for loading off-line diagnostic and utility pr... |
59 |
| troubleshooting:selftest failures, |
60 |
| troubleshooting:selftest failures, |
60 |
| troubleshooting:selftest failures, |
60 |
| Chassis codes are the key to debugging selftest errors. If a failure is found during selftest, ch... |
60 |
| Chassis codes are the key to debugging selftest errors. If a failure is found during selftest, ch... |
60 |
| 1. Using |
60 |
| 1. Using |
60 |
| 1. Using |
60 |
| 2. To get additional information about failures from the Boot Console Handler, use the Service Me... |
60 |
| 2. To get additional information about failures from the Boot Console Handler, use the Service Me... |
60 |
| In the following table, the FRU column shows messages printed on the LCD that refer to system FRU... |
60 |
| troubleshooting:chassis codes, |
61 |
| troubleshooting:chassis codes, |
61 |
| troubleshooting:chassis codes, |
61 |
| Table 3�2. |
61 |
| Table 3�2. |
61 |
| Table 3�2. |
61 |
| <TABLE> |
61 |
| Table�3�2.� Chassis Codes for B1000/C3000 Workstations |
61 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| Ostat |
61 |
| Ostat |
61 |
| Code |
61 |
| Code |
61 |
| FRU |
61 |
| FRU |
61 |
| Message |
61 |
| Message |
61 |
| Description |
61 |
| Description |
61 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n01 |
61 |
| 1 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| HPMC occurred |
61 |
| HPMC occurred |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected HPMC. |
61 |
| CPU |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n02 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| powerfail intrpt |
61 |
| powerfail intrpt |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected power fail interrupt. |
61 |
| CPU |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n03 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| recvry cntr trap |
61 |
| recvry cntr trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected recovery counter trap. |
61 |
| CPU |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n04 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| external intrrpt |
61 |
| external intrrpt |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected external interrupt. |
61 |
| CPU |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n05 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| LPMC occurred |
61 |
| LPMC occurred |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected LPMC. |
61 |
| CPU |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n06 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| ITLB mis/Ipg flt |
61 |
| ITLB mis/Ipg flt |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected ITLB miss or instruction page fault. |
61 |
| CPU |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n07 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| I mem prot trap |
61 |
| I mem prot trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected instruction memory protection trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected instruction memory protection trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n08 |
61 |
| 1n08 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| illegal inst trp |
61 |
| illegal inst trp |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected illegal instruction trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected illegal instruction trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n09 |
61 |
| 1n09 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| break instr trap |
61 |
| break instr trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected break instruction trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected break instruction trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n0A |
61 |
| 1n0A |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| privilgd op trap |
61 |
| privilgd op trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected privileged operation trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected privileged operation trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n0B |
61 |
| 1n0B |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| privlgd reg trap |
61 |
| privlgd reg trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected privileged register trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected privileged register trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n0C |
61 |
| 1n0C |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| overflow trap |
61 |
| overflow trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected overflow trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected overflow trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n0D |
61 |
| 1n0D |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| conditional trap |
61 |
| conditional trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected conditional trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected conditional trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n0E |
61 |
| 1n0E |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| assist exep trap |
61 |
| assist exep trap |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected assist exception trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected assist exception trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n0F |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| DTLB mis/Dpg flt |
61 |
| DTLB mis/Dpg flt |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected DTLB miss or data page fault. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected DTLB miss or data page fault. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n10 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| non-acc ITLB mis |
61 |
| non-acc ITLB mis |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected non-access ITLB miss fault. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected non-access ITLB miss fault. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n11 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| non-acc DTLB mis |
61 |
| non-acc DTLB mis |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected non-access DTLB miss or data page fault. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected non-access DTLB miss or data page fault. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
61 |
| FLT |
61 |
| 1n12 |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| SYS BD |
61 |
| data mem prot tr |
61 |
| data mem prot tr |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory protection trap. |
61 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory protection trap. |
61 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n13 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| data mem brk trp |
62 |
| data mem brk trp |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory break trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory break trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n14 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| TLB dirty bit tr |
62 |
| TLB dirty bit tr |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected TLB dirty bit trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected TLB dirty bit trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n15 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| page refrnce trp |
62 |
| page refrnce trp |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected page reference trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected page reference trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n16 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| assist emul trap |
62 |
| assist emul trap |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected assist emulation trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected assist emulation trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n17 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| hi-priv xfer trp |
62 |
| hi-priv xfer trp |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected higher-privilege transfer trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected higher-privilege transfer trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n18 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| lo-priv xfer trp |
62 |
| lo-priv xfer trp |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected lower-privilege transfer trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected lower-privilege transfer trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n19 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| taken branch trp |
62 |
| taken branch trp |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected taken-branch trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected taken-branch trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n1A |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| data mem acc rts |
62 |
| data mem acc rts |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory access rights trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory access rights trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n1B |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| data mem prot ID |
62 |
| data mem prot ID |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory protection ID trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected data memory protection ID trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n1C |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| unalign data ref |
62 |
| unalign data ref |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected unaligned data reference trap. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected unaligned data reference trap. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| FLT |
62 |
| 1n1D |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| perf mon intrrpt |
62 |
| perf mon intrrpt |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected performance monitor interrupt. |
62 |
| CPU n detected an unexpected performance monitor interrupt. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| 1n20 |
62 |
| 1n20 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| CPUn basic test |
62 |
| CPU |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its basic operations self-test. |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its basic operations self-test. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| 1n21 |
62 |
| 1n21 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| CPUn alu test |
62 |
| CPU |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its arithmetic and logical unit self-test. |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its arithmetic and logical unit self-test. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| 1n22 |
62 |
| 1n22 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| CPUn branch test |
62 |
| CPU |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its branch instruction self-test. |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its branch instruction self-test. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| 1n23 |
62 |
| 1n23 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| CPUn arith cond |
62 |
| CPU |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its arthimetic condition self-test. |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its arthimetic condition self-test. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| 1n24 |
62 |
| 1n24 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| CPUn bit opers |
62 |
| CPU |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its bit operation instruction self-test. |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its bit operation instruction self-test. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| 1n25 |
62 |
| 1n25 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| CPUn cntrl regs |
62 |
| CPU |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its control register self-test. |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its control register self-test. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| TST |
62 |
| 1n26 |
62 |
| 1n26 |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| SYS BD |
62 |
| CPUn ext intrpt |
62 |
| CPU |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its external interrupt self-test. |
62 |
| CPU n is starting its external interrupt self-test. |
62 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n27 |
63 |
| 1n27 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn itimer test |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its interval timer self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its interval timer self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n28 |
63 |
| 1n28 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn multi-media |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its multi-media instructions self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its multi-media instructions self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n29 |
63 |
| 1n29 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn shadow reg |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its shadow register self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its shadow register self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n2A |
63 |
| 1n2A |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn diagnse reg |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its diagnose register self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its diagnose register self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n2B |
63 |
| 1n2B |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn rdr test |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its remote diagnose register self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its remote diagnose register self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n2C |
63 |
| 1n2C |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn bypass test |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its integer bypass operation self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its integer bypass operation self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n30 |
63 |
| 1n30 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn start est |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its early (pre-memory) self-tests. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its early (pre-memory) self-tests. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| WRN |
63 |
| WRN |
63 |
| 1n31 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn skip est |
63 |
| CPU n is bypassing its early self-tests to save time. |
63 |
| CPU n is bypassing its early self-tests to save time. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| FLT |
63 |
| FLT |
63 |
| 1n32 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn bad tst mod |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n detected an unsupported system mode. |
63 |
| CPU n detected an unsupported system mode. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| INI |
63 |
| INI |
63 |
| 1n3C |
63 |
| 1n3C |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn initialize |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is initializing after self-tests. |
63 |
| CPU n is initializing after self-tests. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1n3E |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn exit est |
63 |
| CPU n finished its early self-tests. |
63 |
| CPU n finished its early self-tests. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nA0 |
63 |
| 1nA0 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn fpu tests |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point unit self-tests. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point unit self-tests. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nA1 |
63 |
| 1nA1 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn fpu reg tst |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point register self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point register self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nA2 |
63 |
| 1nA2 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn fpu inst |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point instruction self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point instruction self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nA3 |
63 |
| 1nA3 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn fpu traps |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point trap self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point trap self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nA4 |
63 |
| 1nA4 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn fpu misc |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point miscellaneous operations self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point miscellaneous operations self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nA5 |
63 |
| 1nA5 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn fpu bypass |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point bypassing self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its floating-point bypassing self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nB1 |
63 |
| 1nB1 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn TLB RAM tst |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its TLB register self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its TLB register self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| TST |
63 |
| 1nB2 |
63 |
| 1nB2 |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| SYS BD |
63 |
| CPUn TLB trans |
63 |
| CPU |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its TLB translation self-test. |
63 |
| CPU n is starting its TLB translation self-test. |
63 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 1nBA |
64 |
| 1nBA |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| monarch CPU fail |
64 |
| monarch CPU |
64 |
| The monarch CPU failed. |
64 |
| The monarch CPU failed. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 1nBB |
64 |
| 1nBB |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| bad CPUn number |
64 |
| bad CPU |
64 |
| The CPU identifier was out of range. |
64 |
| The CPU identifier was out of range. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 1nBF |
64 |
| 1nBF |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn halt boot |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| Bootstrap failure--machine halted. |
64 |
| Bootstrap failure--machine halted. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| INI |
64 |
| INI |
64 |
| 1nCA |
64 |
| 1nCA |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn sys bus arb |
64 |
| CPUn sys bus arb |
64 |
| Monarch CPU is initializing the system bus arbitration. |
64 |
| Monarch CPU is initializing the system bus arbitration. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| 1nCD |
64 |
| 1nCD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn deconfig |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n deconfigured itself. |
64 |
| CPU n deconfigured itself. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| 1nCE |
64 |
| 1nCE |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn extinguish |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| PDC_PROC halted CPU n. |
64 |
| PDC_PROC halted CPU n. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 1nCF |
64 |
| 1nCF |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| slaven failed |
64 |
| slave |
64 |
| Slave CPU n failed self-test. |
64 |
| Slave CPU n failed self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| 1mDs |
64 |
| 1mDs |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| slaves deconfig |
64 |
| slaves deconfig |
64 |
| Monarch CPU m deconfigured slave CPU s. |
64 |
| Monarch CPU m deconfigured slave CPU s. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| 1nEF |
64 |
| 1nEF |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn slftst warn |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n detected a non-fatal error during its self-tests. |
64 |
| CPU n detected a non-fatal error during its self-tests. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| WRN |
64 |
| 1mFs |
64 |
| 1mFs |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| monm stop slaves |
64 |
| mon |
64 |
| Monarch CPU m halted slave CPU s. |
64 |
| Monarch CPU m halted slave CPU s. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| INI |
64 |
| INI |
64 |
| 1nFC |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn sync’ing |
64 |
| CPUn sync’ing |
64 |
| CPU n is synchronizing with the rest of the system. |
64 |
| CPU n is synchronizing with the rest of the system. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| INI |
64 |
| INI |
64 |
| 1nFD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn stat wd tst |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n is testing the system status word. |
64 |
| CPU n is testing the system status word. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 1nFF |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| monarchn selftst |
64 |
| monarch |
64 |
| Monarch CPU n failed self-test. |
64 |
| Monarch CPU n failed self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| 2n20 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn icache RAM |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache RAM self-test. |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache RAM self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 2n25 |
64 |
| 2n25 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn ic ld d err |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n detected a data error during data cache load. |
64 |
| CPU n detected a data error during data cache load. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 2n26 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn ic ld t err |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n detected a tag error during data cache load. |
64 |
| CPU n detected a tag error during data cache load. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| 2n30 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn icache tag |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache tag self-test. |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache tag self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| 2n40 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn icache par |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache parity detection self-test. |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache parity detection self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| 2n50 |
64 |
| 2n50 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn dc stor que |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache store queue self-test. |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache store queue self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| FLT |
64 |
| 2n51 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn dc st q err |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n detected an error during its data cache store queue self-test. |
64 |
| CPU n detected an error during its data cache store queue self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| 2n70 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn dcache RAM |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache RAM self-test. |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache RAM self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| TST |
64 |
| 2n80 |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| SYS BD |
64 |
| CPUn dcache tag |
64 |
| CPU |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache tag self-test. |
64 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache tag self-test. |
64 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| 2n90 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| CPUn dcache ECC |
65 |
| CPU |
65 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache ECC self-test. |
65 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache ECC self-test. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 2BAD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| assertion fail |
65 |
| assertion fail |
65 |
| A firmware assertion failed. |
65 |
| A firmware assertion failed. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| 3n00 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| ROM checksum tst |
65 |
| ROM checksum tst |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is testing the boot ROM integrity. |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is testing the boot ROM integrity. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 3n00 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| ROM checksum BAD |
65 |
| ROM checksum BAD |
65 |
| The boot ROM failed checksum. |
65 |
| The boot ROM failed checksum. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| 3n00 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| ROM checksum ok |
65 |
| ROM checksum ok |
65 |
| The boot ROM passed checksum. |
65 |
| The boot ROM passed checksum. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| 3n01 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| PDH control test |
65 |
| PDH control test |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is testing PDH control register. |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is testing PDH control register. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| 3n01 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| PDH control init |
65 |
| PDH control init |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is initializing the PDH control register. |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is initializing the PDH control register. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 3n01 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| PDH control err |
65 |
| PDH control err |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n detected an error in the PDH control register. |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n detected an error in the PDH control register. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| TST |
65 |
| 3n02 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| scratch RAM test |
65 |
| scratch RAM test |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is testing scratch RAM. |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is testing scratch RAM. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| 3n02 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| scratch RAM ok |
65 |
| scratch RAM ok |
65 |
| The scratch RAM test failed. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 3n02 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| scratch RAM bad |
65 |
| scratch RAM bad |
65 |
| The scratch RAM test passed. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| WRN |
65 |
| WRN |
65 |
| 3n03 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| stbl st read err |
65 |
| stbl st read err |
65 |
| CPU n detected a non-fatal error reading the stable store. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 3n03 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| stbl st read err |
65 |
| stbl st read err |
65 |
| CPU n detected a non-fatal error reading the stable store. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| 3nC4 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| clearing EEPROM |
65 |
| clearing EEPROM |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is clearing the EEPROM. |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is clearing the EEPROM. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| 3nD4 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| deflting EEPROM2 |
65 |
| deflting EEPROM2 |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is initializing the EEPROM to system defaults. |
65 |
| Monarch CPU n is initializing the EEPROM to system defaults. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| WRN |
65 |
| 3n04 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| EEPROM write err |
65 |
| EEPROM write err |
65 |
| CPU n detected a non-fatal error writing the EEPROM. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 3n04 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| EEPROM write err |
65 |
| EEPROM write err |
65 |
| CPU n detected a fatal error writing the EEPROM. |
65 |
| CPU n detected a fatal error writing the EEPROM. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 3n05 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| EEPROM wrt limit |
65 |
| EEPROM wrt limit |
65 |
| CPU n detected a fatal error writing the EEPROM. |
65 |
| CPU n detected a fatal error writing the EEPROM. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| WRN |
65 |
| WRN |
65 |
| 3n06 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| EEPROM read err |
65 |
| EEPROM read err |
65 |
| CPU n detected a non-fatal error reading the EEPROM. |
65 |
| CPU n detected a non-fatal error reading the EEPROM. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| FLT |
65 |
| 3n06 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| EEPROM read err |
65 |
| EEPROM read err |
65 |
| CPU n detected a fatal error reading the EEPROM. |
65 |
| CPU n detected a fatal error reading the EEPROM. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
65 |
| INI |
65 |
| 3n07 |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| SYS BD |
65 |
| CPUn invoke LDB |
65 |
| CPUn invoke LDB |
65 |
| CPU n is starting the low-level debugger. |
65 |
| CPU n is starting the low-level debugger. |
65 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3n09 |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| bad sys mde byte |
66 |
| bad sys mde byte |
66 |
| CPU n detected an unsupported system mode. |
66 |
| CPU n detected an unsupported system mode. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| WRN |
66 |
| 3n1A |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| hversion mismtch |
66 |
| hversion mismtch |
66 |
| Stable store hardware version doesn’t match system. |
66 |
| Stable store hardware version doesn’t match system. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| TST |
66 |
| 3n1B |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| chck model strng |
66 |
| chck model strng |
66 |
| Check model string with version in stable store. |
66 |
| Check model string with version in stable store. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| WRN |
66 |
| 3n1B |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| model str msmtch |
66 |
| model str msmtch |
66 |
| Model string doesn’t match that in stable store. |
66 |
| Model string doesn’t match that in stable store. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3n1B |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| fatal model str |
66 |
| fatal model str |
66 |
| Error reading model string from stable store. |
66 |
| Error reading model string from stable store. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| TST |
66 |
| 3n1C |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| test software ID |
66 |
| test software ID |
66 |
| Check LANIC address. |
66 |
| Check LANIC address. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| WRN |
66 |
| 3n1C |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| update sw ID |
66 |
| update sw ID |
66 |
| Update LANIC address. |
66 |
| Update LANIC address. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3n1C |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| update sw ID err |
66 |
| update sw ID err |
66 |
| Error updating LANIC address. |
66 |
| Error updating LANIC address. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| INI |
66 |
| 3n2s |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| Invoke LDB: s |
66 |
| Invoke LDB: s |
66 |
| CPU n is awaiting the low-level debugger for s more seconds. |
66 |
| CPU |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3nBC |
66 |
| 3nBC |
66 |
| 3nBC |
66 |
| IO BD |
66 |
| IO BD |
66 |
| IO BD |
66 |
| tick timeout |
66 |
| tick timeout |
66 |
| tick timeout |
66 |
| The real-time clock is ticking too slowly or not at all. |
66 |
| The real-time clock is ticking too slowly or not at all. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| TST |
66 |
| 3nBC |
66 |
| IO BD |
66 |
| test sys clocks |
66 |
| test sys clocks |
66 |
| CPU n is verifying processor clocks with the real-time clock. |
66 |
| CPU n is verifying processor clocks with the real-time clock. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| INI |
66 |
| 3nBC |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| init sys clocks |
66 |
| init sys clocks |
66 |
| CPU n has initialized the processor clocks. |
66 |
| CPU n has initialized the processor clocks. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3nCD |
66 |
| IO BD |
66 |
| RTC tick timeout |
66 |
| The real time clock is ticking too slowly or not at all. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| TST |
66 |
| 3nCD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| check defaults |
66 |
| check defaults |
66 |
| CPU n is initializing stable store values to system defaults. |
66 |
| CPU |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| INI |
66 |
| 3nCD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| init defaults |
66 |
| init defaults |
66 |
| CPU n finished initializing stable store values. |
66 |
| CPU |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3nCD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| init EEPROM err |
66 |
| init EEPROM err |
66 |
| CPU n detected an error writing to stable store. |
66 |
| CPU |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3nEC |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| bad sys config |
66 |
| bad sys config |
66 |
| CPU n detected an illegal CPU board configuration. |
66 |
| CPU |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3nF4 |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| EEPROM boot limt |
66 |
| EEPROM boot limt |
66 |
| CPU n detected a fatal error writing the EEPROM. |
66 |
| CPU |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| FLT |
66 |
| 3nFC |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| bad sys bd id |
66 |
| bad sys bd id |
66 |
| CPU n cannot identify CPU board. |
66 |
| CPU n cannot identify CPU board. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
66 |
| TST |
66 |
| 4n00 |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| SYS BD |
66 |
| CPUn start lst |
66 |
| CPU |
66 |
| CPU n is starting its late (with memory) self-tests. |
66 |
| CPU n is starting its late (with memory) self-tests. |
66 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| WRN |
67 |
| 4n01 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn skip lst |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is bypassing its late self-tests to save time. |
67 |
| CPU n is bypassing its late self-tests to save time. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n0E |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn exit lst |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n finished its late self-tests. |
67 |
| CPU n finished its late self-tests. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n20 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst erly st |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing some of its early self-tests from system memory. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing some of its early self-tests from system memory. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n21 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst basic |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its basic operations self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its basic operations self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n22 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst alu |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its arithmetic and logic unit self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its arithmetic and logic unit self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n23 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst branch |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its branch instruction self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its branch instruction self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n24 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst arth cd |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its arithmetic conditions self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its arithmetic conditions self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n25 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst bit ops |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its bit operations self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its bit operations self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n26 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst ctl reg |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its control register self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its control register self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n27 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst ext int |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its external interrupt self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its external interrupt self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n28 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst itimer |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its interval timer self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its interval timer self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n29 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst mltimed |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its multi-media instructions self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its multi-media instructions self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n2A |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst shadow |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its shadow register self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its shadow register self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n2B |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst dg regs |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its diagnose register self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its diagnose register self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n2C |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst rdrs |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its remote diagnose register self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its remote diagnose register self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n2D |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn lst bypass |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its integer bypass operation self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is re-executing its integer bypass operation self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n30 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn cache byte |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache sub-word operations self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache sub-word operations self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n40 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn cache flush |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is starting its cache flush self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is starting its cache flush self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
67 |
| TST |
67 |
| 4n50 |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| SYS BD |
67 |
| CPUn icache miss |
67 |
| CPU |
67 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache miss self-test. |
67 |
| CPU n is starting its instruction cache miss self-test. |
67 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| TST |
68 |
| 4n60 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| CPUn dcache miss |
68 |
| CPU |
68 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache miss self-test. |
68 |
| CPU n is starting its data cache miss self-test. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n00 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| unknown bus err |
68 |
| unknown bus err |
68 |
| CPU n detected an unknown error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| CPU n detected an unknown error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n02 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| path err assertd |
68 |
| path err assertd |
68 |
| CPU n detected a path error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| CPU n detected a path error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n04 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| data parity err |
68 |
| data parity err |
68 |
| CPU n detected a data, address, or control parity error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| CPU n detected a data, address, or control parity error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n07 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| Runway dir error |
68 |
| Runway dir error |
68 |
| CPU n detected a directed error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| CPU n detected a directed error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n08 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| Runway broad err |
68 |
| Runway broad err |
68 |
| CPU n detected a broadcast error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| CPU n detected a broadcast error on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n0A |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| illegal response |
68 |
| illegal response |
68 |
| CPU n received data that did not match any outstanding data request. |
68 |
| CPU n received data that did not match any outstanding data request. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n0B |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| bus timeout |
68 |
| bus timeout |
68 |
| CPU n timed out before receiving requested data. The responder is logged in the system responder ... |
68 |
| CPU n timed out before receiving requested data. The responder is logged in the system responder ... |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 5n0C |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| CPU sync failure |
68 |
| CPU sync failure |
68 |
| CPU n’s synchronizer detected a rule violation on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| CPU n’s synchronizer detected a rule violation on the system bus (Runway). |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| INI |
68 |
| 7000 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| start DIMM scan |
68 |
| start DIMM scan |
68 |
| Start looking for installed DIMMs. |
68 |
| Start looking for installed DIMMs. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| INI |
68 |
| 7002 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| init mem tables |
68 |
| init mem tables |
68 |
| Initialize memory data structures. |
68 |
| Initialize memory data structures. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 7004 |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| SYS BD |
68 |
| mem plt upd fail |
68 |
| mem plt upd fail |
68 |
| Error updating memory platform data. |
68 |
| Error updating memory platform data. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 7005 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| insufficient mem |
68 |
| insufficient mem |
68 |
| Insufficient memory detected to continue. |
68 |
| Insufficient memory detected to continue. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| TST |
68 |
| 7010 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| check DIMM order |
68 |
| check DIMM order |
68 |
| Start memory DIMM order check. |
68 |
| Start memory DIMM order check. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| WRN |
68 |
| 7011 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| skip DIMM ord ck |
68 |
| skip DIMM ord ck |
68 |
| Bypass memory DIMM order check. |
68 |
| Bypass memory DIMM order check. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 7012 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM order error |
68 |
| DIMM order error |
68 |
| Memory DIMMs are not in the proper order. |
68 |
| Memory DIMMs are not in the proper order. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 7013 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM order error |
68 |
| DIMM order error |
68 |
| Memory DIMMs are not in the proper order. As a result, the system cannot access one or more DIMMs... |
68 |
| Memory DIMMs are not in the proper order. As a result, the system cannot access one or more DIMMs... |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| TST |
68 |
| 7016 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM pair check |
68 |
| DIMM pair check |
68 |
| Start memory DIMM pair check (DIMMs in a pair (e.g. 0a/0b) must match in J7000). |
68 |
| Start memory DIMM pair check (DIMMs in a pair (e.g. 0a/0b) must match in J7000). |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| WRN |
68 |
| 7017 |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| skip mem pair ck |
68 |
| skip mem pair ck |
68 |
| Bypass memory DIMM set check. |
68 |
| Bypass memory DIMM set check. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
68 |
| FLT |
68 |
| 701F |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| DIMM |
68 |
| no memory found |
68 |
| no memory found |
68 |
| Memory scan couldn’t find any DIMMs. |
68 |
| Memory scan couldn’t find any DIMMs. |
68 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| TST |
69 |
| 7020 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| search for IMM |
69 |
| search for IMM |
69 |
| Try to find a single memory bank to use for the initial memory module. |
69 |
| Try to find a single memory bank to use for the initial memory module. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| TST |
69 |
| 703s |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM s IMM vrfy |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM s was the initial memory module last boot. Verify it still works. |
69 |
| DIMM s was the initial memory module last boot. Verify it still works. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 704s |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM s IMM fail |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM s failed the initial memory module test. |
69 |
| DIMM s failed the initial memory module test. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| TST |
69 |
| 705s |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM s IMM test |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| Test DIMM in slot s as the initial memory module. |
69 |
| Test DIMM in slot s as the initial memory module. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| INI |
69 |
| 706s |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM s is IMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM s chosen as initial memory module. |
69 |
| DIMM s chosen as initial memory module. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| INI |
69 |
| 70F0 |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM scan done |
69 |
| DIMM scan done |
69 |
| Memory DIMM scan complete. |
69 |
| Memory DIMM scan complete. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| TST |
69 |
| 7100 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| mem register tst |
69 |
| mem register tst |
69 |
| Start testing registers in memory controller. |
69 |
| Start testing registers in memory controller. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| WRN |
69 |
| 7101 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| skip mem reg tst |
69 |
| skip mem reg tst |
69 |
| Bypass the memory controller register test. |
69 |
| Bypass the memory controller register test. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 7102 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| mem addr reg tst |
69 |
| mem addr reg tst |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller address registers. |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller address registers. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 7103 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| mem mbat reg tst |
69 |
| mem mbat reg tst |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller bank registers. |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller bank registers. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 7104 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| mem reg tst fail |
69 |
| mem reg tst fail |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller memory registers. |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller memory registers. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 7105 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| mem err reg test |
69 |
| mem err reg test |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller error registers. |
69 |
| Firmware detected an error in the memory controller error registers. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 7106 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| mem err clr fail |
69 |
| mem err clr fail |
69 |
| Firmware was unable to clear the error registers after testing. |
69 |
| Firmware was unable to clear the error registers after testing. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| INI |
69 |
| 7200 |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| strt DIMM detect |
69 |
| strt DIMM detect |
69 |
| Start the Serial Presence Detection (SPD) to search for memory DIMMs. |
69 |
| Start the Serial Presence Detection (SPD) to search for memory DIMMs. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| INI |
69 |
| 7201 |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM detect x% |
69 |
| DIMM detect |
69 |
| SPD is x% finished. |
69 |
| SPD is x% finished. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| WRN |
69 |
| 7202 |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| SYS BD |
69 |
| skip DIMM detect |
69 |
| skip DIMM detect |
69 |
| Bypass Serial Presence Detection. |
69 |
| Bypass Serial Presence Detection. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 7203 |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| unsupp DIMM type |
69 |
| unsupp DIMM type |
69 |
| SPD found an unsupported DIMM type. |
69 |
| SPD found an unsupported DIMM type. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| FLT |
69 |
| 7204 |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| SPD fatal error |
69 |
| SPD fatal error |
69 |
| SPD detected an unexpected, fatal error. |
69 |
| SPD detected an unexpected, fatal error. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| INI |
69 |
| 7205 |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| add HP DIMM type |
69 |
| add HP DIMM type |
69 |
| New HP manufactured DIMM type added to tables. |
69 |
| New HP manufactured DIMM type added to tables. |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
69 |
| INI |
69 |
| 7206 |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| DIMM |
69 |
| non-HP DIMM type |
69 |
| non-HP DIMM type |
69 |
| New non-HP DIMM type added to tables (use at own risk). |
69 |
| New non-HP DIMM type added to tables (use at own risk). |
69 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| 7207 |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM table full |
70 |
| DIMM table full |
70 |
| The DIMM table is full--cannot add new type. |
70 |
| The DIMM table is full--cannot add new type. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| 7208 |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| no DIMMs found |
70 |
| no DIMMs found |
70 |
| SPD didn’t find any memory DIMMs. |
70 |
| SPD didn’t find any memory DIMMs. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 721s |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| is DIMM s inst? |
70 |
| is DIMM |
70 |
| SPD is checking memory slot s. |
70 |
| SPD is checking memory slot s. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 722s |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| ???? DIMM in s |
70 |
| ???? DIMM in s |
70 |
| SPD found a DIMM in slot s, but can’t determine its size. DIMM will not be used. |
70 |
| SPD found a DIMM in slot s, but can’t determine its size. DIMM will not be used. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 723s |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| 128M DIMM in s |
70 |
| 128M DIMM in s |
70 |
| SPD found a 128MB DIMM in slot s. |
70 |
| SPD found a 128MB DIMM in slot s. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 724s |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| 256M DIMM in s |
70 |
| 256M DIMM in s |
70 |
| SPD found a 256MB DIMM in slot s. |
70 |
| SPD found a 256MB DIMM in slot s. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 725s |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| 512M DIMM in s |
70 |
| 512M DIMM in s |
70 |
| SPD found a 512MB DIMM in slot s. |
70 |
| SPD found a 512MB DIMM in slot s. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| 72As |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM s checksum |
70 |
| DIMM s checksum |
70 |
| DIMM in slot s failed SPD checksum and will not be used. |
70 |
| DIMM in slot s failed SPD checksum and will not be used. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| 72Cs |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM s mismatch |
70 |
| DIMM s mismatch |
70 |
| DIMM in slot s didn’t match the other in pair. (J7000 only--DIMMs must be in matched pairs.) |
70 |
| DIMM in slot s didn’t match the other in pair. (J7000 only--DIMMs must be in matched pairs.) |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| 72Ds |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| DIMM s load err |
70 |
| Memory DIMMs are not in the proper order. As a result, the system cannot access DIMM s and has de... |
70 |
| Memory DIMMs are not in the proper order. As a result, the system cannot access DIMM s and has de... |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 7300 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| mem config start |
70 |
| mem config start |
70 |
| Starting main memory configuration. |
70 |
| Starting main memory configuration. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| TST |
70 |
| TST |
70 |
| 7301 |
70 |
| 7301 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| check mem config |
70 |
| check mem config |
70 |
| Checking for memory configuration change since last boot. |
70 |
| Checking for memory configuration change since last boot. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| WRN |
70 |
| 7302 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| mem confg changd |
70 |
| mem confg changd |
70 |
| mem confg changd |
70 |
| Memory physical configuration changed since last boot. |
70 |
| Memory physical configuration changed since last boot. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 7303 |
70 |
| 7303 |
70 |
| 7303 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| use saved config |
70 |
| use saved config |
70 |
| use saved config |
70 |
| Memory physical configuration didn’t change. Use stored configuration data. |
70 |
| Memory physical configuration didn’t change. Use stored configuration data. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 7304 |
70 |
| 7304 |
70 |
| 7304 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| build mem intrlv |
70 |
| build mem intrlv |
70 |
| build mem intrlv |
70 |
| Building memory configuration with all DIMMs interleaved. |
70 |
| Building memory configuration with all DIMMs interleaved. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 7305 |
70 |
| 7305 |
70 |
| 7305 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| save mem config |
70 |
| save mem config |
70 |
| save mem config |
70 |
| Saving memory configuration information in non-volatile memory. |
70 |
| Saving memory configuration information in non-volatile memory. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| WRN |
70 |
| 7306 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| use alt mem conf |
70 |
| use alt mem conf |
70 |
| Memory will be configured from fixed values, instead of detected DIMMs. |
70 |
| Memory will be configured from fixed values, instead of detected DIMMs. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| INI |
70 |
| 7307 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| interleve memory |
70 |
| Generating the memory interleave. |
70 |
| Generating the memory interleave. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| 7308 |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| SYS BD |
70 |
| PDT is disabled |
70 |
| PDT is disabled |
70 |
| Firmware detected bad memory pages, but the Page Deallocation Table is disabled. |
70 |
| Firmware detected bad memory pages, but the Page Deallocation Table is disabled. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| FLT |
70 |
| 7309 |
70 |
| DIMM |
70 |
| insufficient mem |
70 |
| Insufficient error-free memory to continue. |
70 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| FLT |
71 |
| 730C |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| mem intrlv fail |
71 |
| mem intrlv fail |
71 |
| Memory interleave generation failed. |
71 |
| Memory interleave generation failed. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| INI |
71 |
| 730F |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| mem config done |
71 |
| mem config done |
71 |
| Main memory configuration complete. |
71 |
| Main memory configuration complete. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7400 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| non-dest mem tst |
71 |
| non-dest mem tst |
71 |
| Starting non-destructive memory test. |
71 |
| Starting non-destructive memory test. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 740F |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| non-dst tst done |
71 |
| non-dst tst done |
71 |
| Non-destructive memory test complete. |
71 |
| Non-destructive memory test complete. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| INI |
71 |
| 7500 |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| memory reset |
71 |
| memory reset |
71 |
| Resetting memory system. |
71 |
| Resetting memory system. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| WRN |
71 |
| 7501 |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| mem log clr warn |
71 |
| mem log clr warn |
71 |
| Memory error logs didn’t clear on first try. |
71 |
| Memory error logs didn’t clear on first try. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| FLT |
71 |
| 7502 |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| SYS BD |
71 |
| mem err log fail |
71 |
| mem err log fail |
71 |
| Firmware could not clear memory error logs. |
71 |
| Firmware could not clear memory error logs. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7600 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| dest mem test |
71 |
| dest mem test |
71 |
| Starting the destructive memory test. |
71 |
| Starting the destructive memory test. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| WRN |
71 |
| 7601 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| mem init only |
71 |
| mem init only |
71 |
| Skip the test, just initialize memory to save time. |
71 |
| Skip the test, just initialize memory to save time. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7602 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| tst 1st mem page |
71 |
| tst 1st mem page |
71 |
| Starting 3-pass test of first memory page. |
71 |
| Starting 3-pass test of first memory page. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7603 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| tst rest of mem |
71 |
| tst rest of mem |
71 |
| Starting 3-pass test of the rest of memory. |
71 |
| Starting 3-pass test of the rest of memory. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7604 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| start 1st pass |
71 |
| start 1st pass |
71 |
| Starting 1st pass of memory test (write pseudorandom sequence). |
71 |
| Starting 1st pass of memory test (write pseudorandom sequence). |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7605 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| 1st pass x% |
71 |
| 1st pass |
71 |
| First pass is x% complete. |
71 |
| First pass is x% complete. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7606 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| start 2nd pass |
71 |
| start 2nd pass |
71 |
| Starting 2nd pass of memory test (verify pseudorandom sequence, write inverse). |
71 |
| Starting 2nd pass of memory test (verify pseudorandom sequence, write inverse). |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7607 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| 2nd pass x% |
71 |
| 2nd pass |
71 |
| Second pass is x% complete. |
71 |
| Second pass is x% complete. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7608 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| start 3rd pass |
71 |
| start 3rd pass |
71 |
| Starting 3rd pass of memory test (verify inverse sequence). |
71 |
| Starting 3rd pass of memory test (verify inverse sequence). |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 7609 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| 3rd pass x% |
71 |
| 3rd pass x% |
71 |
| Third pass is x% complete. |
71 |
| Third pass is x% complete. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 760A |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| start mem init |
71 |
| start mem init |
71 |
| Starting memory initialization. (Initialize to zero to set ECC.) |
71 |
| Starting memory initialization. (Initialize to zero to set ECC.) |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| TST |
71 |
| 760B |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| mem init x% |
71 |
| mem init |
71 |
| Memory initialization is x% complete. |
71 |
| Memory initialization is x% complete. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| WRN |
71 |
| 760C |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| repeat dest test |
71 |
| repeat dest test |
71 |
| Re-execute destructive test for hardware troubleshooting. |
71 |
| Re-execute destructive test for hardware troubleshooting. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| FLT |
71 |
| 760D |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| mem code cpy err |
71 |
| mem code cpy err |
71 |
| Firmware tried to copy code from ROM to memory, but the copy didn’t match the original. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| FLT |
71 |
| 7610 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| ECC wrt/read err |
71 |
| Writing and reading back good data caused memory ECC error. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
71 |
| FLT |
71 |
| 7611 |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| DIMM |
71 |
| ECC single data |
71 |
| ECC single data |
71 |
| Memory ECC test failed to detect single-bit data error. |
71 |
| Memory ECC test failed to detect single-bit data error. |
71 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7612 |
72 |
| DIMM |
72 |
| DIMM |
72 |
| ECC single ECC |
72 |
| ECC single ECC |
72 |
| Memory ECC test failed to detect single-bit ECC error. |
72 |
| Memory ECC test failed to detect single-bit ECC error. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7613 |
72 |
| DIMM |
72 |
| DIMM |
72 |
| ECC multipl data |
72 |
| ECC multipl data |
72 |
| Memory ECC test failed to detect multiple-bit data error. |
72 |
| Memory ECC test failed to detect multiple-bit data error. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7614 |
72 |
| DIMM |
72 |
| DIMM |
72 |
| ECC multpl signl |
72 |
| ECC multpl signl |
72 |
| Memory ECC test failed to signal multiple-bit error. |
72 |
| Memory ECC test failed to signal multiple-bit error. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7800 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem err summary |
72 |
| mem err summary |
72 |
| Printing memory error summary word to RS-232. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7801 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| bus ctrl par err |
72 |
| bus ctrl par err |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) control parity error detected. |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) control parity error detected. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7802 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| bus addr par err |
72 |
| bus addr par err |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) address parity error detected. |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) address parity error detected. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7803 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| bus data par err |
72 |
| bus data par err |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) data parity error detected. |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) data parity error detected. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7804 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem out of range |
72 |
| mem out of range |
72 |
| Memory access outside configured memory space. |
72 |
| Memory access outside configured memory space. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7805 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| bus broadcst err |
72 |
| bus broadcst err |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) broadcast error detected. |
72 |
| System bus (Runway) broadcast error detected. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7806 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem addr par err |
72 |
| mem addr par err |
72 |
| Memory bus address parity error detected. |
72 |
| Memory bus address parity error detected. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7807 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem ctlr stat wd |
72 |
| Printing memory controller status word to RS-232. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 781s |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| DIMM s uncor err |
72 |
| DIMM s uncor err |
72 |
| Uncorrectable ECC error detected in DIMM s. |
72 |
| Uncorrectable ECC error detected in DIMM s. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 782s |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| DIMM s corr err |
72 |
| DIMM s corr err |
72 |
| Correctable ECC error detected in DIMM s. |
72 |
| Correctable ECC error detected in DIMM s. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7840 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| unexpected HPMC |
72 |
| unexpected HPMC |
72 |
| Unexpected HPMC detected. |
72 |
| Unexpected HPMC detected. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7841 |
72 |
| 7841 |
72 |
| 7841 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem status invld |
72 |
| mem status invld |
72 |
| mem status invld |
72 |
| Memory error status word is invalid. |
72 |
| Memory error status word is invalid. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7842 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem summ invalid |
72 |
| mem summ invalid |
72 |
| Memory summary word is invalid. |
72 |
| Memory summary word is invalid. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7843 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| fwd prog invalid |
72 |
| fwd prog invalid |
72 |
| Memory forward progress word is invalid. |
72 |
| Memory forward progress word is invalid. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7844 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem HPMC summ wd |
72 |
| mem HPMC summ wd |
72 |
| Printing memory error summary word to RS-232. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7845 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem ctlr stat wd |
72 |
| Printing memory controller status word to RS-232. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
72 |
| FLT |
72 |
| 7846 |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| SYS BD |
72 |
| mem err overflow |
72 |
| mem err overflow |
72 |
| Multiple memory errors detected. |
72 |
| Multiple memory errors detected. |
72 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7848 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| addr not mapped |
73 |
| addr not mapped |
73 |
| Memory address outside configured memory space. |
73 |
| Memory address outside configured memory space. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 785s |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| MBE in DIMM s |
73 |
| MBE in DIMM |
73 |
| Destructive memory test detected an uncorrectable memory error in DIMM s. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 786s |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| SBE&MBE DIMM s |
73 |
| SBE&MBE DIMM |
73 |
| Destructive memory test detected both an uncorrectable and a correctable memory error in DIMM s. |
73 |
| Destructive memory test detected both an uncorrectable and a correctable memory error in DIMM s. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 787s |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| mem err DIMM s |
73 |
| mem err DIMM |
73 |
| Destructive memory test detected a pattern compare error in DIMM s. |
73 |
| Destructive memory test detected a pattern compare error in DIMM s. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 788s |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| SBE in DIMM s |
73 |
| SBE in DIMM |
73 |
| Destructive memory test detected a correctable memory error in DIMM s. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7890 |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| MBE overwrt SBE |
73 |
| MBE overwrt SBE |
73 |
| Firmware replaced a correctable memory error entry in the PDT with an uncorrectable memory error ... |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7891 |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| DIMM |
73 |
| dup entry in PDT |
73 |
| dup entry in PDT |
73 |
| The PDT already contains an entry at that address. |
73 |
| The PDT already contains an entry at that address. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7892 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| PDT write error |
73 |
| PDT write error |
73 |
| Error adding the entry to the PDT. |
73 |
| Error adding the entry to the PDT. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7893 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| PDT is full |
73 |
| PDT is full |
73 |
| The PDT is full--cannot add new entry. |
73 |
| The PDT is full--cannot add new entry. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7900 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| no DMT entry |
73 |
| no DMT entry |
73 |
| Internal error--cannot find DIMM entry. |
73 |
| Internal error--cannot find DIMM entry. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7901 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| no rank entry |
73 |
| no rank entry |
73 |
| Internal error--cannot find rank entry. |
73 |
| Internal error--cannot find rank entry. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7902 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| bad refrsh intvl |
73 |
| bad refrsh intvl |
73 |
| Computed refresh interval is invalid. |
73 |
| Computed refresh interval is invalid. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7903 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| mem intrlv fail |
73 |
| mem intrlv fail |
73 |
| Cannot generate memory interleave. |
73 |
| Cannot generate memory interleave. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7904 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| mem reloc failed |
73 |
| mem reloc failed |
73 |
| Cannot interleave with relocated range (3.75GB - 4.0GB). |
73 |
| Cannot interleave with relocated range (3.75GB - 4.0GB). |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 7905 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| mem intrlv error |
73 |
| mem intrlv error |
73 |
| Undefined memory interleave failure. |
73 |
| Undefined memory interleave failure. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| FLT |
73 |
| 79FF |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| mem firmware err |
73 |
| mem firmware err |
73 |
| Internal error--never expected this to happen. |
73 |
| Internal error--never expected this to happen. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| WRN |
73 |
| 80F3 |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| SYS BD |
73 |
| err rd IODC byte |
73 |
| Cannot read IODC from ROM or card. |
73 |
| Cannot read IODC from ROM or card. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| WRN |
73 |
| 80F4 |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| boot read error |
73 |
| Cannot load IODC entry_init for boot device. |
73 |
| Cannot load IODC entry_init for boot device. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| WRN |
73 |
| 80F5 |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| boot exec error |
73 |
| boot exec error |
73 |
| Error initializing boot device. |
73 |
| Error initializing boot device. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| WRN |
73 |
| 80F6 |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| boot read error |
73 |
| boot read error |
73 |
| Cannot load IODC entry_io for boot device. |
73 |
| Cannot load IODC entry_io for boot device. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
73 |
| WRN |
73 |
| 80F7 |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| EXT IO |
73 |
| boot IO error |
73 |
| boot IO error |
73 |
| Error detected during boot device I/O. |
73 |
| Error detected during boot device I/O. |
73 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| 80F8 |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| invalid boot dev |
74 |
| invalid boot dev |
74 |
| Invalid boot device class; bad IODC? |
74 |
| Invalid boot device class; bad IODC? |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| 80FC |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| invalid boot dev |
74 |
| invalid boot dev |
74 |
| Unexpected error; bad IODC? |
74 |
| Unexpected error; bad IODC? |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8800 |
74 |
| IOCARD |
74 |
| IOCARD |
74 |
| PCI BusWlk start |
74 |
| PCI BusWlk start |
74 |
| Starting PCI bus and device discovery. |
74 |
| Starting PCI bus and device discovery. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 88r1 |
74 |
| 88r1 |
74 |
| 88r1 |
74 |
| IOCARD |
74 |
| IOCARD |
74 |
| IOCARD |
74 |
| PCI Rope r walk |
74 |
| PCI Rope |
74 |
| PCI Rope |
74 |
| r |
74 |
| walk |
74 |
| Starting PCI bus and device discovery on Rope r. |
74 |
| Starting PCI bus and device discovery on Rope r. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8802 |
74 |
| 8802 |
74 |
| IOCARD |
74 |
| IOCARD |
74 |
| PCI BusWalk done |
74 |
| PCI BusWalk done |
74 |
| PCI bus and device discovery complete. |
74 |
| PCI bus and device discovery complete. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8803 |
74 |
| 8803 |
74 |
| SYS BD |
74 |
| SYS BD |
74 |
| PCI alloc done |
74 |
| PCI alloc done |
74 |
| Done allocating address space for PCI devices. |
74 |
| Done allocating address space for PCI devices. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8804 |
74 |
| 8804 |
74 |
| 8804 |
74 |
| SYS BD |
74 |
| SYS BD |
74 |
| SYS BD |
74 |
| PCI config done |
74 |
| PCI config done |
74 |
| PCI config done |
74 |
| Done configuring PCI devices. |
74 |
| Done configuring PCI devices. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| 881r |
74 |
| 881 |
74 |
| 881 |
74 |
| r |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| R2PCIr not found |
74 |
| R2PCI |
74 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge r not found. |
74 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge r not found. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| 883r |
74 |
| 883r |
74 |
| 883r |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| Rope r config err |
74 |
| Rope |
74 |
| PCI configuration failed below Rope-to-PCI bridge r. |
74 |
| PCI configuration failed below Rope-to-PCI bridge r. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| 884r |
74 |
| 884r |
74 |
| 884r |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| Rope r tgl fail |
74 |
| Rope r tgl fail |
74 |
| Rope r tgl fail |
74 |
| Rope r debug register toggle failed. |
74 |
| Rope r debug register toggle failed. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8850 |
74 |
| 8850 |
74 |
| 8850 |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| early rope0 init |
74 |
| early rope0 init |
74 |
| early rope0 init |
74 |
| Initializing rope 0 for early RS-232 output. |
74 |
| Initializing rope 0 for early RS-232 output. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| 8850 |
74 |
| 8850 |
74 |
| 8850 |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| rope0 init fail |
74 |
| rope0 init fail |
74 |
| rope0 init fail |
74 |
| Couldn’t initialize rope 0. |
74 |
| Couldn’t initialize rope 0. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8860 |
74 |
| 8860 |
74 |
| 8860 |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| SYS_BD |
74 |
| rope0 init done |
74 |
| rope0 init done |
74 |
| rope0 init done |
74 |
| Rope 0 initialization complete. |
74 |
| Rope 0 initialization complete. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8870 |
74 |
| 8870 |
74 |
| 8870 |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| early R2PCI init |
74 |
| early R2PCI init |
74 |
| early R2PCI init |
74 |
| Initializing rope-to-PCI bridge 0 for early RS-232 output. |
74 |
| Initializing rope-to-PCI bridge 0 for early RS-232 output. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| 8870 |
74 |
| 8870 |
74 |
| 8870 |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| R2PCI init fail |
74 |
| R2PCI init fail |
74 |
| R2PCI init fail |
74 |
| Couldn’t initialize rope-to-PCI bridge 0. |
74 |
| Couldn’t initialize rope-to-PCI bridge 0. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8880 |
74 |
| 8880 |
74 |
| 8880 |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| R2PCI init done |
74 |
| R2PCI init done |
74 |
| R2PCI init done |
74 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge 0 initialization. |
74 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge 0 initialization. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 8890 |
74 |
| 8890 |
74 |
| 8890 |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| early Super init |
74 |
| early Super init |
74 |
| early Super init |
74 |
| Iniitalizing Super-I/O for early RS-232 output. |
74 |
| Iniitalizing Super-I/O for early RS-232 output. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| FLT |
74 |
| 8890 |
74 |
| 8890 |
74 |
| 8890 |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| Super init fail |
74 |
| Super init fail |
74 |
| Super init fail |
74 |
| Couldn’t initialize Super-I/O. |
74 |
| Couldn’t initialize Super-I/O. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| INI |
74 |
| 88A0 |
74 |
| 88A0 |
74 |
| 88A0 |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| IO_BD |
74 |
| Super init done |
74 |
| Super init done |
74 |
| Super init done |
74 |
| Super-I/O initialization complete. |
74 |
| Super-I/O initialization complete. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| 8A03 |
74 |
| 8A03 |
74 |
| 8A03 |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| No graph console |
74 |
| No graph console |
74 |
| No graph console |
74 |
| Cannot re-establish communications with the graphics console. |
74 |
| Cannot re-establish communications with the graphics console. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| 8A04 |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| No USB keyboard |
74 |
| No USB keyboard |
74 |
| Cannot re-establish communications with the USB keyboard. |
74 |
| Cannot re-establish communications with the USB keyboard. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| TST |
74 |
| 8C06 |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| PCI BIST test |
74 |
| PCI BIST test |
74 |
| Running PCI Built-In Self-Test |
74 |
| Running PCI Built-In Self-Test |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| 8C07 |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| EXT IO |
74 |
| PCI BIST error |
74 |
| PCI BIST error |
74 |
| PCI Built-In Self-Test failed. |
74 |
| PCI Built-In Self-Test failed. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| 8C08 |
74 |
| SYS BD |
74 |
| SYS BD |
74 |
| PCI alloc error |
74 |
| PCI alloc error |
74 |
| PCI address space allocation failed. |
74 |
| PCI address space allocation failed. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
74 |
| WRN |
74 |
| 8C09 |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| IO BD |
74 |
| PCI mem mngr err |
74 |
| PCI mem mngr err |
74 |
| Memory allocation for PCI device failed. |
74 |
| Memory allocation for PCI device failed. |
74 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 8C0A |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| PCI mem type err |
75 |
| PCI mem type err |
75 |
| PCI device requested invalid memory type. |
75 |
| PCI device requested invalid memory type. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 8C0B |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| PCI max bus dpth |
75 |
| PCI max bus dpth |
75 |
| PCI bus depth exceeded maximum supported depth. |
75 |
| PCI bus depth exceeded maximum supported depth. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 8C0C |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| PCI dev not cnfg |
75 |
| PCI dev not cnfg |
75 |
| Unable to configure PCI device. |
75 |
| Unable to configure PCI device. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 8C0F |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| dev tree ovrflow |
75 |
| dev tree ovrflow |
75 |
| Data space for PCI devices is full. |
75 |
| Data space for PCI devices is full. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 8DEC |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| init LAN SROM |
75 |
| init LAN SROM |
75 |
| Initializing the core LAN serial EPROM. |
75 |
| Initializing the core LAN serial EPROM. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| SHU |
75 |
| 8DEC |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| resetting system |
75 |
| resetting system |
75 |
| Restarting system after core LAN initialization. |
75 |
| Restarting system after core LAN initialization. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| FLT |
75 |
| 8E10 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| PARALEL port cfg |
75 |
| PARALEL port cfg |
75 |
| Parallel port configuration failed. |
75 |
| Parallel port configuration failed. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| FLT |
75 |
| 8E11 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| SERIAL1 port cfg |
75 |
| SERIAL1 port cfg |
75 |
| Serial 1 port configuration failed. |
75 |
| Serial 1 port configuration failed. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| FLT |
75 |
| 8E12 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| SERIAL2 port cfg |
75 |
| SERIAL2 port cfg |
75 |
| Serial 2 port configuration failed. |
75 |
| Serial 2 port configuration failed. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| FLT |
75 |
| 8E13 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| FLOPPY drive cfg |
75 |
| FLOPPY drive cfg |
75 |
| Floppy drive configuration failed. |
75 |
| Floppy drive configuration failed. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| FLT |
75 |
| 8E20 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| bad USB port cfg |
75 |
| bad USB port cfg |
75 |
| USB port configuration failed. |
75 |
| USB port configuration failed. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 9001 |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| no console found |
75 |
| no console found |
75 |
| Search for console display device failed. |
75 |
| Search for console display device failed. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 9151 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| init SERIAL_1 |
75 |
| init SERIAL_1 |
75 |
| Initializing serial 1 port as console display. |
75 |
| Initializing serial 1 port as console display. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 9152 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| init SERIAL_2 |
75 |
| init SERIAL_2 |
75 |
| Initializing serial 2 port as console display. |
75 |
| Initializing serial 2 port as console display. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 915F |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| init unknown dev |
75 |
| Initializing unknown device as console display. |
75 |
| Initializing unknown device as console display. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 916s |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| init PCI slot s |
75 |
| init PCI slot |
75 |
| Initializing PCI device in slot s as console display. |
75 |
| Initializing PCI device in slot s as console display. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 91DB |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| init SERIAL_LDB |
75 |
| init SERIAL_LDB |
75 |
| Initializing serial LDB port as console display. |
75 |
| Initializing serial LDB port as console display. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 9C51 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| consol is SER_1 |
75 |
| consol is SER_1 |
75 |
| Console display is on serial port 1. |
75 |
| Console display is on serial port 1. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 9C51 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| bad init SERIAL1 |
75 |
| bad init SERIAL1 |
75 |
| Serial port 1 failed to initialize as a console device. |
75 |
| Serial port 1 failed to initialize as a console device. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 9C52 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| consol is SER_2 |
75 |
| consol is SER_2 |
75 |
| Console display is on serial port 2. |
75 |
| Console display is on serial port 2. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| WRN |
75 |
| 9C52 |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| IO BD |
75 |
| bad init SERIAL2 |
75 |
| bad init SERIAL2 |
75 |
| Serial port 2 failed to initialize as a console device. |
75 |
| Serial port 2 failed to initialize as a console device. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
75 |
| INI |
75 |
| 9C6s |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| EXT IO |
75 |
| consol is GRAPHs |
75 |
| consol is GRAPH |
75 |
| Console display is on graphics card in PCI slot s. |
75 |
| Console display is on graphics card in PCI slot s. |
75 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| WRN |
76 |
| 9C6s |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| bad PCI slot s |
76 |
| bad PCI slot |
76 |
| Graphics in PCI slot s failed to initialize as a console device. |
76 |
| Graphics in PCI slot s failed to initialize as a console device. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| 9C8t |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| cnfg mon type t |
76 |
| cnfg mon type |
76 |
| Set graphics console to monitor type t. (Seen when cycling through types.) |
76 |
| Set graphics console to monitor type t. (Seen when cycling through types.) |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| WRN |
76 |
| 9C8t |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| mon type t fail |
76 |
| mon type t fail |
76 |
| Failed to configure console to monitor type t. |
76 |
| Failed to configure console to monitor type t. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| 9CDB |
76 |
| IO BD |
76 |
| IO BD |
76 |
| consl is SER_LDB |
76 |
| consl is SER_LDB |
76 |
| Console display is on serial LDB port. |
76 |
| Console display is on serial LDB port. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| WRN |
76 |
| 9CDB |
76 |
| IO BD |
76 |
| IO BD |
76 |
| bad init SER_LDB |
76 |
| bad init SER_LDB |
76 |
| Serial LDB port failed to initialize as a console device. |
76 |
| Serial LDB port failed to initialize as a console device. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| FLT |
76 |
| A088 |
76 |
| IO BD |
76 |
| IO BD |
76 |
| consl path fault |
76 |
| consl path fault |
76 |
| Unable to boot--no console device found. |
76 |
| Unable to boot--no console device found. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| WRN |
76 |
| A008 |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| no boot device |
76 |
| no boot device |
76 |
| Unable to boot--no bootable device found. |
76 |
| Unable to boot--no bootable device found. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| WRN |
76 |
| A0BD |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| device not ready |
76 |
| device not ready |
76 |
| Boot device not ready--operation may be retried. |
76 |
| Boot device not ready--operation may be retried. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| FLT |
76 |
| A0FF |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| unknown launch |
76 |
| unknown launch |
76 |
| Unable to boot. Explanation may appear on console. |
76 |
| Unable to boot. Explanation may appear on console. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| WRN |
76 |
| A50F |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| init pri pth err |
76 |
| init pri pth err |
76 |
| Unable to boot from primary boot device. |
76 |
| Unable to boot from primary boot device. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| WRN |
76 |
| A70F |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| EXT IO |
76 |
| init otr pth err |
76 |
| init otr pth err |
76 |
| Unable to boot from non-primary boot device. |
76 |
| Unable to boot from non-primary boot device. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C10m |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| CPUm is monarch |
76 |
| CPUm is monarch |
76 |
| CPU m was chosen as the monarch processor. (All other CPUs are slaves.) |
76 |
| CPU m was chosen as the monarch processor. (All other CPUs are slaves.) |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C30m |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| monarchm test |
76 |
| monarchm test |
76 |
| CPU m finished the monarch-only tests and system initialization. |
76 |
| CPU m finished the monarch-only tests and system initialization. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C30C |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| mnrch slv chck |
76 |
| mnrch slv chck |
76 |
| The monarch CPU is checking whether the slaves are in the correct rendezvous. |
76 |
| The monarch CPU is checking whether the slaves are in the correct rendezvous. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C3FF |
76 |
| SYS/IO |
76 |
| SYS/IO |
76 |
| late monarch tst |
76 |
| late monarch tst |
76 |
| The monarch CPU is starting the late (post-memory) monarch-only tests. |
76 |
| The monarch CPU is starting the late (post-memory) monarch-only tests. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| FLT |
76 |
| C3FF |
76 |
| SYS/IO |
76 |
| SYS/IO |
76 |
| late monarch flt |
76 |
| late monarch flt |
76 |
| The late (post-memory) monarch-only tests failed. |
76 |
| The late (post-memory) monarch-only tests failed. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C4CC |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| initialize ccp |
76 |
| initialize ccp |
76 |
| Searching for (lab-only) debugger card. |
76 |
| Searching for (lab-only) debugger card. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C4CD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| no ccp found |
76 |
| no ccp found |
76 |
| Debugger card not found. |
76 |
| Debugger card not found. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C4CE |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| ccp disabled |
76 |
| ccp disabled |
76 |
| Debugger card disabled. |
76 |
| Debugger card disabled. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C4CF |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| ccp found |
76 |
| ccp found |
76 |
| Debugger card found. |
76 |
| Debugger card found. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
76 |
| INI |
76 |
| C500 |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| SYS BD |
76 |
| get primary path |
76 |
| get primary path |
76 |
| Autoboot is reading primary boot path from stable store. |
76 |
| Autoboot is reading primary boot path from stable store. |
76 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| C540 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| init pri path |
77 |
| init pri path |
77 |
| Autoboot is trying to boot from primary boot device. |
77 |
| Autoboot is trying to boot from primary boot device. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| C580 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| load IPL pri pth |
77 |
| load IPL pri pth |
77 |
| Loading IPL from primary boot device. |
77 |
| Loading IPL from primary boot device. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C5F0 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| Error loading IPL from primary boot device. |
77 |
| Error loading IPL from primary boot device. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| FLT |
77 |
| C5F0 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| pri IPL fault |
77 |
| pri IPL fault |
77 |
| Error loading IPL from primary boot device. |
77 |
| Error loading IPL from primary boot device. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C5F1 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--load address invalid. |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--load address invalid. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C5F2 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--file is not IPL image. |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--file is not IPL image. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C5F3 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--IPL image size invalid. |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--IPL image size invalid. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C5F4 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--IPL entry point address invalid. |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--IPL entry point address invalid. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C5F8 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| err read pri IPL |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--IPL image checksum failed. |
77 |
| Cannot load IPL from primary boot device--IPL image checksum failed. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| C5FF |
77 |
| <blank> |
77 |
| launch pri IPL |
77 |
| launch pri IPL |
77 |
| Booting from primary boot path. |
77 |
| Booting from primary boot path. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| C642 |
77 |
| C642 |
77 |
| C642 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| init kybrd consl |
77 |
| init kybrd consl |
77 |
| init kybrd consl |
77 |
| Try to initialize USB keyboard. |
77 |
| Try to initialize USB keyboard. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| FLT |
77 |
| FLT |
77 |
| FLT |
77 |
| C642 |
77 |
| C642 |
77 |
| C642 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| kybd error |
77 |
| kybd error |
77 |
| kybd error |
77 |
| An error was detected trying to access the keyboard. |
77 |
| An error was detected trying to access the keyboard. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C643 |
77 |
| C643 |
77 |
| C643 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| keyboard reinit |
77 |
| keyboard reinit |
77 |
| keyboard reinit |
77 |
| Keyboard was re-initialized. |
77 |
| Keyboard was re-initialized. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C64F |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| reset montr type |
77 |
| reset montr type |
77 |
| The console device failed to initialize with the given monitor type. Try again with type 1. |
77 |
| The console device failed to initialize with the given monitor type. Try again with type 1. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| TST |
77 |
| C68s |
77 |
| SYS BD |
77 |
| SYS BD |
77 |
| test graph in s |
77 |
| test graph in |
77 |
| Look for graphics card in PCI slot s. |
77 |
| Look for graphics card in PCI slot s. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| C68s |
77 |
| SYS BD |
77 |
| SYS BD |
77 |
| init graph in s |
77 |
| init graph in s |
77 |
| Successfully initialized graphics card in PCI slot s. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C68s |
77 |
| SYS BD |
77 |
| SYS BD |
77 |
| fail graph in s |
77 |
| fail graph in |
77 |
| Card in PCI slot s failed graphics initialization or is not a graphics card. |
77 |
| Card in PCI slot s failed graphics initialization or is not a graphics card. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| C740 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| init other path |
77 |
| init other path |
77 |
| Autoboot is trying to boot from non-primary boot device. |
77 |
| Autoboot is trying to boot from non-primary boot device. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| INI |
77 |
| C780 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| ld IPL othr path |
77 |
| ld IPL othr path |
77 |
| Loading IPL from non-primary boot device. |
77 |
| Loading IPL from non-primary boot device. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
77 |
| WRN |
77 |
| C7F0 |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| EXT IO |
77 |
| other IPL fault |
77 |
| other IPL fault |
77 |
| Error loading IPL from non-primary boot device. |
77 |
| Error loading IPL from non-primary boot device. |
77 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| C7F1 |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--load address invalid. |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--load address invalid. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| C7F2 |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--file is not IPL image. |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--file is not IPL image. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| C7F3 |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--IPL image size invalid. |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--IPL image size invalid. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| C7F4 |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--IPL entry point address invalid. |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--IPL entry point address invalid. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| C7F8 |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| EXT IO |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| bad alt IPL read |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--IPL image checksum failed. |
78 |
| Cannot load IPL from non-primary boot device--IPL image checksum failed. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| C7FF |
78 |
| <blank> |
78 |
| launch IPL other |
78 |
| launch IPL other |
78 |
| Booting from a device other than the primary boot path. |
78 |
| Booting from a device other than the primary boot path. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| INI |
78 |
| CB00 |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| TOC initiated |
78 |
| TOC initiated |
78 |
| A Transfer of Control entered the firmware TOC handler. |
78 |
| A Transfer of Control entered the firmware TOC handler. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| CB01 |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| no OS TOC vector |
78 |
| no OS TOC vector |
78 |
| There is no TOC vector for the operating system. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| There is no TOC vector for the operating system. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| CB02 |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| bad OS TOC addr |
78 |
| bad OS TOC addr |
78 |
| The operating system TOC handler vector is invalid. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| The operating system TOC handler vector is invalid. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| CB03 |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| bad OS TOC code |
78 |
| bad OS TOC code |
78 |
| The operating system TOC handler is invalid. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| The operating system TOC handler is invalid. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| CB04 |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| bad OS TOC len |
78 |
| bad OS TOC len |
78 |
| The size of the operating system TOC handler is invalid. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| The size of the operating system TOC handler is invalid. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| CB05 |
78 |
| CB05 |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| bad OS TOC chksm |
78 |
| bad OS TOC chksm |
78 |
| The operating system TOC handler failed the checksum test. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| The operating system TOC handler failed the checksum test. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| CB0A |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| prev TOC logged |
78 |
| prev TOC logged |
78 |
| Firmware detected unread PIM data from a previous TOC and will not overwrite it. (PIM for this TO... |
78 |
| Firmware detected unread PIM data from a previous TOC and will not overwrite it. (PIM for this TO... |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| INI |
78 |
| CB0B |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| branch to OS TOC |
78 |
| branch to OS TOC |
78 |
| Branching to the operating system TOC handler. |
78 |
| Branching to the operating system TOC handler. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
78 |
| WRN |
78 |
| CB0C |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| SYS BD |
78 |
| br OS TOC failed |
78 |
| br OS TOC failed |
78 |
| Branch to the operating system TOC handler failed. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| Branch to the operating system TOC handler failed. Firmware will soft boot the system. |
78 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB10 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| LPMC initiated |
79 |
| LPMC initiated |
79 |
| A Low-Priority Machine Check entered the firmware LPMC handler. The handler should log the error ... |
79 |
| A Low-Priority Machine Check entered the firmware LPMC handler. The handler should log the error ... |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB11 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| icache LPMC err |
79 |
| An instruction cache parity error caused the LPMC. |
79 |
| An instruction cache parity error caused the LPMC. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB12 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| dcache LPMC err |
79 |
| dcache LPMC err |
79 |
| A data cache parity/ECC error caused the LPMC. |
79 |
| A data cache parity/ECC error caused the LPMC. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB13 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| dcache tag error |
79 |
| dcache tag error |
79 |
| The parity error is in the tag portion of the data cache. |
79 |
| The parity error is in the tag portion of the data cache. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB14 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| dcache data err |
79 |
| dcache data err |
79 |
| The parity error is in the data portion of the data cache. |
79 |
| The parity error is in the data portion of the data cache. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| FLT |
79 |
| CB1F |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| OS LPMC failed |
79 |
| OS LPMC failed |
79 |
| Firmware couldn’t branch to the operating system LPMC handler. It will halt the CPU, requiring a ... |
79 |
| Firmware couldn’t branch to the operating system LPMC handler. It will halt the CPU, requiring a ... |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB71 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| HPMC occurred |
79 |
| HPMC occurred |
79 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check caused entry to PDCE_CHECK (the firmware trap handler). |
79 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check caused entry to PDCE_CHECK (the firmware trap handler). |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB72 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| LPMC occurred |
79 |
| LPMC occurred |
79 |
| A Low-Priority Machine Check caused entry to PDCE_CHECK (the firmware trap handler). |
79 |
| A Low-Priority Machine Check caused entry to PDCE_CHECK (the firmware trap handler). |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| WRN |
79 |
| CB73 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| TOC occurred |
79 |
| TOC occurred |
79 |
| A Transfer of Control caused entry to PDCE_CHECK (the firmware trap handler). |
79 |
| A Transfer of Control caused entry to PDCE_CHECK (the firmware trap handler). |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| FLT |
79 |
| CB9r |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| Error on roper |
79 |
| Error on roper |
79 |
| An error was detected on rope r. |
79 |
| An error was detected on rope r. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| FLT |
79 |
| CB99 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| seed IVA handler |
79 |
| seed IVA handler |
79 |
| PDC_SEED_ERROR triggered an HPMC. |
79 |
| PDC_SEED_ERROR triggered an HPMC. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| FLT |
79 |
| CB9A |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| HPMC overwrite |
79 |
| HPMC overwrite |
79 |
| Firmware is overwriting PIM data from a previous HPMC. |
79 |
| Firmware is overwriting PIM data from a previous HPMC. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| OFF |
79 |
| CBA1 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| AIOC int dat err |
79 |
| AIOC int dat err |
79 |
| I/O controller internal error. |
79 |
| I/O controller internal error. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| OFF |
79 |
| CBA2 |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| EtoA rope perr |
79 |
| EtoA rope perr |
79 |
| Parity error between I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
79 |
| Parity error between I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| OFF |
79 |
| CBA3 |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| SYS BD |
79 |
| access invld TLB |
79 |
| access invld TLB |
79 |
| An invalid I/O TLB entry was accessed. |
79 |
| An invalid I/O TLB entry was accessed. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| OFF |
79 |
| CBA4 |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| EtoA rp cmd perr |
79 |
| EtoA rp cmd perr |
79 |
| Command parity error between I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
79 |
| Command parity error between I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
79 |
| OFF |
79 |
| CBA5 |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| IO BD |
79 |
| CDF timeout |
79 |
| CDF timeout |
79 |
| Rope Command/Data FIFO is backed up. |
79 |
| Rope Command/Data FIFO is backed up. |
79 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBA6 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI resp tmout |
80 |
| R2PCI resp tmout |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge timed out. Could be a failure of the PCI card, rope, or R2PCI bridge. |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge timed out. Could be a failure of the PCI card, rope, or R2PCI bridge. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBA7 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| Unknown AIOC err |
80 |
| Unknown AIOC err |
80 |
| Unknown I/O controller error. |
80 |
| Unknown I/O controller error. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBB1 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI timeout |
80 |
| PCI timeout |
80 |
| A PCI card requested the bus but failed to use it. |
80 |
| A PCI card requested the bus but failed to use it. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBB2 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI timeout; OV |
80 |
| PCI timeout; OV |
80 |
| More than once aPCI card requested the bus but failed to use it. |
80 |
| More than once aPCI card requested the bus but failed to use it. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBB3 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
80 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge internal error. |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge internal error. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBB4 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI int err;OV |
80 |
| R2PCI int err;OV |
80 |
| Multiple Rope-to-PCI bridge internal errors. |
80 |
| Multiple Rope-to-PCI bridge internal errors. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBB6 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI data req err |
80 |
| PCI data req err |
80 |
| PCI bus data requestor error: R2PCI detected PERR# assertion. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBB8 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI D req err;OV |
80 |
| PCI D req err;OV |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge detected multiple PERR# assertions. |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge detected multiple PERR# assertions. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBBA |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI data par err |
80 |
| PCI bus data parity error. |
80 |
| PCI bus data parity error. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBBC |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI Dpar err;OV |
80 |
| PCI Dpar err;OV |
80 |
| Multiple PCI bus data parity errors. |
80 |
| Multiple PCI bus data parity errors. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBBE |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
80 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
80 |
| Error in R2PCI internal data to PCI bus. |
80 |
| Error in R2PCI internal data to PCI bus. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBC0 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI int err;OV |
80 |
| R2PCI int err;OV |
80 |
| Multiple R2PCI internal data to PCI bus errors. |
80 |
| Multiple R2PCI internal data to PCI bus errors. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBC2 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI data parity |
80 |
| PCI data parity |
80 |
| PCI data parity error. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
80 |
| PCI data parity error. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBC4 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI data par; OV |
80 |
| PCI data par; OV |
80 |
| Multiple PCI data parity errors. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
80 |
| Multiple PCI data parity errors. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBC6 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
80 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge internal data error: R2PCI detected PERR# assertion. |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge internal data error: R2PCI detected PERR# assertion. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBC8 |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI int err;OV |
80 |
| R2PCI int err;OV |
80 |
| Multiple R2PCI internal data errors: R2PCI detected multiple PERR# assertions. |
80 |
| Multiple R2PCI internal data errors: R2PCI detected multiple PERR# assertions. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBCA |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI data rs err |
80 |
| PCI data rs err |
80 |
| PCI bus data responder error: R2PCI detected PERR# assertion. |
80 |
| PCI bus data responder error: R2PCI detected PERR# assertion. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBCC |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| PCI D rs err; OV |
80 |
| PCI D rs err; OV |
80 |
| Multiple PCI bus data responder errors: R2PCI detected multiple PERR# assertions. |
80 |
| Multiple PCI bus data responder errors: R2PCI detected multiple PERR# assertions. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
80 |
| OFF |
80 |
| CBCE |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| IO BD |
80 |
| R2PCI T-Abort |
80 |
| R2PCI T-Abort |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge signalled Target Abort. |
80 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge signalled Target Abort. |
80 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBD0 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| R2PCI T-Abort;OV |
81 |
| R2PCI T-Abort;OV |
81 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge signalled multiple Target Aborts. |
81 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge signalled multiple Target Aborts. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBD2 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI parity err |
81 |
| PCI parity err |
81 |
| PCI address/command parity error. |
81 |
| PCI address/command parity error. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBD4 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI par err; OV |
81 |
| PCI par err; OV |
81 |
| Multiple PCI address/command parity errors. |
81 |
| Multiple PCI address/command parity errors. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBD6 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI no DEVSEL# |
81 |
| PCI no DEVSEL# |
81 |
| No PCI device selected (DEVSEL# assertion). I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| No PCI device selected (DEVSEL# assertion). I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBD8 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI no DEVSEL;OV |
81 |
| PCI no DEVSEL;OV |
81 |
| Multiple DEVSEL# assertions. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| Multiple DEVSEL# assertions. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBDA |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI target abort |
81 |
| PCI target abort |
81 |
| A PCI device signalled Target Abort. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| A PCI device signalled Target Abort. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBDC |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI T-Abort; OV |
81 |
| PCI T-Abort; OV |
81 |
| A PCI device signalled multiple Target Aborts. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| A PCI device signalled multiple Target Aborts. I/O error log word 3 contains the error address. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBDD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI assrts LOCK# |
81 |
| PCI assrts LOCK# |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted LOCK#. |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted LOCK#. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBDE |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI LOCK#; OV |
81 |
| PCI LOCK#; OV |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted LOCK# multiple times. |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted LOCK# multiple times. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBE0 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI assrts SERR# |
81 |
| PCI assrts SERR# |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted SERR#: address parity error or other system error. |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted SERR#: address parity error or other system error. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBE2 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| PCI SERR#; OV |
81 |
| PCI SERR#; OV |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted SERR# multiple times. |
81 |
| A PCI device asserted SERR# multiple times. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBE3 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| Unknown PCI err |
81 |
| Unknown PCI err |
81 |
| Unknown PCI error detected. |
81 |
| Unknown PCI error detected. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBE6 |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| AtoE rope perr |
81 |
| AtoE rope perr |
81 |
| Parity error between system I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
81 |
| Parity error between system I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBE7 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
81 |
| R2PCI intrnl err |
81 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge internal data error. |
81 |
| Rope-to-PCI bridge internal data error. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBE8 |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| AtoE rope perr |
81 |
| AtoE rope perr |
81 |
| Command parity error between system I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
81 |
| Command parity error between system I/O controller and Rope-to-PCI bridge. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| OFF |
81 |
| CBE9 |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| IO BD |
81 |
| Unknown Rope err |
81 |
| Unknown Rope err |
81 |
| Unknown rope error occurred. |
81 |
| Unknown rope error occurred. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| FLT |
81 |
| CBF0 |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| HPMC initiated |
81 |
| HPMC initiated |
81 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check entered the firmware HPMC handler. |
81 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check entered the firmware HPMC handler. |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
81 |
| FLT |
81 |
| CBF1 |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| SYS BD |
81 |
| no OS HPMC IVA |
81 |
| no OS HPMC IVA |
81 |
| There is no HPMC vector for the operating system. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a power c... |
81 |
| There is no HPMC vector for the operating system. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a power c... |
81 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBF2 |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| bad OS HPMC len |
82 |
| bad OS HPMC len |
82 |
| The size of the operating system HPMC handler is invalid. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a... |
82 |
| The size of the operating system HPMC handler is invalid. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a... |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBF3 |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| bad OS HPMC addr |
82 |
| bad OS HPMC addr |
82 |
| The operating system HPMC handler vector is invalid. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a powe... |
82 |
| The operating system HPMC handler vector is invalid. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a powe... |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBF4 |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| bad OS HPMC cksm |
82 |
| bad OS HPMC cksm |
82 |
| The operating system HPMC handler failed the checksum test. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring... |
82 |
| The operating system HPMC handler failed the checksum test. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring... |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBF5 |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| OS HPMC vector 0 |
82 |
| OS HPMC vector 0 |
82 |
| The size of the operating system HPMC handler is zero. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a po... |
82 |
| The size of the operating system HPMC handler is zero. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a po... |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| WRN |
82 |
| CBFA |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| prev HPMC logged |
82 |
| prev HPMC logged |
82 |
| Firmware detected unread PIM data from a previous HPMC and will overwrite it. |
82 |
| Firmware detected unread PIM data from a previous HPMC and will overwrite it. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBFB |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| brnch to OS HPMC |
82 |
| brnch to OS HPMC |
82 |
| Branching to the operating system HPMC handler. |
82 |
| Branching to the operating system HPMC handler. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBFC |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| OS HPMC br err |
82 |
| OS HPMC br err |
82 |
| Branch to the operating system HPMC handler failed. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a power... |
82 |
| Branch to the operating system HPMC handler failed. Firmware will halt the CPU, requiring a power... |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBFD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| unknown check |
82 |
| unknown check |
82 |
| The firmware trap handler didn’t detect an HPMC, LPMC, or TOC. |
82 |
| The firmware trap handler didn’t detect an HPMC, LPMC, or TOC. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBFE |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| HPMC during TOC |
82 |
| HPMC during TOC |
82 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check occurred during Transfer of Control processing. |
82 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check occurred during Transfer of Control processing. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| FLT |
82 |
| CBFF |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| multiple HPMCs |
82 |
| multiple HPMCs |
82 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check occurred while processing another HPMC. |
82 |
| A High-Priority Machine Check occurred while processing another HPMC. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| INI |
82 |
| CC0n |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| CPUn OS rendezvs |
82 |
| CPUn OS rendezvs |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering the final rendezvous, waiting for the operating system to awaken it. |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering the final rendezvous, waiting for the operating system to awaken it. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| INI |
82 |
| CC1n |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| CPUn early rend |
82 |
| CPU |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering the early rendezvous, waiting for the monarch CPU to initialize scratch RAM ... |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering the early rendezvous, waiting for the monarch CPU to initialize scratch RAM ... |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| INI |
82 |
| CC2n |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| CPUn rendezvous |
82 |
| CPU |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering rendezvous. Slave CPUs enter this rendezvous numerous times during boot. |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering rendezvous. Slave CPUs enter this rendezvous numerous times during boot. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
82 |
| INI |
82 |
| CC3n |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| SYS BD |
82 |
| CPUn cache rend |
82 |
| CPU |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering cached rendezvous, waiting for the monarch CPU to configure the system bus. |
82 |
| Slave CPU n entering cached rendezvous, waiting for the monarch CPU to configure the system bus. |
82 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| INI |
83 |
| CC4n |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| CPUn mem rendez |
83 |
| CPU |
83 |
| Slave CPU n entering memory rendezvous, waiting for the monarch CPU to select a boot device. |
83 |
| Slave CPU n entering memory rendezvous, waiting for the monarch CPU to select a boot device. |
83 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| TST |
83 |
| D000 |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| micro controller |
83 |
| Firmware is initializing communications with the system controller. |
83 |
| Firmware is initializing communications with the system controller. |
83 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| WRN |
83 |
| D004 |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| micro not resp |
83 |
| micro not resp |
83 |
| Firmware detected a communications error with the system controller. |
83 |
| Firmware detected a communications error with the system controller. |
83 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| INI |
83 |
| D005 |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| set dom1 fan spd |
83 |
| set dom1 fan spd |
83 |
| Firmware is initializing communications with the system controller. |
83 |
| Firmware is initializing communications with the system controller. |
83 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| INI |
83 |
| D006 |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| set dom2 fan spd |
83 |
| Firmware is initializing communications with the system controller. |
83 |
| Firmware is initializing communications with the system controller. |
83 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| WRN |
83 |
| D007 |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| SYS BD |
83 |
| bad microctl cmd |
83 |
| bad microctl cmd |
83 |
| Firmware detected a communications error with the system controller. |
83 |
| Firmware detected a communications error with the system controller. |
83 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| FLT |
83 |
| D01n |
83 |
| SYS/IO |
83 |
| SYS/IO |
83 |
| fan n: failure! |
83 |
| fan n: failure! |
83 |
| Firmware detected system fan n stopped. |
83 |
| Firmware detected system fan n stopped. |
83 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
83 |
| WRN |
83 |
| D02n |
83 |
| SYS/IO |
83 |
| SYS/IO |
83 |
| fan n: too slow! |
83 |
| fan n: too slow! |
83 |
| Firmware detected system fan n is running too slowly. |
83 |
| Firmware detected system fan n is running too slowly. |
83 |
| Memory Failures |
83 |
| Memory Failures |
83 |
| The B1000/C3000 system requires Memory Page Deallocation to be implemented. This feature allows t... |
83 |
| The B1000/C3000 system requires Memory Page Deallocation to be implemented. This feature allows t... |
83 |
| HP-UX 10.20 or later uses information to map out failing memory areas and continue normal operati... |
83 |
| # /usr/sbin/sysdiag |
83 |
| # /usr/sbin/sysdiag |
83 |
| Enter |
83 |
| DUI > logtool |
83 |
| DUI > logtool |
83 |
| Enter |
83 |
| LOGTOOL> memrpt detail |
83 |
| LOGTOOL> memrpt detail |
83 |
| Enter |
83 |
| The PDT can also be checked using the |
83 |
| For allowable memory configurations see Chapter 2 of this manual. |
83 |
| troubleshooting:system verification tests, |
84 |
| troubleshooting:system verification tests, |
84 |
| troubleshooting:system verification tests, |
84 |
| HP-UX uses an on-line diagnostics product named Mesa (Support Tools Manager) that allows system o... |
84 |
| HP-UX uses an on-line diagnostics product named Mesa (Support Tools Manager) that allows system o... |
84 |
| Three interfaces are available with the Support Tools Manager: |
84 |
| • a command line interface (accessed through the |
84 |
| • a command line interface (accessed through the |
84 |
| • a command line interface (accessed through the |
84 |
| • a menu-driven interface (accessed through the |
84 |
| • a menu-driven interface (accessed through the |
84 |
| • a graphical user interface (accessed through the |
84 |
| • a graphical user interface (accessed through the |
84 |
| For more information on these user interfaces, see the on-line man pages by entering the followin... |
84 |
| man cstm |
84 |
| man cstm |
84 |
| Enter |
84 |
|
84 |
| man xstm �� |
84 |
| man xstm �� |
84 |
| For information on the enhanced on-line diagnostics, see the enhanced on-line diagnostics, see the |
84 |
| To access the Support Tools Manager, perform the following steps: |
84 |
| 1. In a terminal window, type the following at the # prompt to invoke the command line interface: |
84 |
| 1. In a terminal window, type the following at the # prompt to invoke the command line interface: |
84 |
| 1. In a terminal window, type the following at the # prompt to invoke the command line interface: |
84 |
| # cstm |
84 |
| # cstm |
84 |
| 2. The following message appears: |
84 |
| 2. The following message appears: |
84 |
| Support Tools Manager |
84 |
| Support Tools Manager |
84 |
| Type ‘ |
84 |
| CSTM> |
84 |
| CSTM> |
84 |
| 3. To verify the system operation, type the following at the |
84 |
| 3. To verify the system operation, type the following at the |
84 |
| CSTM> |
84 |
| CSTM> |
84 |
| Messages similar to the following appear: |
84 |
| Verification has started on device (CPU). |
84 |
| Verification has started on device (CPU). |
84 |
| Verification has started on device (FPU). |
84 |
| Verification has started on device (FPU). |
84 |
| CSTM> Verification of(FPU)has completed. |
84 |
| CSTM> Verification of(FPU)has completed. |
84 |
| CSTM> Verification of(CPU) has completed. |
84 |
| CSTM> Verification of(CPU) has completed. |
84 |
| 4. Press |
84 |
| 4. Press |
84 |
| 5. To exit the Support Tools Manager, enter the following: |
85 |
| 5. To exit the Support Tools Manager, enter the following: |
85 |
| CSTM> |
85 |
| If any tests failed, run Self Test and ISL diagnostics to isolate the problem. |
85 |
| troubleshooting:ODE, |
86 |
| troubleshooting:ODE, |
86 |
| troubleshooting:ODE, |
86 |
| The Offline Diagnostic Environment (ODE) consists of diagnostic modules for testing and verifying... |
86 |
| ODE is an ISL utility. To boot ODE: |
86 |
| Not all of the test modules are available on all systems. To see what test modules are available ... |
86 |
| • wdiag |
86 |
| • wdiag |
86 |
| • wdiag |
86 |
| • wdiag |
86 |
| • memtest |
86 |
| • memtest |
86 |
| • memtest |
86 |
| • mapper |
86 |
| • mapper |
86 |
| • mapper |
86 |
| • astrodiag |
86 |
| • astrodiag |
86 |
| • astrodiag |
86 |
| • siodiag |
86 |
| • siodiag |
86 |
| • siodiag |
86 |
| For further information on the various ODE commands and a complete listing of the command set, type |
86 |
| FRU:, |
87 |
| FRU:, |
87 |
| FRU:, |
87 |
| This chapter lists the HP Visualize B1000/C3000 Workstation Field Replaceable Units (FRUs) and pr... |
87 |
| This chapter lists the HP Visualize B1000/C3000 Workstation Field Replaceable Units (FRUs) and pr... |
87 |
| WARNING For all removal and replacement procedures in this chapter, you must power off the workst... |
88 |
| WARNING For all removal and replacement procedures in this chapter, you must power off the workst... |
88 |
| NOTE To maintain FCC/EMI compliance, verify that all covers are replaced and that all screws are ... |
88 |
| NOTE To maintain FCC/EMI compliance, verify that all covers are replaced and that all screws are ... |
88 |
| Use the following tools to remove or replace FRUs: |
88 |
| • Torx T-10 driver |
88 |
| • Torx T-10 driver |
88 |
| • Torx T-10 driver |
88 |
| • Torx T-15 driver |
88 |
| • Torx T-15 driver |
88 |
| • Light duty flat blade screw driver with 6-inch (150mm) blade |
88 |
| • Light duty flat blade screw driver with 6-inch (150mm) blade |
88 |
| • Needle-nose pliers |
88 |
| • Needle-nose pliers |
88 |
| • ESD equipment (see |
88 |
| • ESD equipment (see |
88 |
| • Pen knife |
88 |
| • Pen knife |
88 |
| NOTE To maintain FCC/EMI compliance, verify that all covers are replaced and that all gasket mate... |
88 |
| NOTE To maintain FCC/EMI compliance, verify that all covers are replaced and that all gasket mate... |
88 |
| Figure 4�1. |
88 |
| Figure 4�1. |
88 |
| Refer to this figure for the locations of the various workstation FRUs while performing the FRU r... |
88 |
| B1000/C3000:main components, |
89 |
| B1000/C3000:main components, |
89 |
| B1000/C3000:main components, |
89 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
90 |
| Figure�4�2.� CD Drive Bracket Assembly |
90 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
90 |
| Figure 4�2. |
90 |
| Figure�4�3.� Floppy Drive Bracket Assembly |
91 |
| Figure�4�3.� Floppy Drive Bracket Assembly |
91 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
91 |
| Figure 4�3. |
91 |
| Figure�4�4.� Hard Disk Drive Bracket Assembly |
92 |
| Figure�4�4.� Hard Disk Drive Bracket Assembly |
92 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
92 |
| FRU:exchange and non-exchange, |
93 |
| FRU:exchange and non-exchange, |
93 |
| FRU:exchange and non-exchange, |
93 |
| In this chapter we refer to exchange and non-exchange part numbers. |
93 |
| You must return FRUs with exchange part numbers in exchange for a replacement FRU. Do |
93 |
| Each of the B1000/C3000 workstation exploded views show field replaceable units. Table 4-1 lists ... |
93 |
| FRUs Part Numbers |
94 |
| FRUs Part Numbers |
94 |
| <TABLE> |
94 |
| Table�4�1.� Exchange Parts FRU List |
94 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| Part Number |
94 |
| Description |
94 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A4986-69012 |
94 |
| 300MHz B1000 CPU Assembly |
94 |
| 300MHz B1000 CPU Assembly |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A4986-69014 |
94 |
| 400MHz C3000 CPU Assembly |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A6057-69010 |
94 |
| A6057-69010 |
94 |
| 750MHz C3700 CPU Assembly |
94 |
| 750MHz C3700 CPU Assembly |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A3862-69501 |
94 |
| 256 MByte SDRAM DIMM |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A3860-69501 |
94 |
| A3860-69501 |
94 |
| 128 MByte SDRAM DIMM |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A1658-69028 |
94 |
| 9GB 7200 RPM LVD Disk |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A1658-69026 |
94 |
| 18GB 10K RPM Disk |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A1658-69027 |
94 |
| 9GB 10K RPM Disk |
94 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
94 |
| A4986-69001 |
94 |
| 500W Power Supply |
94 |
| <TABLE> |
95 |
| Table�4�2.� Non-exchange Parts FRU List |
95 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| Part Number |
95 |
| Description |
95 |
| Description |
95 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-66530 |
95 |
| A4986-66530 |
95 |
| SCA Disk Backplane |
95 |
| SCA Disk Backplane |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| D2035-60282 |
95 |
| Floppy Drive |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| D4385-60001 |
95 |
| D4385-60001 |
95 |
| 32x ATAPI CD Drive |
95 |
| 32x ATAPI CD Drive |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-62005 |
95 |
| A4978-62005 |
95 |
| SCA - drive bracket |
95 |
| SCA - drive bracket |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-62006 |
95 |
| A4978-62006 |
95 |
| CD Drive bracket assembly |
95 |
| CD Drive bracket assembly |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-62006 |
95 |
| A4986-62006 |
95 |
| Floppy Disk Drive bracket assembly |
95 |
| Floppy Disk Drive bracket assembly |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| 5063-4513 |
95 |
| 5063-4513 |
95 |
| Speaker |
95 |
| Speaker |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-62025 |
95 |
| A4978-62025 |
95 |
| LCD/ Power Switch |
95 |
| LCD/ Power Switch |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-62012 |
95 |
| A4978-62012 |
95 |
| Fan- 92 mm |
95 |
| Fan- 92 mm |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-62013 |
95 |
| A4978-62013 |
95 |
| Fan - 120 mm |
95 |
| Fan - 120 mm |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-68501 |
95 |
| A4978-68501 |
95 |
| Fan - 80 mm - low profile |
95 |
| Fan - 80 mm - low profile |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4983-60401 |
95 |
| A4983-60401 |
95 |
| USB Keyboard, United States |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4983-60101 |
95 |
| A4983-60101 |
95 |
| USB Mouse, United States |
95 |
| USB Mouse, United States |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-63008 |
95 |
| A4986-63008 |
95 |
| LVD SCSI Terminator |
95 |
| LVD SCSI Terminator |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A1658-63012 |
95 |
| A1658-63012 |
95 |
| NSE SCSI Terminator |
95 |
| NSE SCSI Terminator |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-40007 |
95 |
| A4986-40007 |
95 |
| PCI Retainer Clip |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-62003 |
95 |
| A4986-62003 |
95 |
| Front Bezel w/ CD Filler (blank) |
95 |
| Front Bezel w/ CD Filler (blank) |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-63002 |
95 |
| A4986-63002 |
95 |
| Cable - CD Signal |
95 |
| Cable - CD Signal |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| 5182-1857 |
95 |
| 5182-1857 |
95 |
| CD Audio Cable |
95 |
| CD Audio Cable |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-63003 |
95 |
| A4986-63003 |
95 |
| Cable - Ultra SCSI Signal |
95 |
| Cable - Ultra SCSI Signal |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-63004 |
95 |
| A4986-63004 |
95 |
| Cable - Floppy Signal |
95 |
| Cable - Floppy Signal |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-63005 |
95 |
| Floppy/CD ROM Power Cable |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-63006 |
95 |
| LCD Signal Cable |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-62005 |
95 |
| SCA Drive Bracket Assembly |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-62001 |
95 |
| Main Chassis w/ keys, fans |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-00026 |
95 |
| PCI Air Separator (Divider) |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4986-00039 |
95 |
| Fan Bracket- Disk/Memory |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| 0624-0727 |
95 |
| 0624-0727 |
95 |
| Screw - 6-32 X 0.437���T-15 w/ slot |
95 |
| Screw - 6-32 X 0.437���T-15 w/ slot |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
95 |
| A4978-00039 |
95 |
| A4978-00039 |
95 |
| 6-32 Thumbscrew |
95 |
| 6-32 Thumbscrew |
95 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
96 |
| 0624-0727 |
96 |
| 0624-0727 |
96 |
| Screw -�T-15 w/ slot |
96 |
| Screw -�T-15 w/ slot |
96 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
96 |
| 1826-4269 |
96 |
| Real Time Clock Module (internal battery) |
96 |
| FRU:removal and replacement, |
97 |
| FRU:removal and replacement, |
97 |
| FRU:removal and replacement, |
97 |
| The procedures in this section describe how to remove field replaceable units (FRUs). Observe any... |
97 |
| The procedures in this section describe how to remove field replaceable units (FRUs). Observe any... |
97 |
| Before performing these procedures, observe the following precautions: |
97 |
| Step 1. Power off the system, the monitor, and any peripheral devices. |
97 |
| Step 1. Power off the system, the monitor, and any peripheral devices. |
97 |
| Step 1. Power off the system, the monitor, and any peripheral devices. |
97 |
| NOTE There is no need to manually shutdown the HP-UX operating system on the workstation before s... |
97 |
| NOTE There is no need to manually shutdown the HP-UX operating system on the workstation before s... |
97 |
| CAUTION Unplugging the power cord while HP-UX is running can damage the system files. Do |
97 |
| CAUTION Unplugging the power cord while HP-UX is running can damage the system files. Do |
97 |
| Step 2. Unplug the workstation power cord and the power cord of any peripheral devices from AC wa... |
97 |
| Step 2. Unplug the workstation power cord and the power cord of any peripheral devices from AC wa... |
97 |
| Step 3. Unplug the system unit power cord from the AC input connector. |
97 |
| Step 3. Unplug the system unit power cord from the AC input connector. |
97 |
| Step 4. Disconnect any external cables from the connectors on the front and rear of the system unit. |
97 |
| Step 4. Disconnect any external cables from the connectors on the front and rear of the system unit. |
97 |
| Step 5. Attach a static-grounding wrist strap to your wrist and a location on the system chassis ... |
97 |
| Step 5. Attach a static-grounding wrist strap to your wrist and a location on the system chassis ... |
97 |
| Step 6. Lay the workstation on a flat stable surface, such as a table top or floor. To protect ag... |
97 |
| Step 6. Lay the workstation on a flat stable surface, such as a table top or floor. To protect ag... |
97 |
| CAUTION Follow normal ESD, anti-static precautions when handling the workstation or any of its co... |
97 |
| CAUTION Follow normal ESD, anti-static precautions when handling the workstation or any of its co... |
97 |
| Step 7. If installed, remove any locking device from the security loop on the rear of the system ... |
97 |
| Step 7. If installed, remove any locking device from the security loop on the rear of the system ... |
97 |
| front panel: |
98 |
| front panel: |
98 |
| front panel: |
98 |
| This section describes how to open and close the workstation front panel. |
98 |
| This section describes how to open and close the workstation front panel. |
98 |
| Opening the System Unit Front Panel |
98 |
| Opening the System Unit Front Panel |
98 |
| Perform the following steps to open the system unit. |
98 |
| 1. Power off the workstation, and unplug the power cord from the electrical outlet. |
98 |
| 1. Power off the workstation, and unplug the power cord from the electrical outlet. |
98 |
| 1. Power off the workstation, and unplug the power cord from the electrical outlet. |
98 |
| 2. Attach the static-grounding wrist strap by following the instructions on the package. Attach t... |
98 |
| 2. Attach the static-grounding wrist strap by following the instructions on the package. Attach t... |
98 |
| 3. Unlock the front panel (also known as the front bezel) by pressing in on the two latch buttons... |
98 |
| 3. Unlock the front panel (also known as the front bezel) by pressing in on the two latch buttons... |
98 |
| Figure�4�5.� Opening the Front Bezel |
98 |
| Figure�4�5.� Opening the Front Bezel |
98 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
98 |
| 4. Swing the panel clockwise on its left snap hinges until the panel comes free and place the fro... |
98 |
| Closing the System Unit Front Panel |
98 |
| Closing the System Unit Front Panel |
98 |
| Perform the following steps to close the system unit. |
98 |
| 1. Locate the snap hinges on the left side of the front panel, and insert them into the holes loc... |
98 |
| 1. Locate the snap hinges on the left side of the front panel, and insert them into the holes loc... |
98 |
| 1. Locate the snap hinges on the left side of the front panel, and insert them into the holes loc... |
98 |
| 2. Rotate the front panel counterclockwise until you hear the two latch buttons snap in place. Th... |
98 |
| 2. Rotate the front panel counterclockwise until you hear the two latch buttons snap in place. Th... |
98 |
| 3. Plug in the system unit power cord, and power on the system. |
99 |
| 3. Plug in the system unit power cord, and power on the system. |
99 |
| Left Side Panel of the System Unit |
99 |
| Left Side Panel of the System Unit |
99 |
| This section explains how to open and close the left side panel of the system unit. This side pan... |
99 |
| This section explains how to open and close the left side panel of the system unit. This side pan... |
99 |
| Opening the Left Side Panel of the System Unit |
99 |
| Opening the Left Side Panel of the System Unit |
99 |
| Perform these steps to open the left side panel. |
99 |
| safety interlock switch:warning, |
99 |
| safety interlock switch:warning, |
99 |
| safety interlock switch:warning, |
99 |
| 1. Turn the computer around so the rear is facing you. On the right edge of the computer, there a... |
99 |
| 1. Turn the computer around so the rear is facing you. On the right edge of the computer, there a... |
99 |
| 1. Turn the computer around so the rear is facing you. On the right edge of the computer, there a... |
99 |
| 2. Grasp the back edge of the left side panel and rotate it outward approximately 45 degrees to t... |
99 |
| 2. Grasp the back edge of the left side panel and rotate it outward approximately 45 degrees to t... |
99 |
| left side panel, |
100 |
| left side panel, |
100 |
| left side panel, |
100 |
| safety interlock switch:location, |
100 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
100 |
| NOTE The EMI gasket, as shown in Figure 4-6, must not be removed from the side panel. |
100 |
| Closing the Left Side Panel of the System Unit |
101 |
| Closing the Left Side Panel of the System Unit |
101 |
| Perform these steps to close the left side panel. |
101 |
| NOTE Power supply thumbscrews must be fully tightened before closing the left side panel. Failure... |
101 |
| NOTE Power supply thumbscrews must be fully tightened before closing the left side panel. Failure... |
101 |
| 1. Hold the left side panel so that the hook hinges can be inserted into their hinge slots. See F... |
101 |
| 1. Hold the left side panel so that the hook hinges can be inserted into their hinge slots. See F... |
101 |
| 1. Hold the left side panel so that the hook hinges can be inserted into their hinge slots. See F... |
101 |
| 2. Swing the back edge of the panel toward the system unit’s back edge and press the outside edge... |
101 |
| 2. Swing the back edge of the panel toward the system unit’s back edge and press the outside edge... |
101 |
| 3. Secure the side panel in place by screwing the top and bottom slotted T-15 Torx thumb screws i... |
101 |
| 3. Secure the side panel in place by screwing the top and bottom slotted T-15 Torx thumb screws i... |
101 |
| FRU:power supply, |
102 |
| FRU:power supply, |
102 |
| FRU:power supply, |
102 |
| This section will prove important to you as you begin to service the system. For example, you may... |
102 |
| WARNING To prevent injury, unplug the workstation power cord from the electrical outlet before se... |
102 |
| WARNING To prevent injury, unplug the workstation power cord from the electrical outlet before se... |
102 |
| The topics covered in this section are: |
102 |
| • Propping up the Power Supply |
102 |
| • Propping up the Power Supply |
102 |
| • Propping up the Power Supply |
102 |
| • Removing the Power Supply |
102 |
| • Removing the Power Supply |
102 |
| Propping Up the Power Supply |
102 |
| Propping Up the Power Supply |
102 |
| To prop the power supply up, follow these steps: |
102 |
| 1. Lay the system on its side on a cushioned surface to protect against damage to the exterior wo... |
102 |
| 1. Lay the system on its side on a cushioned surface to protect against damage to the exterior wo... |
102 |
| 2. Open the left side panel of the system unit by following the procedure in the section “Opening... |
102 |
| 2. Open the left side panel of the system unit by following the procedure in the section “Opening... |
102 |
| 3. Unscrew the two screws on the power supply chassis as shown in |
102 |
| 3. Unscrew the two screws on the power supply chassis as shown in |
102 |
| Figure�4�7.� Unscrewing the Power Supply Captive Screws |
102 |
| Figure�4�7.� Unscrewing the Power Supply Captive Screws |
102 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
102 |
| 4. Lift up on the power supply handle. The power supply bail automatically engages once the power... |
102 |
| Figure�4�8.� Propping Up the Power Supply |
103 |
| Figure�4�8.� Propping Up the Power Supply |
103 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
103 |
| Closing the System |
103 |
| Once you have completed the task you set out to perform, you are ready to close the system. To cl... |
103 |
| Once you have completed the task you set out to perform, you are ready to close the system. To cl... |
103 |
| 1. Push slightly back on the power supply until you are able to remove the bail from the bail loc... |
103 |
| 1. Push slightly back on the power supply until you are able to remove the bail from the bail loc... |
103 |
| 1. Push slightly back on the power supply until you are able to remove the bail from the bail loc... |
103 |
| 2. Tighten both captive screws in place as seen in |
103 |
| 2. Tighten both captive screws in place as seen in |
103 |
| 3. Replace the left side panel of the system unit as shown in the section “Closing the Left Side ... |
103 |
| 3. Replace the left side panel of the system unit as shown in the section “Closing the Left Side ... |
103 |
| Removing the Power Supply |
103 |
| Removing the Power Supply |
103 |
| To remove the power supply follow these steps: |
103 |
| 1. Follow the steps covered in the section “Propping Up the Power Supply.” |
103 |
| 1. Follow the steps covered in the section “Propping Up the Power Supply.” |
103 |
| 1. Follow the steps covered in the section “Propping Up the Power Supply.” |
103 |
| 2. Disconnect both power cables from the system board, the control cable, and the power cable for... |
103 |
| 2. Disconnect both power cables from the system board, the control cable, and the power cable for... |
103 |
| Figure�4�9.� Disconnecting the Power Supply Cables |
104 |
| Figure�4�9.� Disconnecting the Power Supply Cables |
104 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
104 |
| 3. Remove the bail from the bail lock. See Figure 4-10. |
104 |
| 4. Grasp the power supply by the handle and slide the spring hinge lever to the right and rotate ... |
104 |
| 4. Grasp the power supply by the handle and slide the spring hinge lever to the right and rotate ... |
104 |
| Figure�4�10.� Removing the Power Supply |
105 |
| Figure�4�10.� Removing the Power Supply |
105 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
105 |
| Closing the System |
105 |
| Once you have completed the task you set out to perform, you are ready to close the system. To cl... |
105 |
| FRU:I/O cards, |
106 |
| FRU:I/O cards, |
106 |
| FRU:I/O cards, |
106 |
| The B1000 and C3000 computer’s PCI assembly has six slots. Slots 5 and 6 are half-size Peripheral... |
106 |
| Figure�4�11.� PCI Card Slot Numbering and Capabilities |
106 |
| Figure�4�11.� PCI Card Slot Numbering and Capabilities |
106 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
106 |
| NOTE To maintain good graphics performance, you should always use slot 2 (SL2) as the primary gra... |
106 |
| The six I/O slots as seen from the back of the computer are labeled from top to bottom starting w... |
106 |
| I/O slot:numbering, |
106 |
| I/O slot:numbering, |
106 |
| I/O slot:numbering, |
106 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
107 |
| Removing I/O Cards |
107 |
| This section assumes that you already have I/O cards loaded in the system unit, and you would lik... |
107 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
107 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
107 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
107 |
| 2. Pull evenly in the direction of the arrow on both sides of the I/O card retainer to remove it.... |
107 |
| 2. Pull evenly in the direction of the arrow on both sides of the I/O card retainer to remove it.... |
107 |
| Figure�4�13.� Removing the I/O Card Retainer |
107 |
| Figure�4�13.� Removing the I/O Card Retainer |
107 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
107 |
| 3. Locate the I/O card you want to remove and using a T-15 Torx driver or flat blade screw driver... |
107 |
| Figure�4�14.� Removing the I/O Card |
107 |
| Figure�4�14.� Removing the I/O Card |
107 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
107 |
| 4. Pull evenly on the outside edges of the I/O card to remove it. |
107 |
| Installing I/O Cards |
108 |
| Installing I/O Cards |
108 |
| To install a new I/O card, do the following: |
108 |
| NOTE Slots two and four are the graphics card slots. The primary graphics card slot is slot numbe... |
108 |
| NOTE Slots two and four are the graphics card slots. The primary graphics card slot is slot numbe... |
108 |
| 1. Open the left side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side... |
108 |
| 1. Open the left side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side... |
108 |
| 1. Open the left side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side... |
108 |
| 2. Locate the appropriate slot for the I/O card that is to be installed. See Figure 4-12. |
108 |
| 2. Locate the appropriate slot for the I/O card that is to be installed. See Figure 4-12. |
108 |
| 3. Unscrew the T-15 Torx screw from the bulkhead blank of the slot you have chosen. If no blank i... |
108 |
| 3. Unscrew the T-15 Torx screw from the bulkhead blank of the slot you have chosen. If no blank i... |
108 |
| 4. Pull evenly in the direction of the arrow on both sides of the I/O card retainer to remove it.... |
108 |
| 4. Pull evenly in the direction of the arrow on both sides of the I/O card retainer to remove it.... |
108 |
| 5. Insert the I/O card into the slot you have chosen with the bulkhead appropriately positioned. ... |
108 |
| 5. Insert the I/O card into the slot you have chosen with the bulkhead appropriately positioned. ... |
108 |
| 6. Replace the I/O card retainer by placing the bottom retainer clip in the slot on the air divid... |
108 |
| 6. Replace the I/O card retainer by placing the bottom retainer clip in the slot on the air divid... |
108 |
| 7. Close the left side panel of the system unit by following the procedure in the section “Closin... |
108 |
| 7. Close the left side panel of the system unit by following the procedure in the section “Closin... |
108 |
| FRU:fans, |
109 |
| FRU:fans, |
109 |
| FRU:fans, |
109 |
| The B1000/C3000 has five fans that are used to cool various areas within the unit. If one of thes... |
109 |
| • Removing the fan from the hard disk drive area |
109 |
| • Removing the fan from the hard disk drive area |
109 |
| • Removing the fan from the hard disk drive area |
109 |
| • Removing the fans from the CPU area |
109 |
| • Removing the fans from the CPU area |
109 |
| • Removing the fan and speaker from the I/O card area. |
109 |
| • Removing the fan and speaker from the I/O card area. |
109 |
| Figure�4�15.� Fan Cooling Areas for the System Unit |
109 |
| Figure�4�15.� Fan Cooling Areas for the System Unit |
109 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
110 |
| FRU:hard disk drive fan, |
110 |
| FRU:hard disk drive fan, |
110 |
| This section provides the procedure for removing the cooling fan from the back of the hard disk d... |
110 |
| • SCA disk interface board |
110 |
| • SCA disk interface board |
110 |
| • SCA disk interface board |
110 |
| • System board |
110 |
| • System board |
110 |
| • DIMM cards |
110 |
| • DIMM cards |
110 |
| Here are the steps necessary for removing the fan from the hard disk drive chassis. |
110 |
| 1. Remove the system unit’s side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Syste... |
110 |
| 1. Remove the system unit’s side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Syste... |
110 |
| 1. Remove the system unit’s side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Syste... |
110 |
| 2. Lay the system unit on its right side (determined by facing the workstation front panel), and ... |
110 |
| 2. Lay the system unit on its right side (determined by facing the workstation front panel), and ... |
110 |
| 3. Unplug the fan power cable from the system board. If you are removing the hard disk drive fan ... |
110 |
| 3. Unplug the fan power cable from the system board. If you are removing the hard disk drive fan ... |
110 |
| 4. Lift up on the handle of the fan bracket to remove the fan. See Figure 4-16. As you lift up on... |
110 |
| 4. Lift up on the handle of the fan bracket to remove the fan. See Figure 4-16. As you lift up on... |
110 |
| Figure�4�16.� Removing the Fan from the Hard Disk Drive Chassis |
111 |
| Figure�4�16.� Removing the Fan from the Hard Disk Drive Chassis |
111 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
111 |
| FRU:system fans, |
111 |
| FRU:system fans, |
111 |
| This section provides the procedure for removing the cooling fans from the CPU area of the system... |
111 |
| Here are the steps necessary for removing the fans from the CPU area of the system unit’s chassis. |
111 |
| 1. Remove the system units left side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the S... |
111 |
| 1. Remove the system units left side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the S... |
111 |
| 1. Remove the system units left side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the S... |
111 |
| 2. Lay the system unit on its right side (determined by facing the system units front panel), and... |
111 |
| 2. Lay the system unit on its right side (determined by facing the system units front panel), and... |
111 |
| 3. Unplug the power cables for the fans as shown in |
111 |
| 3. Unplug the power cables for the fans as shown in |
111 |
| Figure�4�17.� Removing the Fan Rivets |
112 |
| Figure�4�17.� Removing the Fan Rivets |
112 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
112 |
| 4. Remove the plastic mounting rivets that hold the fans in place. See Figure 4-17. To remove the... |
112 |
| Figure�4�18.� Removing CPU Area Fans |
113 |
| Figure�4�18.� Removing CPU Area Fans |
113 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
113 |
| Installing the Fans for the CPU Area |
113 |
| Installing the Fans for the CPU Area |
113 |
| To replace the system board fans, do the following: |
113 |
| Installing the Bottom Fan |
113 |
| Installing the Bottom Fan |
113 |
| 1. Position the bottom fan so its power cable channel is against the system unit chassis, and the... |
113 |
| 1. Position the bottom fan so its power cable channel is against the system unit chassis, and the... |
113 |
| 1. Position the bottom fan so its power cable channel is against the system unit chassis, and the... |
113 |
| 2. Slide the lower left corner of the fan into the fan support. See |
113 |
| 2. Slide the lower left corner of the fan into the fan support. See |
113 |
| 3. Line up the rivet holes of the fan with the rivet holes of the system unit chassis. |
113 |
| 3. Line up the rivet holes of the fan with the rivet holes of the system unit chassis. |
113 |
| 4. Press the plastic rivets into place. See |
113 |
| 4. Press the plastic rivets into place. See |
113 |
| 5. Plug the fan power cable into its connector on the system board. See |
113 |
| 5. Plug the fan power cable into its connector on the system board. See |
113 |
| Installing the Top Fan |
113 |
| Installing the Top Fan |
113 |
| 1. Position the top fan so its power cable channel is up against the workstation chassis, and the... |
113 |
| 1. Position the top fan so its power cable channel is up against the workstation chassis, and the... |
113 |
| 1. Position the top fan so its power cable channel is up against the workstation chassis, and the... |
113 |
| 2. Line up the rivet holes of the fan with the rivet holes of the system unit chassis. |
113 |
| 2. Line up the rivet holes of the fan with the rivet holes of the system unit chassis. |
113 |
| 3. Press the plastic rivets into place. See |
113 |
| 3. Press the plastic rivets into place. See |
113 |
| 4. Plug the fan power cable into its connector on the system board. See |
113 |
| 4. Plug the fan power cable into its connector on the system board. See |
113 |
| FRU:I/O fan, |
114 |
| FRU:I/O fan, |
114 |
| FRU:I/O fan, |
114 |
| The I/O area of the system unit has its own cooling fan. Note that there is a speaker attached to... |
114 |
| To remove the I/O cooling fan or |
114 |
| 1. Remove the workstation left side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sy... |
114 |
| 1. Remove the workstation left side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sy... |
114 |
| 1. Remove the workstation left side panel. See the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sy... |
114 |
| 2. Lay the workstation on its side, and remove all of the I/O cards. See the section “Removing I/... |
114 |
| 2. Lay the workstation on its side, and remove all of the I/O cards. See the section “Removing I/... |
114 |
| 3. Remove the system unit air divider as shown in Figure 4-19 by unscrewing the two T-15 Torx scr... |
114 |
| 3. Remove the system unit air divider as shown in Figure 4-19 by unscrewing the two T-15 Torx scr... |
114 |
| Figure�4�19.� Removing the System Unit Air Divider |
114 |
| Figure�4�19.� Removing the System Unit Air Divider |
114 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
114 |
| 4. Remove the fan and speaker cables from the system board and lift up on the bracket mounting cl... |
114 |
| Figure�4�20.� Removing the Fan and Speaker from the I/O Area |
115 |
| Figure�4�20.� Removing the Fan and Speaker from the I/O Area |
115 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
115 |
| 6. Remove the fan from the bracket by slightly pulling the left and right fan mounting clips away... |
116 |
| 6. Remove the fan from the bracket by slightly pulling the left and right fan mounting clips away... |
116 |
| Installing a Fan or Speaker in the I/O Card Area |
116 |
| Installing a Fan or Speaker in the I/O Card Area |
116 |
| If you are replacing a fan or speaker in the I/O card area, follow the steps covered in this sect... |
116 |
| 1. Remove the fan or speaker from the I/O card area by following the procedure in the section “Re... |
116 |
| 1. Remove the fan or speaker from the I/O card area by following the procedure in the section “Re... |
116 |
| 1. Remove the fan or speaker from the I/O card area by following the procedure in the section “Re... |
116 |
| 2. Install the fan by positioning the fan power cable channel so that it is located in the lower ... |
116 |
| 2. Install the fan by positioning the fan power cable channel so that it is located in the lower ... |
116 |
| 3. Install the speaker by positioning it so that the speaker cable can be easily run out of the h... |
116 |
| 3. Install the speaker by positioning it so that the speaker cable can be easily run out of the h... |
116 |
| 4. Replace the fan/speaker bracket in the chassis by inserting the bottom and in first between th... |
116 |
| 4. Replace the fan/speaker bracket in the chassis by inserting the bottom and in first between th... |
116 |
| 5. Position the fan power cable, speaker cable and LCD ribbon cable so that they run along the sy... |
116 |
| 5. Position the fan power cable, speaker cable and LCD ribbon cable so that they run along the sy... |
116 |
| 6. Place the air divider into its proper position as shown in |
116 |
| 6. Place the air divider into its proper position as shown in |
116 |
| 7. Replace all I/O cards into their proper slots as explained in the section “I/O Cards” in this ... |
116 |
| 7. Replace all I/O cards into their proper slots as explained in the section “I/O Cards” in this ... |
116 |
| 8. Close the system unit as discussed in the section “Closing the System Unit” in this chapter. |
116 |
| 8. Close the system unit as discussed in the section “Closing the System Unit” in this chapter. |
116 |
| FRU:removable media, |
117 |
| FRU:removable media, |
117 |
| FRU:removable media, |
117 |
| There are only two removable media devices allowed in a B1000/C3000 computer: |
117 |
| • CD Drive |
117 |
| • CD Drive |
117 |
| • CD Drive |
117 |
| • 3.5-inch floppy disk drive. |
117 |
| • 3.5-inch floppy disk drive. |
117 |
| The procedures provided in the subsequent sections explain how to install and remove media devices. |
117 |
| FRU:CD drive, |
117 |
| FRU:CD drive, |
117 |
| FRU:CD drive, |
117 |
| Install the CD drive by following the procedure covered in this section. |
117 |
| WARNING Turn the workstation off and unplug the power cord before installing the CD drive. |
117 |
| WARNING Turn the workstation off and unplug the power cord before installing the CD drive. |
117 |
| Note you will have to verify that the master/slave/CSEL jumper is set in the CSEL position. Since... |
117 |
| CAUTION CD drives are susceptible to mechanical and electronic shock. When handling the drive, al... |
117 |
| CAUTION CD drives are susceptible to mechanical and electronic shock. When handling the drive, al... |
117 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
117 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
117 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
117 |
| 2. Remove the CD Drive rear cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in Figure 4-22. Note... |
117 |
| 2. Remove the CD Drive rear cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in Figure 4-22. Note... |
117 |
| Figure�4�22.� Removing the CD Drive Rear Cover |
118 |
| Figure�4�22.� Removing the CD Drive Rear Cover |
118 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
118 |
| 3. Rotate the system unit around until you see the front of the unit as shown in |
118 |
| Figure�4�23.� Front of System Unit with the Front Panel Removed |
118 |
| Figure�4�23.� Front of System Unit with the Front Panel Removed |
118 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
118 |
| 4. Remove both CD Drive bracket screws (T-15 Torx screws) and pull the CD Drive bracket out of th... |
118 |
| Figure�4�24.� Removing the CD Drive Bracket and Blank |
119 |
| Figure�4�24.� Removing the CD Drive Bracket and Blank |
119 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
119 |
| 5. Read the CAUTION statement at the beginning of this section. Next remove the CD Drive from its... |
119 |
| Figure�4�25.� Installing the CD Drive |
120 |
| Figure�4�25.� Installing the CD Drive |
120 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
120 |
| 6. Slide the CD Drive and its bracket into the system unit chassis as shown in Figure 4-25. There... |
120 |
| 7. Tighten the two CD Drive bracket screws as shown in Figure 4-26. |
120 |
| 7. Tighten the two CD Drive bracket screws as shown in Figure 4-26. |
120 |
| Figure�4�26.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
120 |
| Figure�4�26.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
120 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
120 |
| 8. Plug the ATAPI and power cables into their appropriate connectors. Note that the connectors ar... |
120 |
| Figure�4�27.� Plugging in the ATAPI and Power Cables |
121 |
| Figure�4�27.� Plugging in the ATAPI and Power Cables |
121 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
121 |
| 9. Make sure that the ATAPI and power cables are positioned so that they come out of the bottom e... |
121 |
| Figure�4�28.� Replacing the Rear EMI CD Drive Cover |
121 |
| Figure�4�28.� Replacing the Rear EMI CD Drive Cover |
121 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
121 |
| 10. Complete the installation of the CD Drive by replacing the front and side panels of the syste... |
121 |
| Removing a CD Drive |
121 |
| Removing a CD Drive |
121 |
| This section explains how to remove a CD Drive from you system unit. |
121 |
| CAUTION CD Drives are susceptible to mechanical and electronic shock. When handling the drive, al... |
121 |
| CAUTION CD Drives are susceptible to mechanical and electronic shock. When handling the drive, al... |
121 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
122 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
122 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
122 |
| 2. Remove the CD Drive rear disk cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in |
122 |
| 2. Remove the CD Drive rear disk cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in |
122 |
| Figure�4�29.� Removing the CD Drive’s Rear Cover |
122 |
| Figure�4�29.� Removing the CD Drive’s Rear Cover |
122 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
122 |
| 3. Rotate the system unit around until you see the front of the unit as shown in Figure 4-30. |
122 |
| Figure�4�30.� Front of the System Unit with the Front Panel Removed |
122 |
| Figure�4�30.� Front of the System Unit with the Front Panel Removed |
122 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
122 |
| 4. Remove both CD Drive bracket screws (T-15 Torx screws) and pull the CD Drive out of the chassi... |
122 |
| Figure�4�31.� Removing the CD Drive |
123 |
| Figure�4�31.� Removing the CD Drive |
123 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
123 |
| 5. Insert the CD Drive blank in the CD Drive bracket and tighten the four CD Drive mounting screw... |
123 |
| Figure�4�32.� Installing the CD Drive Blank |
124 |
| Figure�4�32.� Installing the CD Drive Blank |
124 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
124 |
| 6. Tighten the two CD Drive bracket screws as shown in Figure 4-33. |
124 |
| Figure�4�33.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
124 |
| Figure�4�33.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
124 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
124 |
| 7. Place the ATAPI cable and power cables inside the CD Drive chassis, and position the cables so... |
124 |
| Figure�4�34.� Replacing the CD Drive Rear Cover |
125 |
| Figure�4�34.� Replacing the CD Drive Rear Cover |
125 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
125 |
| FRU:floppy disk drive, |
125 |
| FRU:floppy disk drive, |
125 |
| Install the floppy disk drive by following the procedure covered in this section. Note there are ... |
125 |
| WARNING Turn the workstation off and unplug the power cord before installing the floppy disk drive. |
125 |
| WARNING Turn the workstation off and unplug the power cord before installing the floppy disk drive. |
125 |
| CAUTION Floppy disk drives are susceptible to mechanical and electronic shock. When handling the ... |
125 |
| CAUTION Floppy disk drives are susceptible to mechanical and electronic shock. When handling the ... |
125 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
125 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
125 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
125 |
| 2. Remove the floppy rear-disk cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in |
125 |
| 2. Remove the floppy rear-disk cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in |
125 |
| Figure�4�35.� Removing the Floppy Disk’s Rear Cover |
126 |
| Figure�4�35.� Removing the Floppy Disk’s Rear Cover |
126 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
126 |
| 3. Rotate the system unit around until you see the front of the workstation as shown in |
126 |
| Figure�4�36.� Front of Workstation with the Front Panel Removed |
126 |
| Figure�4�36.� Front of Workstation with the Front Panel Removed |
126 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
126 |
| 4. Remove both floppy disk bracket screws (T-15 Torx screws) and pull the floppy disk bracket out... |
126 |
| Figure�4�37.� Removing the Floppy Disk Bracket and Blank |
127 |
| Figure�4�37.� Removing the Floppy Disk Bracket and Blank |
127 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
127 |
| 5. Read the CAUTION statement at the beginning of this section. Next remove the floppy disk drive... |
127 |
| Figure�4�38.� Installing the Floppy Disk Drive |
128 |
| Figure�4�38.� Installing the Floppy Disk Drive |
128 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
128 |
| 6. Slide the floppy disk and its bracket into the system unit chassis as shown in |
128 |
| 7. Tighten the two floppy bracket screws as shown in |
128 |
| 7. Tighten the two floppy bracket screws as shown in |
128 |
| Figure�4�39.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
128 |
| Figure�4�39.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
128 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
128 |
| 8. Plug the data and power cables into their appropriate connectors. Note that the connectors are... |
128 |
| Figure�4�40.� Plugging in the Data and Power Cables |
129 |
| Figure�4�40.� Plugging in the Data and Power Cables |
129 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
129 |
| 9. Verify that the data and power cables are positioned to come out of the top edge of the rear f... |
129 |
| Figure�4�41.� Replacing the Rear Floppy Cover |
129 |
| Figure�4�41.� Replacing the Rear Floppy Cover |
129 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
129 |
| 10. Complete the installation of the floppy disk drive by replacing the front and side panels of ... |
129 |
| Removing a Floppy Disk Drive |
129 |
| Removing a Floppy Disk Drive |
129 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
129 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
129 |
| 1. Perform the procedures in the sections “Opening the System Unit Front Panel” and “Opening the ... |
129 |
| 2. Remove the floppy rear disk cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in |
130 |
| 2. Remove the floppy rear disk cover by unscrewing the T-15 Torx screw as shown in |
130 |
| Figure�4�42.� Removing the Floppy Disk’s Rear Cover |
130 |
| Figure�4�42.� Removing the Floppy Disk’s Rear Cover |
130 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
130 |
| 3. Rotate the workstation around until you can see the front of the unit as shown in |
130 |
| Figure�4�43.� Front of Workstation with the Front Panel Removed |
130 |
| Figure�4�43.� Front of Workstation with the Front Panel Removed |
130 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
130 |
| 4. Remove both floppy disk bracket screws (T-15 torx screws) and pull the floppy disk drive out o... |
130 |
| Figure�4�44.� Removing the Floppy Disk Drive |
131 |
| Figure�4�44.� Removing the Floppy Disk Drive |
131 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
131 |
| 5. Place the floppy disk blank in the floppy disk bracket and insert the four floppy disk mountin... |
131 |
| Figure�4�45.� Installing the Floppy Disk Blank and Bracket |
132 |
| Figure�4�45.� Installing the Floppy Disk Blank and Bracket |
132 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
132 |
| 6. Slide the floppy disk blank and its bracket into the system unit chassis as shown in |
132 |
| 7. Tighten the two floppy disk bracket screws as shown in |
132 |
| 7. Tighten the two floppy disk bracket screws as shown in |
132 |
| Figure�4�46.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
132 |
| Figure�4�46.� Tightening the Bracket Screws |
132 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
133 |
| 8. Inspect and verify that the data and power cables are positioned to come out of the top edge o... |
133 |
| Figure�4�47.� Replacing the Rear Floppy Cover |
133 |
| Figure�4�47.� Replacing the Rear Floppy Cover |
133 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
133 |
| 9. Complete the installation of the floppy disk drive by replacing the front and side panels of t... |
133 |
| FRU:hard disk drive, |
134 |
| FRU:hard disk drive, |
134 |
| FRU:hard disk drive, |
134 |
| This section describes installation and removal of hard disk drives in the B1000/C3000 workstatio... |
134 |
| NOTE Do not use SCSI ID 7 for any of the internal or external disk drives. The host SCSI controll... |
134 |
| NOTE Do not use SCSI ID 7 for any of the internal or external disk drives. The host SCSI controll... |
134 |
| hard disk drive: |
134 |
| hard disk drive: |
134 |
| hard disk drive: |
134 |
| NOTE If you are installing a new hard disk drive, the slotted pan screws for attaching the drive ... |
134 |
| NOTE If you are installing a new hard disk drive, the slotted pan screws for attaching the drive ... |
134 |
| 1. Open the front panel of the workstation, refer to the section “Opening the System Unit Front P... |
134 |
| 1. Open the front panel of the workstation, refer to the section “Opening the System Unit Front P... |
134 |
| 1. Open the front panel of the workstation, refer to the section “Opening the System Unit Front P... |
134 |
| Figure�4�48.� The Hard Drive Slots |
135 |
| Figure�4�48.� The Hard Drive Slots |
135 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
135 |
| 2. Open the hard drive slot by pressing the plastic release hook upward and pulling outward on th... |
135 |
| Figure�4�49.� Removing the Hard Drive Bracket |
136 |
| Figure�4�49.� Removing the Hard Drive Bracket |
136 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
136 |
| 3. Mount the hard disk drive on the hard drive bracket using the four T-10 torx screws and rubber... |
136 |
| NOTE If you are installing a hard disk drive, you will need to mount it and create a file system ... |
136 |
| NOTE If you are installing a hard disk drive, you will need to mount it and create a file system ... |
136 |
| To mount a hard disk drive and create a file system on it use the procedure in the section “Addin... |
136 |
| Figure�4�50.� Inserting the Hard Disk Drive |
137 |
| Figure�4�50.� Inserting the Hard Disk Drive |
137 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
137 |
| Removing a Hard Disk Drive |
137 |
| This procedure explains how to remove the hard disk drive. Note that there are no cables for you ... |
137 |
| 1. Open the front panel of the system using the instructions found in the section “Opening the Sy... |
137 |
| 1. Open the front panel of the system using the instructions found in the section “Opening the Sy... |
137 |
| 1. Open the front panel of the system using the instructions found in the section “Opening the Sy... |
137 |
| Figure�4�51.� The Hard Drive Slots |
138 |
| Figure�4�51.� The Hard Drive Slots |
138 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
138 |
| 2. Open the hard drive slot by pressing the plastic release hook upward and pulling outward on th... |
138 |
| Figure�4�52.� Removing the Hard Disk Drive |
138 |
| Figure�4�52.� Removing the Hard Disk Drive |
138 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
139 |
| 3. Remove the four T-15 Torx screws from the hard disk drive bracket. See |
139 |
| Figure�4�53.� Removing the Hard Disk Drive from the Bracket |
139 |
| Figure�4�53.� Removing the Hard Disk Drive from the Bracket |
139 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
139 |
| 4. Slide the assembly into its hard drive slot, and push inward on the release lever until the fr... |
139 |
| Figure�4�54.� Replacing the Hard Disk Drive Bracket |
140 |
| Figure�4�54.� Replacing the Hard Disk Drive Bracket |
140 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
141 |
| FRU:DIMM cards, |
141 |
| FRU:DIMM cards, |
141 |
| This section contains information regarding the installation and removal of memory (DIMM cards). ... |
141 |
| • Use the procedure described in |
141 |
| • Use the procedure described in |
141 |
| • Use the procedure described in |
141 |
| • Review the steps involved in installing memory DIMMs before you begin. |
141 |
| • Review the steps involved in installing memory DIMMs before you begin. |
141 |
| • Insert DIMMs in the order shown. Please refer to |
141 |
| • Insert DIMMs in the order shown. Please refer to |
141 |
| • Note the proper orientation for DIMMs when inserting them into their connectors because the con... |
141 |
| • Note the proper orientation for DIMMs when inserting them into their connectors because the con... |
141 |
| • Use the “Boot Console Handler” to verify that the computer recognizes the additional DIMMs when... |
141 |
| • Use the “Boot Console Handler” to verify that the computer recognizes the additional DIMMs when... |
141 |
| Installing Additional Memory |
141 |
| Installing Additional Memory |
141 |
| Perform the following steps to add memory (DIMM cards) to the workstation. |
141 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
141 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
141 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
141 |
| 2. Lay the system on its side as shown in |
141 |
| 2. Lay the system on its side as shown in |
141 |
| Figure�4�55.� Propping Up the Power Supply |
141 |
| Figure�4�55.� Propping Up the Power Supply |
141 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
141 |
| 3. Prop up the system unit power supply as explained in the section “Propping Up the System Unit ... |
141 |
| 4. For ease in installation of additional memory the hard disk drive fan may need to be removed. ... |
142 |
| 4. For ease in installation of additional memory the hard disk drive fan may need to be removed. ... |
142 |
| 5. Load the DIMM cards in the slots using the loading sequence provided in |
142 |
| 5. Load the DIMM cards in the slots using the loading sequence provided in |
142 |
| DIMM:card slot numbering, |
142 |
| DIMM:card slot numbering, |
142 |
| DIMM:card slot numbering, |
142 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
142 |
| NOTE When installing DIMMs, you need to orient the notches on the bottom edge of the DIMM card so... |
142 |
| 6. Press downward on the ejector tabs located on both sides of the DIMM connector. See |
142 |
| 6. Press downward on the ejector tabs located on both sides of the DIMM connector. See |
142 |
| Figure�4�57.� Installing Memory Cards |
143 |
| Figure�4�57.� Installing Memory Cards |
143 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
143 |
| 7. Place the DIMM card in the connector, lining it up with the guides. Make sure to put the notch... |
143 |
| 8. Close the ejector tab. |
143 |
| 8. Close the ejector tab. |
143 |
| 9. Press firmly and evenly on the DIMM card to ensure that it seats properly. The ejector tabs en... |
143 |
| 9. Press firmly and evenly on the DIMM card to ensure that it seats properly. The ejector tabs en... |
143 |
| 10. Replace the power supply and workstation left side panel. You may now plug the power cord bac... |
143 |
| 10. Replace the power supply and workstation left side panel. You may now plug the power cord bac... |
143 |
| 11. Verify that this installation was successful by following the steps in Chapter 6, “The Boot C... |
143 |
| 11. Verify that this installation was successful by following the steps in Chapter 6, “The Boot C... |
143 |
| Once you have completed the steps listed above, the DIMM cards are properly loaded. |
143 |
| FRU:memory:removing, |
143 |
| FRU:memory:removing, |
143 |
| FRU:memory:removing, |
143 |
| Perform the following steps to remove memory (DIMM cards) from the system unit. |
143 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
143 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
143 |
| 1. Open the side panel of the system unit as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Pane... |
143 |
| 2. Lay the system on its side as shown in |
143 |
| 2. Lay the system on its side as shown in |
143 |
| Figure�4�58.� Propping Up the Power Supply |
144 |
| Figure�4�58.� Propping Up the Power Supply |
144 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
144 |
| 3. Prop up the system unit power supply as explained in the section “Propping Up the System Unit ... |
144 |
| 4. For ease in removing memory cards, remove the fan from the hard disk drive chassis. See the se... |
144 |
| 4. For ease in removing memory cards, remove the fan from the hard disk drive chassis. See the se... |
144 |
| 5. Press downward on the ejector tabs located on both sides of the DIMM connector. See |
144 |
| 5. Press downward on the ejector tabs located on both sides of the DIMM connector. See |
144 |
| Figure�4�59.� Removing Memory Cards |
144 |
| Figure�4�59.� Removing Memory Cards |
144 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
144 |
| 6. Lift up evenly on the outside edges of the DIMM card. See |
144 |
| 7. Replace the power supply and system unit side panel. You may now plug the power cord back into... |
144 |
| 7. Replace the power supply and system unit side panel. You may now plug the power cord back into... |
144 |
| 8. Verify that the removal was successful by following the steps in Chapter 6, “Boot Console Hand... |
144 |
| 8. Verify that the removal was successful by following the steps in Chapter 6, “Boot Console Hand... |
144 |
| FRU:LCD, |
145 |
| FRU:LCD, |
145 |
| FRU:LCD, |
145 |
| This section describes how to remove and replace the B1000/C3000 workstation power switch/LCD ass... |
145 |
| Removing the System Unit LCD |
145 |
| Removing the System Unit LCD |
145 |
| To remove the LCD assembly, perform the following steps: |
145 |
| 1. Open the system unit’s front panel as shown in the section “Opening the System Unit Front Panel.” |
145 |
| 1. Open the system unit’s front panel as shown in the section “Opening the System Unit Front Panel.” |
145 |
| 1. Open the system unit’s front panel as shown in the section “Opening the System Unit Front Panel.” |
145 |
| 2. Unplug the LCD’s connector as shown in Figure 4-60. |
145 |
| 2. Unplug the LCD’s connector as shown in Figure 4-60. |
145 |
| Figure�4�60.� Removing the System Unit LCD |
145 |
| Figure�4�60.� Removing the System Unit LCD |
145 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
145 |
| 3. Press inward on the mount clip located on the right side of the LCD mount and pull the right s... |
145 |
| Replacing the |
145 |
| Replacing the |
145 |
| To replace the power switch/LCD assembly, do the following: |
145 |
| 1. Open the system unit’s front panel as shown in the section “Opening the System Unit Front Panel.” |
145 |
| 1. Open the system unit’s front panel as shown in the section “Opening the System Unit Front Panel.” |
145 |
| 1. Open the system unit’s front panel as shown in the section “Opening the System Unit Front Panel.” |
145 |
| 2. Insert the LCD’s left-side mounting clips into the slots shown on the system unit chassis. See |
145 |
| 2. Insert the LCD’s left-side mounting clips into the slots shown on the system unit chassis. See |
145 |
| 3. Plug in the LCD connector as shown in Figure 4-60. |
145 |
| 3. Plug in the LCD connector as shown in Figure 4-60. |
145 |
| 4. Replace the system unit’s front panel. This completes the installation of the system LCD assem... |
146 |
| 4. Replace the system unit’s front panel. This completes the installation of the system LCD assem... |
146 |
| FRU:system board, |
147 |
| FRU:system board, |
147 |
| FRU:system board, |
147 |
| The system board contains the I/O section, computer main memory, CPU, and all of the circuitry an... |
147 |
| Removing the |
147 |
| Removing the |
147 |
| To remove the system board tray assembly, do the following: |
147 |
| 1. Remove the left side panel as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sys... |
147 |
| 1. Remove the left side panel as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sys... |
147 |
| 1. Remove the left side panel as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sys... |
147 |
| NOTE Remove the terminators on the rear panel of the workstation. |
147 |
| NOTE Remove the terminators on the rear panel of the workstation. |
147 |
| 2. Remove the two T-15 Torx screws that secure the system board tray assembly to the rear panel o... |
147 |
| 2. Remove the two T-15 Torx screws that secure the system board tray assembly to the rear panel o... |
147 |
| 3. Remove the system unit power supply as covered in the section “System Unit Power Supply” in th... |
147 |
| 3. Remove the system unit power supply as covered in the section “System Unit Power Supply” in th... |
147 |
| 4. Remove the hard disk drive fan as described in the section “Removing the Fan from the Hard Dis... |
147 |
| 4. Remove the hard disk drive fan as described in the section “Removing the Fan from the Hard Dis... |
147 |
| 5. Remove the DIMM cards as explained in the section “Removing Memory” in this chapter. |
147 |
| 5. Remove the DIMM cards as explained in the section “Removing Memory” in this chapter. |
147 |
| 6. Remove the PCI retainer, the I/O cards from their PCI slots and the air divider as covered ear... |
147 |
| 6. Remove the PCI retainer, the I/O cards from their PCI slots and the air divider as covered ear... |
147 |
| 7. Unplug the following cables from the system board: |
147 |
| 7. Unplug the following cables from the system board: |
147 |
| a. Floppy disk drive data cable |
147 |
| a. Floppy disk drive data cable |
147 |
| b. CD drive data cable |
147 |
| b. CD drive data cable |
147 |
| c. Hard disk drive fan cable |
147 |
| c. Hard disk drive fan cable |
147 |
| d. Fan/Speaker cables |
147 |
| d. Fan/Speaker cables |
147 |
| e. LCD ribbon cable |
147 |
| e. LCD ribbon cable |
147 |
| f. CD drive audio cable |
147 |
| f. CD drive audio cable |
147 |
| g. System board fan cables (2) |
147 |
| g. System board fan cables (2) |
147 |
| h. Ultra2 Wide LVD SCSI cable |
147 |
| h. Ultra2 Wide LVD SCSI cable |
147 |
| Figure�4�61.� Removing the System Board |
148 |
| Figure�4�61.� Removing the System Board |
148 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
148 |
| 8. Fold back the workstation cables to avoid interference or damage. |
148 |
| 9. Grasp the system board tray handle and slide the system board to the front of the workstation.... |
148 |
| 9. Grasp the system board tray handle and slide the system board to the front of the workstation.... |
148 |
| FRU:system board:installation, |
148 |
| FRU:system board:installation, |
148 |
| FRU:system board:installation, |
148 |
| To install the system board perform the following steps: |
148 |
| 1. Angle the system board assembly diagonally as you begin installation. Position the system boar... |
148 |
| 1. Angle the system board assembly diagonally as you begin installation. Position the system boar... |
148 |
| 1. Angle the system board assembly diagonally as you begin installation. Position the system boar... |
148 |
| Figure�4�62.� Installing the System Board |
149 |
| Figure�4�62.� Installing the System Board |
149 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
149 |
| 2. Re-attach the cables described in step 7 of |
149 |
| 3. Replace the following components: |
149 |
| 3. Replace the following components: |
149 |
| a. Power supply |
149 |
| a. Power supply |
149 |
| a. Power supply |
149 |
| b. DIMM cards |
149 |
| b. DIMM cards |
149 |
| c. Hard disk drive fan |
149 |
| c. Hard disk drive fan |
149 |
| d. PCI air divider |
149 |
| d. PCI air divider |
149 |
| e. PCI cards |
149 |
| e. PCI cards |
149 |
| f. PCI retainer |
149 |
| f. PCI retainer |
149 |
| 4. Replace the left side panel as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sy... |
149 |
| 4. Replace the left side panel as explained in the section “Opening the Left Side Panel of the Sy... |
149 |
| FRU:battery, |
150 |
| FRU:battery, |
150 |
| FRU:battery, |
150 |
| The battery in the B1000/C3000 workstation is contained within the real time clock module, part n... |
150 |
| The battery in the B1000/C3000 workstation is contained within the real time clock module, part n... |
150 |
| 1. Close all open applications on the workstation then use the power button on the front panel to... |
150 |
| 1. Close all open applications on the workstation then use the power button on the front panel to... |
150 |
| 1. Close all open applications on the workstation then use the power button on the front panel to... |
150 |
| 2. Unplug the power cord from the workstation to disconnect all AC power. Remove the workstation ... |
150 |
| 2. Unplug the power cord from the workstation to disconnect all AC power. Remove the workstation ... |
150 |
| 3. Remove the two captive screws for the power supply shown in |
150 |
| 4. Carefully remove the defective real time clock module. Note the polarity dot which is silk-scr... |
150 |
| 4. Carefully remove the defective real time clock module. Note the polarity dot which is silk-scr... |
150 |
| CAUTION Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equ... |
150 |
| CAUTION Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equ... |
150 |
| CAUTION Il y a danger d´explosion s´il y a remplacement incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer uniqu... |
150 |
| CAUTION Il y a danger d´explosion s´il y a remplacement incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer uniqu... |
150 |
| 5. Insert the |
150 |
| 5. Insert the |
150 |
| 6. Reconnect the 6-pin power supply cable to the system board. Push back slightly on the power su... |
150 |
| 6. Reconnect the 6-pin power supply cable to the system board. Push back slightly on the power su... |
150 |
| 7. Replace the left side panel of the system unit as shown in the section “Closing the left Side ... |
150 |
| 7. Replace the left side panel of the system unit as shown in the section “Closing the left Side ... |
150 |
| Carefully inspect the seating of the left side panel in the mainframe chassis to assure that the |
150 |
| Apply AC power to the workstation and cycle the power button to the on position. |
150 |
| 8. The B1000/C3000 workstation is now ready to reboot with the operational battery. |
150 |
| Diagrams: |
151 |
| Diagrams: |
151 |
| Diagrams: |
151 |
| This chapter provides functional information about the B1000/C3000 workstations. The following bl... |
151 |
| This chapter provides functional information about the B1000/C3000 workstations. The following bl... |
151 |
| Diagrams:system power, |
152 |
| Diagrams:system power, |
152 |
| Diagrams:system power, |
152 |
| Figure 5–1 shows the system power distribution. |
152 |
| Figure 5–1 shows the system power distribution. |
152 |
| Figure�5�1.� Power Distribution Diagram |
152 |
| Figure�5�1.� Power Distribution Diagram |
152 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
153 |
| Diagrams:functional block, |
153 |
| Diagrams:functional block, |
153 |
| Diagrams:functional block, |
153 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
155 |
| 6� Boot Console Handler |
155 |
| This chapter explains how to use the Boot Console Handler, which provides an interactive environm... |
155 |
| This chapter explains how to use the Boot Console Handler, which provides an interactive environm... |
155 |
| Here are the topics covered in this chapter: |
156 |
| • Boot Console Handler Features |
156 |
| • Boot Console Handler Features |
156 |
| • Boot Console Handler Features |
156 |
| • Accessing the Boot Console Handler |
156 |
| • Accessing the Boot Console Handler |
156 |
| • Booting the Workstation |
156 |
| • Booting the Workstation |
156 |
| • Searching for Bootable Media |
156 |
| • Searching for Bootable Media |
156 |
| • Resetting the Workstation |
156 |
| • Resetting the Workstation |
156 |
| • Displaying and Setting Paths |
156 |
| • Displaying and Setting Paths |
156 |
| • Displaying and Setting the Monitor type |
156 |
| • Displaying and Setting the Monitor type |
156 |
| • Changing the Console to an External Terminal |
156 |
| • Changing the Console to an External Terminal |
156 |
| • Displaying the Current Memory Configuration |
156 |
| • Displaying the Current Memory Configuration |
156 |
| • Display the Status of the System I/O |
156 |
| • Display the Status of the System I/O |
156 |
| • Setting the Auto Boot and Auto Search |
156 |
| • Setting the Auto Boot and Auto Search |
156 |
| • Displaying and Setting the Security Mode |
156 |
| • Displaying and Setting the Security Mode |
156 |
| • Displaying and setting the Fastboot |
156 |
| • Displaying and setting the Fastboot |
156 |
| • Displaying the LAN station address |
156 |
| • Displaying the LAN station address |
156 |
| • Displaying System Information |
156 |
| • Displaying System Information |
156 |
| • Displaying PIM information |
156 |
| • Displaying PIM information |
156 |
| Boot Console Handler:features, |
157 |
| Boot Console Handler:features, |
157 |
| Boot Console Handler:features, |
157 |
| There are times when you want to interact directly with the hardware of your computer before it b... |
157 |
| There are times when you want to interact directly with the hardware of your computer before it b... |
157 |
| Here are some of the things you can do: |
157 |
| • Boot your computer |
157 |
| • Boot your computer |
157 |
| • Boot your computer |
157 |
| • Search for bootable media |
157 |
| • Search for bootable media |
157 |
| • Reset your computer |
157 |
| • Reset your computer |
157 |
| • Display and set boot paths |
157 |
| • Display and set boot paths |
157 |
| • Display and set your monitor type |
157 |
| • Display and set your monitor type |
157 |
| • Display memory configuration information |
157 |
| • Display memory configuration information |
157 |
| • Display the status of the PCI slots |
157 |
| • Display the status of the PCI slots |
157 |
| • Set Auto Boot, Auto Search, and Auto Start |
157 |
| • Set Auto Boot, Auto Search, and Auto Start |
157 |
| • Set Fastboot |
157 |
| • Set Fastboot |
157 |
| • Display LAN information |
157 |
| • Display LAN information |
157 |
| • Display system information |
157 |
| • Display system information |
157 |
| The boot console menus follow, showing the various tasks you can perform and the available inform... |
157 |
| The shortened version of all commands is indicated by the uppercase letters. |
157 |
| Boot Console Handler:help, |
157 |
| Boot Console Handler:help, |
157 |
| Boot Console Handler:accessing, |
158 |
| Boot Console Handler:accessing, |
158 |
| Boot Console Handler:accessing, |
158 |
| If the workstation has crashed or power was turned off for some reason, press the power switch an... |
158 |
| 1. Close any files and applications on your computer. |
158 |
| 1. Close any files and applications on your computer. |
158 |
| 1. Close any files and applications on your computer. |
158 |
| 2. Press the power switch on the front panel of the workstation. |
158 |
| 2. Press the power switch on the front panel of the workstation. |
158 |
| NOTE There is no need to manually shut down the HP-UX operating system on your computer before po... |
158 |
| NOTE There is no need to manually shut down the HP-UX operating system on your computer before po... |
158 |
| Make sure you do not unplug the system’s power cord or otherwise interrupt power to the system un... |
158 |
| 3. Power on the workstation after it has completely shut down. If |
158 |
| 3. Power on the workstation after it has completely shut down. If |
158 |
| NOTE If you are using a power-saving monitor, you will have less than 10 seconds from the time th... |
158 |
| NOTE If you are using a power-saving monitor, you will have less than 10 seconds from the time th... |
158 |
| 4. Press a key. You will then see the message: ����� |
158 |
| 4. Press a key. You will then see the message: ����� |
158 |
| Boot Console Handler:menus, |
159 |
| Boot Console Handler:menus, |
159 |
| Boot Console Handler:menus, |
159 |
| The boot console menus follow, showing the various tasks you can perform and the available inform... |
159 |
| The boot console menus follow, showing the various tasks you can perform and the available inform... |
159 |
| The shortened version of all commands is indicated by the uppercase letters. |
159 |
| Help is available for all the menus and commands by typing either help, he or ? and the menu or c... |
159 |
| Boot Console Handler:main menu, |
160 |
| Boot Console Handler:main menu, |
160 |
| ---------------- Main Menu ------------------------------------------------ |
160 |
| Command������������������������ ����������Description |
160 |
| -----------�������������������������������---------------------------------- |
160 |
| BOot [PRI|ALT|<path>]���������� �����Boot from specified path PAth [PRI|ALT|CON|KEY|[<path>]� ���... |
160 |
| COnfiguration ��[<command>] ���������Access Configuration menu/commands INformation [<command>]��... |
160 |
| DIsplay��������������������������� ��Redisplay the current menu HElp [<menu>|<commands>]���������... |
160 |
| ------------- Main Menu: Enter command > |
160 |
| BOot [<menu>|<command>]��������� ��� Display help for menu or command DIsplay��������������������... |
161 |
| ----- Configuration Menu: Enter command > |
161 |
| ------------- |
162 |
| ------ Information Menu: Enter command > |
162 |
| PIM [<proc> [HPMC|LPMC|TOC]]��Display PIM information ScRoll [ON|OFF] ������������� Display or ch... |
163 |
| BOot [PRI|ALT|<path>]���������Boot from specified path DIsplay�����������������������Redisplay th... |
163 |
| ----- Service Menu: Enter command > |
163 |
| Boot Console Handler:booting the workstation, |
164 |
| Boot Console Handler:booting the workstation, |
164 |
| Boot Console Handler:booting the workstation, |
164 |
| In general the B1000/C3000 workstation is started by the power switch and HP-UX boots automatical... |
164 |
| In general the B1000/C3000 workstation is started by the power switch and HP-UX boots automatical... |
164 |
| For example, you may want to start the workstation from an operating system that is stored on a d... |
164 |
| Here are some possible booting scenarios you may encounter: |
164 |
| • If you know which device you want to boot from, and you know that it contains a bootable operat... |
164 |
| • If you know which device you want to boot from, and you know that it contains a bootable operat... |
164 |
| • If you know which device you want to boot from, and you know that it contains a bootable operat... |
164 |
|
164 |
| where |
164 |
|
164 |
| • If �you do not know which device you want to boot from, then type the following at the prompt a... |
164 |
| • If �you do not know which device you want to boot from, then type the following at the prompt a... |
164 |
|
164 |
| A message similar to the following will be displayed: |
164 |
| Path Number ����Device Path �������������������Device Type |
164 |
| Path Number ����Device Path �������������������Device Type |
164 |
| -----------���----------------�����������------------------ |
164 |
| P0���������������IDE����������������������������TEAC CD-532E-B |
164 |
| P0���������������IDE����������������������������TEAC CD-532E-B |
164 |
| P1���������������FWSCSI.6.0���������������������SEAGATE ST39102LC |
164 |
| P1���������������FWSCSI.6.0���������������������SEAGATE ST39102LC |
164 |
| At the prompt, you might type the following and press |
164 |
|
164 |
| Note that the operating system on the specified device ( |
164 |
| • If you wish to interact with the Initial System Loader (ISL) before booting the workstation, fo... |
164 |
| • If you wish to interact with the Initial System Loader (ISL) before booting the workstation, fo... |
164 |
|
164 |
| The following prompt will appear: |
164 |
|
164 |
| Answering yes ( |
165 |
|
165 |
| ISL is the program that actually controls the loading of the operating system. By interacting wit... |
165 |
| For example, if the usual kernel ( |
165 |
|
165 |
| • If you do not know which media in your file systems have bootable operating systems, you can fi... |
165 |
| • If you do not know which media in your file systems have bootable operating systems, you can fi... |
165 |
| Boot Console Handler:bootable media search, |
166 |
| Boot Console Handler:bootable media search, |
166 |
| Boot Console Handler:bootable media search, |
166 |
| To list devices that contain bootable media, follow the directions in “Accessing the Boot Console... |
166 |
| Main Menu: Enter command > search ipl |
166 |
| Main Menu: Enter command > search ipl |
166 |
| The search command searches all buses. The search may turn up more devices than there are lines o... |
166 |
| • To hold the display temporarily, press Ctrl S |
166 |
| • To hold the display temporarily, press Ctrl S |
166 |
| • To hold the display temporarily, press Ctrl S |
166 |
| • To continue the display, press Ctrl Q |
166 |
| • To continue the display, press Ctrl Q |
166 |
| • To halt the search, press any other key |
166 |
| • To halt the search, press any other key |
166 |
| These flow-control commands do not work with a bit-mapped display, but such a display can show mo... |
166 |
| To search for devices of just one type that actually contain bootable media, follow the direction... |
166 |
| Main Menu: Enter command> search ipl device_type |
166 |
| Main Menu: Enter command> search ipl device_type |
166 |
| Where |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| • ����� |
166 |
| For more information about the |
166 |
| Main Menu: Enter command> help search |
166 |
| Main Menu: Enter command> help search |
166 |
| Boot Console Handler:default values, |
167 |
| Boot Console Handler:default values, |
167 |
| Boot Console Handler:default values, |
167 |
| To reset your workstation to its predefined values, follow the directions in “Accessing the Boot ... |
167 |
|
167 |
| When the Configuration Menu appears, type the following at the prompt and press |
167 |
|
167 |
| When the Configuration Menu appears, type the following at the prompt and press |
167 |
|
167 |
| Boot Console Handler:displaying and setting paths, |
168 |
| Boot Console Handler:displaying and setting paths, |
168 |
| Boot Console Handler:displaying and setting paths, |
168 |
| A path is the hardware address of a device that is attached to the I/O system of your workstation... |
168 |
| A path is the hardware address of a device that is attached to the I/O system of your workstation... |
168 |
| The path command sets and displays the hardware address of a specified device attached to the I/O... |
168 |
| <TABLE> |
168 |
| Table�6�1.� System Paths |
168 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| Path Type |
168 |
| Path Type |
168 |
| Device |
168 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| primary or pri |
168 |
| primary |
168 |
| primary |
168 |
| Your workstation’s default boot device (usually the root disk) |
168 |
| Your workstation’s default boot device (usually the root disk) |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| alternate or alt |
168 |
| alternate |
168 |
| alternate |
168 |
| Your workstation’s alternate boot device (usually a DDS-format tape device) |
168 |
| Your workstation’s alternate boot device (usually a DDS-format tape device) |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| console or con |
168 |
| console |
168 |
| console |
168 |
| Your workstation’s primary display device |
168 |
| Your workstation’s primary display device |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| keyboard or key |
168 |
| keyboard |
168 |
| keyboard |
168 |
| Your workstation’s primary ASCII input device |
168 |
| Your workstation’s primary ASCII input device |
168 |
| To display the current settings for the system paths, type the following at the prompt and press |
168 |
|
168 |
| The paths are displayed in Mnemonic Style Notation, as shown in |
168 |
| <TABLE> |
168 |
| Table�6�2.� Mnemonic Style Notation |
168 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| I/O |
168 |
| I/O |
168 |
| Specification Format |
168 |
| Specification Format |
168 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| Built-in LVD SCSI |
168 |
| Built-in LVD SCSI |
168 |
| fwscsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| fwscsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| fwscsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| Built-in NSE SCSI |
168 |
| Built-in NSE SCSI |
168 |
| scsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| scsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| scsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| Optional SCSI |
168 |
| Optional SCSI |
168 |
| pcin.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| pcin.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| pcin.scsi_address.logical_unit_number |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| Built-in LAN |
168 |
| lan.server_address.init_timeout.io_timeout |
168 |
| lan.server_address.init_timeout.io_timeout |
168 |
| lan.server_address.init_timeout.io_timeout |
168 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
168 |
| Built-in IDE |
168 |
| Built-in IDE |
168 |
| IDE |
168 |
| IDE |
168 |
| IDE |
168 |
| To display the current setting for a particular system path, follow the directions in “Accessing ... |
168 |
|
168 |
| where |
168 |
| For example, to get the path to the primary boot device, follow the directions in “Accessing Boot... |
168 |
|
168 |
| To set a system path to a new value, follow the directions in “Accessing the Boot Console Handler... |
168 |
|
169 |
| where |
169 |
|
169 |
| Boot Console Handler:monitor type, |
170 |
| Boot Console Handler:monitor type, |
170 |
| Boot Console Handler:monitor type, |
170 |
| The workstation ships from the factory preset to use a monitor with a specific resolution and fre... |
170 |
| The workstation ships from the factory preset to use a monitor with a specific resolution and fre... |
170 |
| The |
170 |
| The |
170 |
| The |
170 |
| The |
170 |
| NOTE The monitor command lets you change your workstation’s graphics configuration before you rep... |
170 |
| NOTE The monitor command lets you change your workstation’s graphics configuration before you rep... |
170 |
| To display the current graphics and console information, enter the following command: |
170 |
|
170 |
|
170 |
| The correct usage for setting the graphics configurations is: |
170 |
|
170 |
| where valid graphics_path parameters are: |
170 |
|
170 |
|
170 |
|
170 |
|
170 |
|
170 |
|
170 |
| and type is the numerical monitor type as shown with the monitor list command. See |
170 |
| NOTE No space/blank characters may be used in the |
170 |
| NOTE No space/blank characters may be used in the |
170 |
| Displaying the Current |
171 |
| Displaying the Current |
171 |
| To display the current monitor configuration for your system from the Configuration Menu of the B... |
171 |
|
171 |
| This places you in the Configuration Menu. From here, type the following command at the prompt an... |
171 |
|
171 |
| The screen displays a list of the current graphics adapters and their monitor types configured fo... |
171 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION |
171 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION |
171 |
|
171 |
| ------- ��----- ----��------ �� ��---------- �----- ---- ------- |
171 |
| ------- ��----- ----��------ �� ��---------- �----- ---- ------- |
171 |
| GRAPHICS(2) |
171 |
| GRAPHICS(2) |
171 |
| Configuration Menu: Enter command> |
171 |
| Configuration Menu: Enter command> |
171 |
| In this example, only the graphics adapter, |
171 |
| Setting the |
172 |
| Setting the |
172 |
| You can set the monitor type for a graphics adapter by typing the following at the prompt and pre... |
172 |
|
172 |
| Where n is the number of the graphics adapter and tt is the monitor type. To display a list of su... |
172 |
|
172 |
| A list of valid monitor types similar to the following is displayed: |
172 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION Path�������Slot�Head�Type����Size����Freq�Class ----�������----�----�----��--... |
172 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION Path�������Slot�Head�Type����Size����Freq�Class ----�������----�----�----��--... |
172 |
| To set the monitor type for |
172 |
|
172 |
| This will take effect on the next reboot. |
172 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION |
172 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION |
172 |
| ----- ���----- �-----�------ ����----------- ------ --- �------- |
172 |
| ----- ���----- �-----�------ ����----------- ------ --- �------- |
172 |
| GRAPHICS(2) |
172 |
| GRAPHICS(2) |
172 |
| Configuration Menu: ��Enter command> |
172 |
| Configuration Menu: ��Enter command> |
172 |
| The boot console may display a message that tells you that your new monitor selection will take e... |
173 |
| Trying to change the monitor type to a number not listed for that graphics device fails and gives... |
173 |
| Value of monitor type n out of range (n - nn) |
173 |
| Value of monitor type n out of range (n - nn) |
173 |
| Trying to change the monitor type on an empty slot fails and gives you the following warning mess... |
173 |
|
173 |
| Setting the Monitor Type at Power On |
173 |
| Setting the Monitor Type at Power On |
173 |
| If you replace your workstation’s monitor with a different monitor type, you need to let the comp... |
173 |
| Once you have rebooted the system by turning it off, wait for a short time for the hard disk driv... |
173 |
| NOTE It takes approximately one to two minutes after powering on the workstation before the |
173 |
| NOTE It takes approximately one to two minutes after powering on the workstation before the |
173 |
| Wait two seconds after the |
173 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION |
173 |
| MONITOR INFORMATION |
173 |
|
173 |
| ------ ��------ ----��----- ��------- � ----- ------- |
173 |
| ------ ��------ ----��----- ��------- � ----- ------- |
173 |
| GRAPHICS(2) |
173 |
| GRAPHICS(2) |
173 |
| Press[RETURN]to select this monitor type(type n of n types) |
173 |
| Press[RETURN]to select this monitor type(type n of n types) |
173 |
| Note that if you do not select this monitor type, the system cycles through all of the available ... |
173 |
| Once you have made your monitor type selection, the system queries you to confirm your selection.... |
173 |
| If you press any key other than |
173 |
|
173 |
| At this point, the new monitor type is active, but not saved. Because you didn’t save the monitor... |
174 |
| Next, the following message is displayed: |
174 |
|
174 |
| To restart the monitor selection process, press |
174 |
| Boot Console Handler:monitor problems, |
174 |
| Boot Console Handler:monitor problems, |
174 |
| Boot Console Handler:monitor problems, |
174 |
| In the event that your console stops displaying to your graphics device, use the following proced... |
174 |
| In the event that your console stops displaying to your graphics device, use the following proced... |
174 |
| 1. Turn the workstation power off. |
174 |
| 1. Turn the workstation power off. |
174 |
| 1. Turn the workstation power off. |
174 |
| 2. Disconnect the USB keyboard connector from the rear panel. |
174 |
| 2. Disconnect the USB keyboard connector from the rear panel. |
174 |
| 3. Connect a serial terminal emulator to the Serial 1 connector (the left serial connector) on th... |
174 |
| 3. Connect a serial terminal emulator to the Serial 1 connector (the left serial connector) on th... |
174 |
| 4. Power on the system. The system will now display the console to the terminal connected to Seri... |
174 |
| 4. Power on the system. The system will now display the console to the terminal connected to Seri... |
174 |
| 5. Set the monitor type and path using the Boot Console Handler. For information, reference the s... |
174 |
| 5. Set the monitor type and path using the Boot Console Handler. For information, reference the s... |
174 |
| Boot Console Handler:memory configuration, |
175 |
| Boot Console Handler:memory configuration, |
175 |
| Boot Console Handler:memory configuration, |
175 |
| The following sample screen output uses the |
175 |
| To display the current memory configuration for you system, from the Information Menu of the boot... |
175 |
| Memory:information sample, |
176 |
| Memory:information sample, |
176 |
| Memory:information sample, |
176 |
| The following sample shows the memory information when memory modules are properly installed and ... |
176 |
| MEMORY INFORMATION MEMORY STATUS TABLE ���Slot����Size���������Status ��-----���--------����� ---... |
176 |
| MEMORY INFORMATION MEMORY STATUS TABLE ���Slot����Size���������Status ��-----���--------����� ---... |
176 |
| 0������256MB��������Active |
176 |
| MEMORY FAULT TABLE |
176 |
| MEMORY FAULT TABLE |
176 |
| Slot ���� Size ��������Status |
176 |
| Active, Installed Memory�������������: 640MB of SDRAM |
176 |
| Active, Installed Memory�������������: 640MB of SDRAM |
176 |
| Deallocated Pages �������������������: 0 Pages |
176 |
| Deallocated Pages �������������������: 0 Pages |
176 |
| ���������������� ����������... |
176 |
| Available Memory ��������������������: 640 MB |
176 |
| Available Memory ��������������������: 640 MB |
176 |
| Good Memory Required by OS ����������: ������������0 (not initialized) |
176 |
| Good Memory Required by OS ����������: ������������0 (not initialized) |
176 |
| ������� �������Memory |
176 |
| ������� �������Memory |
176 |
| �HVERSION �SVERSION |
176 |
| -------- ��--------- |
176 |
| -------- ��--------- |
176 |
| Boot Console Handler:I/O slot status, |
177 |
| Boot Console Handler:I/O slot status, |
177 |
| Boot Console Handler:I/O slot status, |
177 |
| The I/O command lets you identify all built-in I/O devices and optional I/O devices installed in ... |
177 |
| ... |
177 |
| I/O MODULE INFORMATION Path�������Decimal�������Type���������� Location��HVER��SVER��Vers��Dep --... |
177 |
| I/O MODULE INFORMATION Path�������Decimal�������Type���������� Location��HVER��SVER��Vers��Dep --... |
177 |
| Boot Console Handler:auto boot and auto search, |
178 |
| Boot Console Handler:auto boot and auto search, |
178 |
| Boot Console Handler:auto boot and auto search, |
178 |
| The |
178 |
| The |
178 |
| To examine the state of the |
178 |
|
178 |
| If |
178 |
| The state of the |
178 |
| To change the state of the auto boot or auto search flags, type the following at the prompt and p... |
178 |
|
178 |
| or |
178 |
|
178 |
| where |
178 |
| Auto search |
178 |
| Auto search |
178 |
| Primary Boot Path (can be set by the user) |
178 |
| Alternate Boot Path (can be set by the user) |
178 |
| Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI (built-in) |
178 |
| PCI 1 through PCI 6 (plug-in interface cards) |
178 |
| Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI (built-in) |
178 |
| LAN (built-in) |
178 |
| Boot Console Handler:security mode, |
179 |
| Boot Console Handler:security mode, |
179 |
| Boot Console Handler:security mode, |
179 |
| The |
179 |
| The |
179 |
| When the |
179 |
| Note that the |
179 |
|
179 |
| To display the current setting for the |
179 |
|
179 |
| To set the |
179 |
|
179 |
| To set the |
179 |
|
179 |
| Boot Console Handler:fastboot mode, |
180 |
| Boot Console Handler:fastboot mode, |
180 |
| Boot Console Handler:fastboot mode, |
180 |
| When |
180 |
| When |
180 |
| When |
180 |
| If you are experiencing difficulty in booting the workstation, set |
180 |
| To display the status of |
180 |
|
180 |
| To disable |
180 |
|
180 |
| To enable |
180 |
|
180 |
| Boot Console Handler:LAN station address, |
181 |
| Boot Console Handler:LAN station address, |
181 |
| Boot Console Handler:LAN station address, |
181 |
| It is sometimes necessary to supply the LAN station address of the workstation to other users. Fo... |
181 |
| It is sometimes necessary to supply the LAN station address of the workstation to other users. Fo... |
181 |
| A LAN station address for the workstation is the label that uniquely identifies the LAN connectio... |
181 |
| To display the workstation’s LAN station address, type the following at the prompt and press |
181 |
|
181 |
| The LAN station address is displayed as a twelve-digit number in hexadecimal notation, similar to... |
181 |
|
181 |
| The address is for the workstation’s built-in LAN interface. |
181 |
| Boot Console Handler:system information, |
182 |
| Boot Console Handler:system information, |
182 |
| Boot Console Handler:system information, |
182 |
| The |
182 |
|
182 |
| This information is paged to allow you to view it as necessary, unless the |
182 |
| Boot Console Handler:PIM, |
183 |
| Boot Console Handler:PIM, |
183 |
| Boot Console Handler:PIM, |
183 |
| The |
183 |
|
183 |
| You can use pim in the following ways: |
183 |
|
183 |
|
183 |
|
183 |
| where |
183 |
| Stable Storage |
184 |
| Stable Storage |
184 |
| Stable storage is non-volatile memory associated with the PA-RISC processor module. Stable storag... |
184 |
| • Device path information |
184 |
| • Device path information |
184 |
| • Device path information |
184 |
| • The state of the boot flags |
184 |
| • The state of the boot flags |
184 |
| • HPMC error information |
184 |
| • HPMC error information |
184 |
| • Operating system initialization data |
184 |
| • Operating system initialization data |
184 |
| Boot Console Handler:ISL, |
185 |
| Boot Console Handler:ISL, |
185 |
| Boot Console Handler:ISL, |
185 |
| The ISL environment provides the means to load the operating system (HP-UX) environment. The ISL ... |
185 |
| The ISL program is the first program loaded into main memory from an external medium (LAN, disk, ... |
185 |
| The ISL environment provides the following capabilities: |
185 |
| • Execute user-entered commands to modify boot device paths and boot options in stable storage. |
185 |
| • Execute user-entered commands to modify boot device paths and boot options in stable storage. |
185 |
| • Execute user-entered commands to modify boot device paths and boot options in stable storage. |
185 |
| • Run offline diagnostic programs and utilities |
185 |
| • Run offline diagnostic programs and utilities |
185 |
| • Provide automatic booting of the HP-UX operating system after power-on or reset |
185 |
| • Provide automatic booting of the HP-UX operating system after power-on or reset |
185 |
| Invoking ISL from the Boot Console Handler |
185 |
| Invoking ISL from the Boot Console Handler |
185 |
| Perform the following steps to invoke ISL from the boot console handler: |
185 |
| Step 1. Follow the directions in |
185 |
| Step 1. Follow the directions in |
185 |
| Step 1. Follow the directions in |
185 |
|
185 |
| You are prompted: |
185 |
|
185 |
| Step 2. Answering yes ( |
185 |
| Step 2. Answering yes ( |
185 |
|
185 |
| ISL is the program that actually controls the loading of the operating system. By interacting wit... |
185 |
| For example, if the usual kernel ( |
185 |
|
185 |
| ISL: |
185 |
| ISL: |
185 |
| ISL: |
185 |
| The following commands available in the ISL environment allow you to display and modify the boot ... |
185 |
| • help |
185 |
| • help |
185 |
| • help |
185 |
| • help |
185 |
| • display |
186 |
| • display |
186 |
| • display |
186 |
| • primpath |
186 |
| • primpath |
186 |
| • primpath |
186 |
| • altpath |
186 |
| • altpath |
186 |
| • altpath |
186 |
| • conspath |
186 |
| • conspath |
186 |
| • conspath |
186 |
| • listautofl |
186 |
| • listautofl |
186 |
| • listautofl |
186 |
| • support |
186 |
| • support |
186 |
| • support |
186 |
| • readss |
186 |
| • readss |
186 |
| • readss |
186 |
| Boot Console Handler:firmware, |
187 |
| Boot Console Handler:firmware, |
187 |
| Boot Console Handler:firmware, |
187 |
| To update a system’s firmware, the firmware patch must be obtained from the patch server website ... |
187 |
| To update a system’s firmware, the firmware patch must be obtained from the patch server website ... |
187 |
| The patch file is a combined shar’ed file that contains an ASCII cataloging file, a readme type A... |
187 |
| Step 1. Verify the checksum of the file \ |
187 |
| Step 1. Verify the checksum of the file \ |
187 |
| Step 1. Verify the checksum of the file \ |
187 |
| Step 2. Use the \ |
187 |
| Step 2. Use the \ |
187 |
| Identify Current Version of Firmware (on system to be updated) |
187 |
| Step 1. Re-boot your system and do the following: |
187 |
| Step 1. Re-boot your system and do the following: |
187 |
| Step 1. Re-boot your system and do the following: |
187 |
| a. Interrupt the boot process and from the Boot Console Handler�prompt, type < |
187 |
| b. Identify your firmware revision. The last two digits in the patch name indicate the revision. ... |
187 |
| To install the firmware update |
187 |
| To install the firmware update |
187 |
| The following are the directions from the readme file that are the firmware updating instructions... |
187 |
| Step 1. Install the tape you have just created into your tape drive. |
187 |
| Step 1. Install the tape you have just created into your tape drive. |
187 |
| Step 1. Install the tape you have just created into your tape drive. |
187 |
| Step 2. Shutdown your system via the power switch and power back on, or execute the reboot comman... |
187 |
| Step 2. Shutdown your system via the power switch and power back on, or execute the reboot comman... |
187 |
| Step 3. When the display reads \ |
187 |
| Step 3. When the display reads \ |
187 |
| Step 4. Boot from the appropriate boot path. (You must boot from the device that contains the fir... |
187 |
| Step 4. Boot from the appropriate boot path. (You must boot from the device that contains the fir... |
187 |
| NOTE This process is automatic and requires no interaction until directed to do so. Please do not... |
188 |
| NOTE This process is automatic and requires no interaction until directed to do so. Please do not... |
188 |
| Step 5. A warning message will be issued, followed by \ |
188 |
| Step 5. A warning message will be issued, followed by \ |
188 |
| After several screens go by, you will be informed as to what firmware image is on your system and... |
188 |
| If the image on the tape has a higher revision number, type < |
188 |
| NOTE FROM THIS POINT FORWARD, THIS PROCESS CANNOT BE INTERRUPTED UNTIL COMPLETION. INTERRUPTING T... |
188 |
| NOTE FROM THIS POINT FORWARD, THIS PROCESS CANNOT BE INTERRUPTED UNTIL COMPLETION. INTERRUPTING T... |
188 |
| DURING THE EXECUTION OF THIS UPDATE, THE FIRMWARE FONTS FILE WILL BE RE-WRITTEN. IF THESE ARE NEW... |
188 |
| You will see 2 carriage returns and 2 line feeds and then the display will remain the same. In ap... |
188 |
| The system will continue the normal boot process from the default primary path. |
188 |
| Firmware:update example, |
188 |
| Firmware:update example, |
188 |
| Firmware:update example, |
188 |
| When you update the firmware, you will see the following information on the display. |
188 |
| launch IPL other |
189 |
| Product specifications: |
191 |
| Product specifications: |
191 |
| Product specifications: |
191 |
| This appendix lists the regulatory specifications, safety requirements, environmental specificati... |
191 |
| This appendix lists the regulatory specifications, safety requirements, environmental specificati... |
191 |
| B1000/C3000:regulatory statements, |
192 |
| B1000/C3000:regulatory statements, |
192 |
| B1000/C3000:regulatory statements, |
192 |
| This section lists the regulatory and safety statements for the B1000 and the C3000 workstations. |
192 |
| This section lists the regulatory and safety statements for the B1000 and the C3000 workstations. |
192 |
| B1000/C3000:declaration of conformity, |
193 |
| B1000/C3000:declaration of conformity, |
194 |
| B1000/C3000:emissions regulations, |
194 |
| B1000/C3000:emissions regulations, |
194 |
| Federal Communications Commission (FCC) |
194 |
| This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, ... |
194 |
| Hewlett-Packard’s system certification tests were conducted with HP-supported peripheral devices ... |
194 |
| Operation of this device is subject to the following conditions: |
194 |
| • This device may not cause harmful interference. |
194 |
| • This device may not cause harmful interference. |
194 |
| • This device may not cause harmful interference. |
194 |
| • This device must accept interference received, including interference that may cause undesired ... |
194 |
| • This device must accept interference received, including interference that may cause undesired ... |
194 |
| • Cables used with this device must be properly shielded to comply with the requirements of the FCC. |
194 |
| • Cables used with this device must be properly shielded to comply with the requirements of the FCC. |
194 |
| B1000/C3000:video statement, |
194 |
| B1000/C3000:video statement, |
194 |
| B1000/C3000:video statement, |
194 |
| When a Video Out card has a cable connected to its video out connector, the HP Visualize B1000/C3... |
194 |
| Figure�A�1.� VCCI Class B ITE (Japan) |
195 |
| Figure�A�1.� VCCI Class B ITE (Japan) |
195 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
195 |
| Figure�A�2.� RRL Class A EMI (Korea) |
195 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
195 |
| Figure�A�3.� EMI Class A (Taiwan) |
195 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
195 |
| B1000/C3000:emissions regulations, |
195 |
| B1000/C3000:emissions regulations, |
195 |
| Any third-party I/O device installed in HP system(s) must be in accordance with the requirements ... |
195 |
| B1000/C3000:acoustics, |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:acoustics, |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:acoustics, |
196 |
| Regulation On Noise Declaration For Machines -3. GSGV |
196 |
| Lpa <70dB����������� ������������������������� ���� Lpa <70dB |
196 |
| operator position ����������������������������� �am Arbeitsplatz |
196 |
| normal operation �������������������������������normaler Betrieb |
196 |
| per ISO 7779��������������������������������� �����nach DIN 45635 T.19 |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:laser statements, |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:laser statements, |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:laser statements, |
196 |
| (For workstations that have a CD drive installed.) |
196 |
| The CD-ROM mass-storage system is certified as a Class 1 laser product under the U.S. Department ... |
196 |
| This means that the mass-storage system does not produce hazardous laser radiation. Because laser... |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:LEDs, |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:LEDs, |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:LEDs, |
196 |
| The LEDs on this product are classified as “Class 1 LED PRODUCT” in accordance with EN 60825-1. |
196 |
| Electrostatic Discharge:ESD precautions, |
196 |
| Electrostatic Discharge:ESD precautions, |
196 |
| Electrostatic Discharge:ESD precautions, |
196 |
| Electrostatic charges can damage the integrated circuits on printed circuits boards. To prevent s... |
196 |
| • Stand on a static-free mat. |
196 |
| • Stand on a static-free mat. |
196 |
| • Stand on a static-free mat. |
196 |
| • Wear a static strap to ensure that any accumulated electrostatic charge is discharged from your... |
196 |
| • Wear a static strap to ensure that any accumulated electrostatic charge is discharged from your... |
196 |
| • Connect all equipment together, including the static-free mat, static strap, routing nodes, and... |
196 |
| • Connect all equipment together, including the static-free mat, static strap, routing nodes, and... |
196 |
| • Keep uninstalled printed circuit boards in their protective antistatic bags. |
196 |
| • Keep uninstalled printed circuit boards in their protective antistatic bags. |
196 |
| • Handle printed circuit boards by their edges, once you have removed them from their protective ... |
196 |
| • Handle printed circuit boards by their edges, once you have removed them from their protective ... |
196 |
| B1000/C3000:warnings, |
197 |
| B1000/C3000:warnings, |
197 |
| B1000/C3000:warnings, |
197 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
197 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
198 |
| B1000/C3000:environmental specifications, |
198 |
| B1000/C3000:environmental specifications, |
198 |
| Acoustics |
198 |
| Acoustics |
198 |
| Deskside:���4.7 bels typical @ 25� C |
198 |
| 4.9 bels typical @ 30� C�� |
198 |
| Altitude |
198 |
| Altitude |
198 |
| Operating:���� �����0-10,000 ft. above sea level (0-3000m) |
198 |
| Non-operating (storage or shipping):� �0-15,000 ft. above sea level (0-4500m) |
198 |
| DC Magnetic Field Interference |
198 |
| DC Magnetic Field Interference |
198 |
| Operating: ��<1 Gauss at surface of product������� |
198 |
| Non-operating: <2 mGauss @ 7 feet |
198 |
| Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) |
198 |
| Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) |
198 |
| Emissions: �����FCC Class B, CISPR B |
198 |
| Immunity: � ��� EN61000-4-2: 1995 - 4KV contact discharge, 8KV air discharge (ESD) |
198 |
| EN61000-4-3: 1991 - 10V/m (radiated immunity) |
198 |
| EN61000-4-4: 1995 - 2kV signal lines, 4kV power lines (EFT) |
198 |
| Temperature |
198 |
| Temperature |
198 |
| Operating: ��������5 to +40� C |
198 |
| Non-operating (shipping or storage): �-40 to +70� C |
198 |
| Humidity (Non-condensing) |
198 |
| Humidity (Non-condensing) |
198 |
| Operating: ���������15 to 80% RH |
198 |
| Non-operating: ��0 to 90% RH��(storage or shipping) |
198 |
| Leakage Current |
198 |
| Leakage Current |
198 |
| Less than 3 milliamps |
198 |
| Shock |
198 |
| Shock |
198 |
| Operating: 20g at 3ms, 1/2 sine in normal axis with no hard errors |
198 |
| Non-operating (shipping): 80g at 3ms, 1/2 sine, normal axis |
198 |
| Vibration |
199 |
| Vibration |
199 |
| Operating random: ���0.21 Grms, 5-500 Hz |
199 |
| Swept sine survival (shipping): �0.5 G (0-peak), 5-500 Hz |
199 |
| Random survival (shipping): �����2.09 Grms, 5-500 Hz |
199 |
| B1000/C3000:electrical specifications, |
200 |
| B1000/C3000:electrical specifications, |
200 |
| B1000/C3000:electrical specifications, |
200 |
| B1000/C3000:electrical specifications, |
200 |
| Input Power ��������� |
200 |
| Input Power ��������� |
200 |
| For B1000 and C3000 workstations: |
200 |
| <TABLE> |
200 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| 7.4 Amps RMS max @ 100V |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| 6.2 Amps RMS max @ 120V |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| 3.8 Amps RMS max @ 200V |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| 3.2 Amps RMS max @ 230V |
200 |
| line power, |
200 |
| line power, |
200 |
| line power, |
200 |
| <TABLE> |
200 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| AC Frequency: 48-66 Hz |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| AC Voltage: 90-264V |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| Maximum Power Input: 805 Watts |
200 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
200 |
| Maximum Current Load: 10 Amps |
200 |
| SCSI: |
201 |
| SCSI: |
201 |
| SCSI: |
201 |
| This appendix provides information about connecting Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) device... |
201 |
| The following topics are covered within this section: |
202 |
| • SCSI bus differences |
202 |
| • SCSI bus differences |
202 |
| • SCSI restrictions |
202 |
| • Determining SCSI bus length |
202 |
| • Assigning SCSI device IDs |
202 |
| • Connecting to the SCSI ports |
202 |
| If you are on a B1000/C3000 workstation, the instructions in this chapter assume you are using HP... |
202 |
| NOTE When attaching external SCSI devices, be sure to terminate the last device on the external S... |
202 |
| NOTE When attaching external SCSI devices, be sure to terminate the last device on the external S... |
202 |
| SCSI:bus differences |
203 |
| SCSI:bus differences |
203 |
| SCSI:bus differences |
203 |
| A Small Computer Systems Interface (SCSI) bus is an IEEE standard bus for connecting your worksta... |
203 |
| There are two types of SCSI buses available with this workstation—an Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SC... |
203 |
| SCSI:mixing NSE and LVD devices on the same bus |
203 |
| SCSI:mixing NSE and LVD devices on the same bus |
203 |
| SCSI:mixing NSE and LVD devices on the same bus |
203 |
| <TABLE> |
203 |
| Table�B�1.� SCSI Bus Differences |
203 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
203 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
203 |
| Type |
203 |
| Transfer Rate |
203 |
| Transfer Rate |
203 |
| Data Bus Width |
203 |
| Data Bus Width |
203 |
| Available SCSI Addresses1 |
203 |
| Maximum Cable Length |
203 |
| Maximum Cable Length |
203 |
| Device Physical Location2 |
203 |
| Device Physical Location2 |
203 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
203 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
203 |
| Ultra Narrow Single-Ended |
203 |
| Ultra Narrow Single-Ended |
203 |
| Up to 20 Mbytes/sec |
203 |
| Up to 20 Mbytes/sec |
203 |
| 8 bits |
203 |
| 8 bits |
203 |
| 0 through 6 |
203 |
| 0 through 6 |
203 |
| 3.0 meters (9.84 feet) |
203 |
| 3.0 meters (9.84 feet) |
203 |
| External |
203 |
| External |
203 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
203 |
| Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential |
203 |
| Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential |
203 |
| Up to 80 Mbytes/sec |
203 |
| Up to 80 Mbytes/sec |
203 |
| 16 bits |
203 |
| 16 bits |
203 |
| 0 through 6; 8 through 15 |
203 |
| 0 through 6; 8 through 15 |
203 |
| 12 meters (39.37 feet) |
203 |
| 12 meters (39.37 feet) |
203 |
| Internal and external |
203 |
| Internal and external |
203 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
203 |
| 1. Address 7 is reserved for host controller use on all buses. |
203 |
| 1. Address 7 is reserved for host controller use on all buses. |
203 |
| 2. This information is specific to the HP Visualize B1000/C3000 workstations. |
203 |
| SCSI:scsi restrictions |
204 |
| SCSI:scsi restrictions |
204 |
| SCSI:scsi restrictions |
204 |
| This section describes the SCSI restrictions that apply to your workstation in the following areas: |
204 |
| This section describes the SCSI restrictions that apply to your workstation in the following areas: |
204 |
| • Cables |
204 |
| • Cables |
204 |
| • Cables |
204 |
| • Terminators |
204 |
| • Terminators |
204 |
| • Number of Devices Per SCSI Bus |
204 |
| • Considerations for Selecting SCSI Devices |
204 |
| NOTE The Ultra Narrow, single-ended SCSI bus supports only 7 devices because address 7 is reserve... |
204 |
| NOTE The Ultra Narrow, single-ended SCSI bus supports only 7 devices because address 7 is reserve... |
204 |
| Cables |
204 |
| Cables |
204 |
| Only SCSI cables approved by HP can be used to connect your workstation and any SCSI devices. HP ... |
204 |
| <TABLE> |
204 |
| Table�B�2.� Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI Cables |
204 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
204 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
204 |
| Cable Number |
204 |
| Cable Length |
204 |
| Cable Length |
204 |
| Description |
204 |
| Description |
204 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
204 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
204 |
| C2955A |
204 |
| 0.5m |
204 |
| 0.5m |
204 |
| 50-pin HDTS to 50-pin HDTS |
204 |
| 50-pin HDTS |
204 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
204 |
| C2908A |
204 |
| C2908A |
204 |
| 1.0m |
204 |
| 1.0m |
204 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
204 |
| C2956A |
204 |
| C2956A |
204 |
| 1.5m |
204 |
| 1.5m |
204 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
204 |
| C2957A |
204 |
| C2957A |
204 |
| 2.0m |
204 |
| 2.0m |
204 |
| HP offers the following SCSI cables for connecting externally connected devices to the system Ult... |
205 |
| <TABLE> |
205 |
| Table�B�3.� Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI Cables |
205 |
| <TABLE HEADING> |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| Cable Number |
205 |
| Cable Number |
205 |
| Cable Length |
205 |
| Cable Length |
205 |
| Description |
205 |
| Description |
205 |
| <TABLE BODY> |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2978A |
205 |
| C2978A |
205 |
| 0.5m |
205 |
| 0.5m |
205 |
| 68-pin HDTS to 68-pin HDTS |
205 |
| 68-pin HDTS |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2979A |
205 |
| C2979A |
205 |
| 1.5m |
205 |
| 1.5m |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2911B |
205 |
| C2911B |
205 |
| 1.0m |
205 |
| 1.0m |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2924B |
205 |
| C2924B |
205 |
| 2.5m |
205 |
| 2.5m |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2361A |
205 |
| C2361A |
205 |
| 1.0m |
205 |
| 1.0m |
205 |
| 68-pin VHDCI to 68-pin HDTS |
205 |
| 68-pin VHDCI |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2362A |
205 |
| C2362A |
205 |
| 2.5m |
205 |
| 2.5m |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2363A |
205 |
| C2363A |
205 |
| 10.0m |
205 |
| 10.0m |
205 |
| <TABLE ROW> |
205 |
| C2365A |
205 |
| C2365A |
205 |
| 5.0m |
205 |
| 5.0m |
205 |
| CAUTION SCSI cables approved by HP are designed to function within the SCSI tolerances for HP dev... |
205 |
| CAUTION SCSI cables approved by HP are designed to function within the SCSI tolerances for HP dev... |
205 |
| Always use the shortest possible cable(s) for your configuration. |
205 |
| NOTE See “Determining SCSI Bus Length” later in this Appendix to determine the total length of yo... |
205 |
| NOTE See “Determining SCSI Bus Length” later in this Appendix to determine the total length of yo... |
205 |
| SCSI:terminators |
206 |
| SCSI:terminators |
206 |
| SCSI:terminators |
206 |
| The terminators for Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI (LVD SCSI) and Ultra Narrow Single-... |
206 |
| CAUTION It is necessary to put a terminator on unused SCSI connectors on the back panel of the sy... |
206 |
| CAUTION It is necessary to put a terminator on unused SCSI connectors on the back panel of the sy... |
206 |
| Number of Devices Per SCSI Bus |
206 |
| Number of Devices Per SCSI Bus |
206 |
| The number of SCSI devices per bus is limited (see |
206 |
| This workstation offers the following types of SCSI buses, each with their own configuration cons... |
206 |
| • Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI bus |
206 |
| • Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI bus |
206 |
| • Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI bus |
206 |
| • Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI bus |
206 |
| • Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI bus |
206 |
| Considerations for Selecting SCSI Devices |
206 |
| Considerations for Selecting SCSI Devices |
206 |
| SCSI devices supported by the Hewlett-Packard Company for the Ultra Narrow Single-Ended (NSE) and... |
206 |
| If devices other than those supported by HP are connected to the Ultra Narrow Single-Ended or the... |
206 |
| Because Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI is a relatively new technology, there can be pr... |
206 |
| Low-voltage differential signaling specifications are described in the |
207 |
| Global Engineering Documents |
207 |
| 15 Inverness Way East |
207 |
| Englewood, CO 80112-5704 |
207 |
| (800) 854-7179 or (303) 397-7956 |
207 |
| SCSI:bus lengths |
208 |
| SCSI:bus lengths |
208 |
| SCSI:bus lengths |
208 |
| This section discusses SCSI bus length constraints for the Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI bus and... |
208 |
| This section discusses SCSI bus length constraints for the Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI bus and... |
208 |
| SCSI:Ultra Narrow Single-Ended, |
208 |
| SCSI:Ultra Narrow Single-Ended, |
208 |
| SCSI:Ultra Narrow Single-Ended, |
208 |
| The maximum cable length for a Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI bus is 3 meters. The HP Visualize B... |
208 |
| NOTE When calculating the total Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI cable/bus/trace length used extern... |
208 |
| NOTE When calculating the total Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI cable/bus/trace length used extern... |
208 |
| There are two total cable length specifications that apply to the Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI ... |
208 |
| The total cable length specifications are described below: |
208 |
| • For a total of one to four devices being connected to the NSE SCSI bus the total length of cabl... |
208 |
| • For a total of one to four devices being connected to the NSE SCSI bus the total length of cabl... |
208 |
| • For a total of one to four devices being connected to the NSE SCSI bus the total length of cabl... |
208 |
| • For a total of five to eight devices being connected to the NSE SCSI bus the total length of ca... |
208 |
| • For a total of five to eight devices being connected to the NSE SCSI bus the total length of ca... |
208 |
| NOTE Remember that the workstation is counted as one of the total device, and the internal length... |
208 |
| NOTE Remember that the workstation is counted as one of the total device, and the internal length... |
208 |
| SCSI:Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential, |
208 |
| SCSI:Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential, |
208 |
| SCSI:Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential, |
208 |
| The maximum cable length for a Ultra Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI bus is 12 meters. The HP ... |
208 |
| The maximum cable length for a Ultra Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI bus is 12 meters. The HP ... |
208 |
| NOTE When calculating the total Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI cable/bus/trace length ... |
209 |
| NOTE When calculating the total Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI cable/bus/trace length ... |
209 |
| SCSI:device IDs, |
210 |
| SCSI:device IDs, |
210 |
| SCSI:device IDs, |
210 |
| Before assigning a SCSI device ID to your drive, you need to check the existing SCSI device IDs. ... |
210 |
| 1. At a command line prompt, enter the following: |
210 |
| 1. At a command line prompt, enter the following: |
210 |
| 1. At a command line prompt, enter the following: |
210 |
| /usr/sbin/ioscan -f |
210 |
| /usr/sbin/ioscan -f |
210 |
| After a few moments, the ioscan utility lists all of the SCSI I/O devices it could find. The list... |
210 |
| Class I H/W Path Driver S/W State H/W Type Description |
210 |
| Assigning Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI Device IDs |
211 |
| Assigning Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI Device IDs |
211 |
| You can determine which Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI (NSE SCSI) devices are currently in use by... |
211 |
| You can determine which Ultra Narrow Single-Ended SCSI (NSE SCSI) devices are currently in use by... |
211 |
| Here is the break down of the hardware path: |
211 |
| SCSI device � 10/0/15/ |
211 |
| NSE SCSI ���� |
211 |
| SCSI ID 2 ���� � |
211 |
| CAUTION Do not use SCSI device ID 7 for any device. It is reserved for the built-in SCSI bus cont... |
211 |
| CAUTION Do not use SCSI device ID 7 for any device. It is reserved for the built-in SCSI bus cont... |
211 |
| Assigning Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI Device IDs |
211 |
| Assigning Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI Device IDs |
211 |
| You can determine which Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI (LVD SCSI) devices are currentl... |
211 |
| You can determine which Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI (LVD SCSI) devices are currentl... |
211 |
| SCSI device ���10/0/15/1.5.0 |
211 |
| LVD SCSI ������10/0/15/1.5.0 |
211 |
| SCSI ID 5 ������10/0/15/1.5.0 |
211 |
| CAUTION Do not use SCSI device ID 7 for any device. It is reserved for the built-in SCSI bus cont... |
211 |
| CAUTION Do not use SCSI device ID 7 for any device. It is reserved for the built-in SCSI bus cont... |
211 |
| SCSI:connecting to the ports, |
212 |
| SCSI:connecting to the ports, |
212 |
| SCSI:connecting to the ports, |
212 |
| This section describes how to connect to the system SCSI ports (Ultra Narrow Single-Ended and Ult... |
212 |
| System SCSI Port Connection |
212 |
| System SCSI Port Connection |
212 |
| The system contains two SCSI connectors: |
212 |
| • Ultra Narrow, Single-Ended SCSI (NSE SCSI) connector |
212 |
| • Ultra Narrow, Single-Ended SCSI (NSE SCSI) connector |
212 |
| • Ultra Narrow, Single-Ended SCSI (NSE SCSI) connector |
212 |
| • Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI (LVD SCSI) connector |
212 |
| Figure B-1 shows the two SCSI connectors. SCSI cables connect to these ports with a high-density ... |
212 |
| Figure�B�1.� SCSI Ports |
212 |
| Figure�B�1.� SCSI Ports |
212 |
| Figure�B�1.� SCSI Ports |
212 |
| <GRAPHIC> |
213 |
| NOTE It is necessary to put a terminator on unused SCSI connectors on the rear panel, or the last... |
213 |
| Reference documentation: |
215 |
| Reference documentation: |
215 |
| Reference documentation: |
215 |
| This appendix provides part numbers and titles to related documentation. |
215 |
| This appendix provides part numbers and titles to related documentation. |
215 |
| Installation Manual |
216 |
| Installation Manual |
216 |
| • A4985-90010 - |
216 |
| • A4985-90010 - |
216 |
| • A4985-90010 - |
216 |
| Service Manuals |
216 |
| Service Manuals |
216 |
| • B2355-90040 - System Administration Tasks Manual HP 9000 Series 700 |
216 |
| • B2355-90040 - System Administration Tasks Manual HP 9000 Series 700 |
216 |
| • B2355-90040 - System Administration Tasks Manual HP 9000 Series 700 |
216 |
| • B3782-90176 - |
216 |
| • B3782-90176 - |
216 |
| • A4033-90099 - HP A4032/A4033 Color Monitors CE Handbook |
216 |
| • A4033-90099 - HP A4032/A4033 Color Monitors CE Handbook |
216 |
| • A4033-90099 - HP A4032/A4033 Color Monitors CE Handbook |
216 |
| Reference Manuals |
216 |
| Reference Manuals |
216 |
| • A5992-90001 - |
216 |
| • A5992-90001 - |
216 |
| • A5992-90001 - |
216 |
| Glossary |
217 |
| Glossary |
217 |
| A |
217 |
| A |
217 |
| absolute pathname |
217 |
| absolute pathname |
217 |
| The full pathname of a file, including all the directories leading to it, starting with the root ... |
217 |
| The full pathname of a file, including all the directories leading to it, starting with the root ... |
217 |
| See also file, filename, pathname. |
217 |
| access permissions |
217 |
| access permissions |
217 |
| Settings that allow (or prevents) a user or group of users to read, write, or execute files |
217 |
| Settings that allow (or prevents) a user or group of users to read, write, or execute files |
217 |
| See also file access permissions. |
217 |
| active window |
217 |
| active window |
217 |
| The window that is receiving input from the keyboard at the present time. If there is no active w... |
217 |
| The window that is receiving input from the keyboard at the present time. If there is no active w... |
217 |
| ANSI |
217 |
| ANSI |
217 |
| The American National Standards Institute, a non-profit organization, made up of various expert c... |
217 |
| The American National Standards Institute, a non-profit organization, made up of various expert c... |
217 |
| argument |
217 |
| argument |
217 |
| A part of a command line or line of source code that identifies the file, directory, or other dat... |
217 |
| A part of a command line or line of source code that identifies the file, directory, or other dat... |
217 |
| attachment unit interface (AUI) |
217 |
| attachment unit interface (AUI) |
217 |
| A transceiver cable that conforms to IEEE 802.3 specifications. |
217 |
| A transceiver cable that conforms to IEEE 802.3 specifications. |
217 |
| B |
217 |
| B |
217 |
| back up |
217 |
| back up |
217 |
| v. To make a copy of one or more files on a tape or disk that can be stored separately from the o... |
217 |
| v. To make a copy of one or more files on a tape or disk that can be stored separately from the o... |
217 |
| backup |
217 |
| backup |
217 |
| n. A spare copy of one or more files on a tape or disk that can be used to restore data into its ... |
217 |
| n. A spare copy of one or more files on a tape or disk that can be used to restore data into its ... |
217 |
| bitmap |
217 |
| bitmap |
217 |
| Generally speaking, an array of data bits that define a graphical image. Strictly speaking, a bit... |
217 |
| Generally speaking, an array of data bits that define a graphical image. Strictly speaking, a bit... |
217 |
| boot |
217 |
| boot |
217 |
| Short for “bootstrap,” from the phrase “pulling oneself up by one’s bootstraps.” Indicates the be... |
217 |
| Short for “bootstrap,” from the phrase “pulling oneself up by one’s bootstraps.” Indicates the be... |
217 |
| boot console handler |
218 |
| boot console handler |
218 |
| The interactive firmware that enables you to interact with the hardware of your workstation befor... |
218 |
| The interactive firmware that enables you to interact with the hardware of your workstation befor... |
218 |
| boot ROM |
218 |
| boot ROM |
218 |
| A read-only memory that is incorporated into a workstation for the purpose of loading and startin... |
218 |
| A read-only memory that is incorporated into a workstation for the purpose of loading and startin... |
218 |
| bootstrap service |
218 |
| bootstrap service |
218 |
| See boot. |
218 |
| byte |
218 |
| byte |
218 |
| A fundamental character-code unit, usually consisting of 8 bits. |
218 |
| A fundamental character-code unit, usually consisting of 8 bits. |
218 |
| C |
218 |
| C |
218 |
| CD-RAM |
218 |
| CD-RAM |
218 |
| Compact Disk Random-Access Memory. |
218 |
| Compact Disk Random-Access Memory. |
218 |
| See also CD-RAM disk, CD-RAM drive. |
218 |
| CD-RAM disk |
218 |
| CD-RAM disk |
218 |
| CD-RAM disks are identical to the audio compact disks (CDs) used to record stereo music, except c... |
218 |
| CD-RAM disks are identical to the audio compact disks (CDs) used to record stereo music, except c... |
218 |
| CD-RAM drive |
218 |
| CD-RAM drive |
218 |
| A random-access, read/write, mass-storage device that uses removable CD-RAM disks. The drive cont... |
218 |
| A random-access, read/write, mass-storage device that uses removable CD-RAM disks. The drive cont... |
218 |
| CD-ROM |
218 |
| CD-ROM |
218 |
| Compact Disk Read-Only Memory. |
218 |
| Compact Disk Read-Only Memory. |
218 |
| See also CD-ROM disk, CD-ROM drive. |
218 |
| CD-ROM disk |
218 |
| CD-ROM disk |
218 |
| CD-ROM disks are identical to the audio compact disks (CDs) used to record stereo music, except t... |
218 |
| CD-ROM disks are identical to the audio compact disks (CDs) used to record stereo music, except t... |
218 |
| CD-ROM drive |
218 |
| CD-ROM drive |
218 |
| A random-access, read-only, mass-storage device that uses removable CD-ROM disks. The drive conta... |
218 |
| A random-access, read-only, mass-storage device that uses removable CD-ROM disks. The drive conta... |
218 |
| Central Processing Unit (CPU) |
219 |
| Central Processing Unit (CPU) |
219 |
| The part of a workstation that interprets and executes instructions; the “brain.” |
219 |
| The part of a workstation that interprets and executes instructions; the “brain.” |
219 |
| child directory |
219 |
| child directory |
219 |
| See subdirectory. |
219 |
| click |
219 |
| click |
219 |
| To press and immediately release a mouse button. The term comes from the fact that pressing and r... |
219 |
| To press and immediately release a mouse button. The term comes from the fact that pressing and r... |
219 |
| cluster |
219 |
| cluster |
219 |
| A group of workstations connected via a Local Area Network (LAN). One workstation, the cluster se... |
219 |
| A group of workstations connected via a Local Area Network (LAN). One workstation, the cluster se... |
219 |
| See also cluster client, cluster node, cluster server. |
219 |
| cluster client. |
219 |
| cluster client. |
219 |
| A cluster node that does not have a local HP-UX file system. Its file system resides on the clust... |
219 |
| A cluster node that does not have a local HP-UX file system. Its file system resides on the clust... |
219 |
| See also cluster, cluster node, cluster server. |
219 |
| cluster node |
219 |
| cluster node |
219 |
| A member of a group of workstations connected via a Local Area Network (LAN). One workstation, th... |
219 |
| A member of a group of workstations connected via a Local Area Network (LAN). One workstation, th... |
219 |
| See also cluster, cluster client, cluster server. |
219 |
| cluster server |
219 |
| cluster server |
219 |
| A workstation that provides file access, login access, file transfer, printing, and other service... |
219 |
| A workstation that provides file access, login access, file transfer, printing, and other service... |
219 |
| See also cluster, cluster client, cluster node, host. |
219 |
| cold install. |
219 |
| cold install. |
219 |
| A process that requires the booting of an install kernel from an install server over a network or... |
219 |
| A process that requires the booting of an install kernel from an install server over a network or... |
219 |
| command. |
219 |
| command. |
219 |
| An instruction that you enter into the system at a prompt, to execute a program or perform a task. |
219 |
| An instruction that you enter into the system at a prompt, to execute a program or perform a task. |
219 |
| See also shell command. |
219 |
| command argument |
219 |
| command argument |
219 |
| Information you provide on a command line to describe the object (often a file or directory) to b... |
219 |
| Information you provide on a command line to describe the object (often a file or directory) to b... |
219 |
| command interpreter |
220 |
| command interpreter |
220 |
| A program that reads lines of text from standard input (typed at the keyboard or read from a file... |
220 |
| A program that reads lines of text from standard input (typed at the keyboard or read from a file... |
220 |
| See also shell. |
220 |
| command option |
220 |
| command option |
220 |
| Information you provide on a command line to indicate any special action you want the command to ... |
220 |
| Information you provide on a command line to indicate any special action you want the command to ... |
220 |
| See also default. |
220 |
| configuration |
220 |
| configuration |
220 |
| The arrangement of a workstation or network as defined by the nature, number, and chief character... |
220 |
| The arrangement of a workstation or network as defined by the nature, number, and chief character... |
220 |
| console. |
220 |
| console. |
220 |
| The tty (terminal) the system was booted from. The console is associated with the monitor where a... |
220 |
| The tty (terminal) the system was booted from. The console is associated with the monitor where a... |
220 |
| control key sequence |
220 |
| control key sequence |
220 |
| A keystroke combination used as a shorthand way of specifying commands. To enter a control key se... |
220 |
| A keystroke combination used as a shorthand way of specifying commands. To enter a control key se... |
220 |
| cpu |
220 |
| cpu |
220 |
| See Central Processing Unit. |
220 |
| current directory |
220 |
| current directory |
220 |
| See current working directory. |
220 |
| current session |
220 |
| current session |
220 |
| The work and processes that have been created since you logged into the system (and before you lo... |
220 |
| The work and processes that have been created since you logged into the system (and before you lo... |
220 |
| See also session. |
220 |
| current working directory |
220 |
| current working directory |
220 |
| The directory from which a relative-pathname search begins, as well as the directory in which you... |
220 |
| The directory from which a relative-pathname search begins, as well as the directory in which you... |
220 |
| cursor |
220 |
| cursor |
220 |
| The small, usually blinking, box or underline displayed in whatever screen or window is active at... |
220 |
| The small, usually blinking, box or underline displayed in whatever screen or window is active at... |
220 |
| D |
220 |
| D |
220 |
| daisy-chaining |
221 |
| daisy-chaining |
221 |
| A method of connecting devices in which the signal passes from one device to the next in serial f... |
221 |
| A method of connecting devices in which the signal passes from one device to the next in serial f... |
221 |
| DDS tape drive |
221 |
| DDS tape drive |
221 |
| A device that stores data on Digital Data Storage (DDS) cassettes. |
221 |
| A device that stores data on Digital Data Storage (DDS) cassettes. |
221 |
| default |
221 |
| default |
221 |
| Most commands give you a choice of one or more options. If you don’t specify an option, the comma... |
221 |
| Most commands give you a choice of one or more options. If you don’t specify an option, the comma... |
221 |
| See also command option. |
221 |
| dialog box |
221 |
| dialog box |
221 |
| A special type of HP CDE screen that contains controls and settings, and with which the user can ... |
221 |
| A special type of HP CDE screen that contains controls and settings, and with which the user can ... |
221 |
| DIMM |
221 |
| DIMM |
221 |
| See Dual In-line Memory Module. |
221 |
| Dual In-line Memory Module |
221 |
| Dual In-line Memory Module |
221 |
| A memory board whose connectors on each side of the board are connected to different chips. This ... |
221 |
| A memory board whose connectors on each side of the board are connected to different chips. This ... |
221 |
| directory |
221 |
| directory |
221 |
| A special type of “container” object that contains information about the objects beneath it in th... |
221 |
| A special type of “container” object that contains information about the objects beneath it in th... |
221 |
| See also file. |
221 |
| disk |
221 |
| disk |
221 |
| A thin, round plate with a magnetic or optical surface coating on which data is stored by magneti... |
221 |
| A thin, round plate with a magnetic or optical surface coating on which data is stored by magneti... |
221 |
| disked workstation |
221 |
| disked workstation |
221 |
| A workstation that has its own hard disk drive. |
221 |
| A workstation that has its own hard disk drive. |
221 |
| diskette |
221 |
| diskette |
221 |
| See floppy diskette. |
221 |
| double click |
221 |
| double click |
221 |
| To press and release a mouse button twice in rapid succession. The amount of time that discrimina... |
221 |
| To press and release a mouse button twice in rapid succession. The amount of time that discrimina... |
221 |
| drag |
221 |
| drag |
221 |
| To move the mouse (and hence the pointer on the screen) while holding down one or more of its but... |
221 |
| To move the mouse (and hence the pointer on the screen) while holding down one or more of its but... |
221 |
| See also drop. |
222 |
| drive |
222 |
| drive |
222 |
| See CD-ROM drive, DDS tape drive, floppy drive, hard disk drive |
222 |
| drop |
222 |
| drop |
222 |
| To release the mouse button after having moved the mouse with its button held down, in order to p... |
222 |
| To release the mouse button after having moved the mouse with its button held down, in order to p... |
222 |
| See also drag. |
222 |
| E |
222 |
| E |
222 |
| EEPROM. |
222 |
| EEPROM. |
222 |
| Electronically erasable read-only memory. Usually bytes or words can be erased and reprogrammed i... |
222 |
| Electronically erasable read-only memory. Usually bytes or words can be erased and reprogrammed i... |
222 |
| environment |
222 |
| environment |
222 |
| The conditions in which your commands or programs are executed. These conditions include your wor... |
222 |
| The conditions in which your commands or programs are executed. These conditions include your wor... |
222 |
| See also environment variables. |
222 |
| environment variables |
222 |
| environment variables |
222 |
| The set of defined shell variables (some of which are PATH, TERM, SHELL, EXINIT, and HOME) that d... |
222 |
| The set of defined shell variables (some of which are PATH, TERM, SHELL, EXINIT, and HOME) that d... |
222 |
| See also environment. |
222 |
| Ethernet |
222 |
| Ethernet |
222 |
| The LAN developed jointly by Digital Equipment Corporation, Intel, and Xerox Corporation, upon wh... |
222 |
| The LAN developed jointly by Digital Equipment Corporation, Intel, and Xerox Corporation, upon wh... |
222 |
| F |
222 |
| F |
222 |
| Fast Narrow Single-Ended SCSI |
222 |
| Fast Narrow Single-Ended SCSI |
222 |
| An 8-bit-wide SCSI bus with standard receivers and drivers that runs at 20 Mbytes/second, which a... |
222 |
| An 8-bit-wide SCSI bus with standard receivers and drivers that runs at 20 Mbytes/second, which a... |
222 |
| See also Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI, Small Computer System Interface. |
223 |
| file |
223 |
| file |
223 |
| The basic named unit of data stored on disk |
223 |
| The basic named unit of data stored on disk |
223 |
| See also directory, filename. |
223 |
| file access permissions |
223 |
| file access permissions |
223 |
| The access rights given to a particular file or directory. Every file and directory has a set of ... |
223 |
| The access rights given to a particular file or directory. Every file and directory has a set of ... |
223 |
| See also access permissions. |
223 |
| File Manager |
223 |
| File Manager |
223 |
| The HP CDE application that allows you to manage your files and directories, and to set viewing p... |
223 |
| The HP CDE application that allows you to manage your files and directories, and to set viewing p... |
223 |
| filename |
223 |
| filename |
223 |
| The name given to a particular file |
223 |
| The name given to a particular file |
223 |
| See also absolute pathname, file, pathname. |
223 |
| file server |
223 |
| file server |
223 |
| A workstation whose primary task is to control the storage and retrieval of data from hard disks.... |
223 |
| A workstation whose primary task is to control the storage and retrieval of data from hard disks.... |
223 |
| file system |
223 |
| file system |
223 |
| The hierarchically organized set of files and directories on a hard disk. |
223 |
| The hierarchically organized set of files and directories on a hard disk. |
223 |
| firmware |
223 |
| firmware |
223 |
| The control software that is embedded in ROM and is always resident regardless of the status of t... |
223 |
| The control software that is embedded in ROM and is always resident regardless of the status of t... |
223 |
| floppy diskette |
223 |
| floppy diskette |
223 |
| A thin, flexible, disk-shaped sheet of plastic that magnetically stores data on its coated surfac... |
223 |
| A thin, flexible, disk-shaped sheet of plastic that magnetically stores data on its coated surfac... |
223 |
| floppy drive |
223 |
| floppy drive |
223 |
| A device that stores data on a floppy diskette. |
223 |
| A device that stores data on a floppy diskette. |
223 |
| H |
223 |
| H |
223 |
| hard disk |
223 |
| hard disk |
223 |
| A type of disk that is rigid—often aluminum—as opposed to a thin plastic diskette, which is flexi... |
223 |
| A type of disk that is rigid—often aluminum—as opposed to a thin plastic diskette, which is flexi... |
223 |
| hard disk drive |
224 |
| hard disk drive |
224 |
| A device that stores data on a hard disk. The hard disk can be a permanent part of the drive and ... |
224 |
| A device that stores data on a hard disk. The hard disk can be a permanent part of the drive and ... |
224 |
| Help Manager |
224 |
| Help Manager |
224 |
| The HP CDE application that provides online help. |
224 |
| The HP CDE application that provides online help. |
224 |
| $HOME |
224 |
| $HOME |
224 |
| The environment variable that contains the name of a user’s home directory. This is the directory... |
224 |
| The environment variable that contains the name of a user’s home directory. This is the directory... |
224 |
| See also home directory. |
224 |
| home directory |
224 |
| home directory |
224 |
| A shorthand way of referring to a frequently used directory, almost always the login directory. |
224 |
| A shorthand way of referring to a frequently used directory, almost always the login directory. |
224 |
| host |
224 |
| host |
224 |
| A computer that offers one or more services; may be local or remote (accessible via a network) |
224 |
| A computer that offers one or more services; may be local or remote (accessible via a network) |
224 |
| See also cluster server. |
224 |
| host name |
224 |
| host name |
224 |
| See internet protocol address. |
224 |
| HP CDE |
224 |
| HP CDE |
224 |
| See HP Common Desktop Environment. |
224 |
| HP Common Desktop Environment |
224 |
| HP Common Desktop Environment |
224 |
| A user interface that draws a graphical layer over the complexities of the other layers of the sy... |
224 |
| A user interface that draws a graphical layer over the complexities of the other layers of the sy... |
224 |
| HP-UX. |
224 |
| HP-UX. |
224 |
| This is Hewlett-Packard’s version of the UNIX® operating system. |
224 |
| This is Hewlett-Packard’s version of the UNIX® operating system. |
224 |
| HP-UX cluster |
224 |
| HP-UX cluster |
224 |
| See cluster node, cluster server. |
224 |
| I |
224 |
| I |
224 |
| icon |
224 |
| icon |
224 |
| A small, graphic representation of an object. Objects can be “iconized” (turned into icons) to cl... |
224 |
| A small, graphic representation of an object. Objects can be “iconized” (turned into icons) to cl... |
224 |
| iconify |
224 |
| iconify |
224 |
| See iconize. |
224 |
| iconize |
224 |
| iconize |
224 |
| To turn a window or shell into an icon |
224 |
| To turn a window or shell into an icon |
224 |
| See also icon. |
225 |
| Initial System Loader |
225 |
| Initial System Loader |
225 |
| The program that actually controls the loading of the operating system. |
225 |
| The program that actually controls the loading of the operating system. |
225 |
| input device |
225 |
| input device |
225 |
| Any of several pieces of hardware equipment used to give information to a system. Examples includ... |
225 |
| Any of several pieces of hardware equipment used to give information to a system. Examples includ... |
225 |
| See also output device. |
225 |
| input window |
225 |
| input window |
225 |
| The window that displays a program’s prompt and any commands typed but not yet executed. |
225 |
| The window that displays a program’s prompt and any commands typed but not yet executed. |
225 |
| Instant Ignition. |
225 |
| Instant Ignition. |
225 |
| When the user’s computer is turned on and it automatically boots up and is ready for use. Instant... |
225 |
| When the user’s computer is turned on and it automatically boots up and is ready for use. Instant... |
225 |
| install server. |
225 |
| install server. |
225 |
| This is a networked computer from which file sets and operating systems can be installed. |
225 |
| This is a networked computer from which file sets and operating systems can be installed. |
225 |
| internet protocol address (IP address) |
225 |
| internet protocol address (IP address) |
225 |
| A string of characters, in the format nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn, that uniquely identifies a workstation in ... |
225 |
| A string of characters, in the format nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn, that uniquely identifies a workstation in ... |
225 |
| invisible filename |
225 |
| invisible filename |
225 |
| A filename in which the first character is a period (.). Invisible filenames are not displayed by... |
225 |
| A filename in which the first character is a period (.). Invisible filenames are not displayed by... |
225 |
| IP address |
225 |
| IP address |
225 |
| See internet protocol address. |
225 |
| ISL |
225 |
| ISL |
225 |
| See Initial System Loader. |
225 |
| K-L |
225 |
| K-L |
225 |
| kernel |
225 |
| kernel |
225 |
| The part of the operating system that is an executable piece of code responsible for managing the... |
225 |
| The part of the operating system that is an executable piece of code responsible for managing the... |
225 |
| LAN |
225 |
| LAN |
225 |
| See local area network. |
225 |
| LAN station address |
225 |
| LAN station address |
225 |
| See local area network station address. |
225 |
| link |
225 |
| link |
225 |
| n. A special object that contains the name of another object. When you specify a link as a pathna... |
225 |
| n. A special object that contains the name of another object. When you specify a link as a pathna... |
225 |
| local area network (LAN) |
226 |
| local area network (LAN) |
226 |
| A data communications system that allows a number of independent devices to communicate with each... |
226 |
| A data communications system that allows a number of independent devices to communicate with each... |
226 |
| local area network system address |
226 |
| local area network system address |
226 |
| The label that uniquely identifies the local area network (LAN) connection for your workstation a... |
226 |
| The label that uniquely identifies the local area network (LAN) connection for your workstation a... |
226 |
| log in |
226 |
| log in |
226 |
| v. To initially sign on to the system so that you may begin to use it. This creates your first us... |
226 |
| v. To initially sign on to the system so that you may begin to use it. This creates your first us... |
226 |
| login |
226 |
| login |
226 |
| n. A session. Or, a string of characters that uniquely identifies a user of the system |
226 |
| n. A session. Or, a string of characters that uniquely identifies a user of the system |
226 |
| See also session, user account, and username. |
226 |
| login directory |
226 |
| login directory |
226 |
| The directory in which you are placed when you log in, usually your home directory |
226 |
| The directory in which you are placed when you log in, usually your home directory |
226 |
| See also home directory. |
226 |
| Login Manager |
226 |
| Login Manager |
226 |
| The program that controls the initial startup of HP CDE and accepts the user’s username and password |
226 |
| The program that controls the initial startup of HP CDE and accepts the user’s username and password |
226 |
| login script |
226 |
| login script |
226 |
| The shell program that runs at each login, and sets the login environment for your system. |
226 |
| The shell program that runs at each login, and sets the login environment for your system. |
226 |
| M |
226 |
| M |
226 |
| menu bar |
226 |
| menu bar |
226 |
| An area at the top or bottom of a window that contain the titles of the pull-down or pop-up menus... |
226 |
| An area at the top or bottom of a window that contain the titles of the pull-down or pop-up menus... |
226 |
| minimize button |
226 |
| minimize button |
226 |
| In HP CDE, a push-button on the window frame that turns a screen into an icon. |
226 |
| In HP CDE, a push-button on the window frame that turns a screen into an icon. |
226 |
| See also icon, iconize. |
226 |
| monitor type. |
226 |
| monitor type. |
226 |
| A monitor path name (graphics(1) through graphics(6)) that is associated with a particular resolu... |
226 |
| A monitor path name (graphics(1) through graphics(6)) that is associated with a particular resolu... |
226 |
| mouse pointer |
227 |
| mouse pointer |
227 |
| See pointer. |
227 |
| N |
227 |
| N |
227 |
| name |
227 |
| name |
227 |
| A character string associated with a file, directory, or link. A name can include various alphanu... |
227 |
| A character string associated with a file, directory, or link. A name can include various alphanu... |
227 |
| See also pathname. |
227 |
| network |
227 |
| network |
227 |
| Two or more workstations sharing information |
227 |
| Two or more workstations sharing information |
227 |
| See also cluster, workstation. |
227 |
| network controller |
227 |
| network controller |
227 |
| A printed circuit board that passes bit streams between the network and the main memory of the wo... |
227 |
| A printed circuit board that passes bit streams between the network and the main memory of the wo... |
227 |
| node |
227 |
| node |
227 |
| A computer that is on a network. Each node in the network can use the data, programs, and devices... |
227 |
| A computer that is on a network. Each node in the network can use the data, programs, and devices... |
227 |
| See also disked workstation, diskless workstation, workstation. |
227 |
| node name |
227 |
| node name |
227 |
| A unique identifying name given to a workstation in a cluster |
227 |
| A unique identifying name given to a workstation in a cluster |
227 |
| See also cluster, node. |
227 |
| nonvolatile memory |
227 |
| nonvolatile memory |
227 |
| System memory that retains its contents even after workstation power is turned off. |
227 |
| System memory that retains its contents even after workstation power is turned off. |
227 |
| O |
227 |
| O |
227 |
| object |
227 |
| object |
227 |
| Any file, directory, or link in the network. See also directory, file, link, pathname. |
227 |
| Any file, directory, or link in the network. See also directory, file, link, pathname. |
227 |
| operating system |
227 |
| operating system |
227 |
| The program that supervises the execution of other programs on your workstation. For example, the... |
227 |
| The program that supervises the execution of other programs on your workstation. For example, the... |
227 |
| See also kernel. |
227 |
| option |
227 |
| option |
227 |
| See command option. |
227 |
| output device |
227 |
| output device |
227 |
| Any of several pieces of hardware used for receiving messages from the computer and storing them,... |
227 |
| Any of several pieces of hardware used for receiving messages from the computer and storing them,... |
227 |
| See also input device. |
227 |
| output window |
227 |
| output window |
227 |
| The window that displays a process response to your command. |
227 |
| The window that displays a process response to your command. |
227 |
| P |
228 |
| P |
228 |
| parent directory |
228 |
| parent directory |
228 |
| A directory that contains other directories, each of which is then called a subdirectory |
228 |
| A directory that contains other directories, each of which is then called a subdirectory |
228 |
| See also subdirectory. |
228 |
| password |
228 |
| password |
228 |
| The secret word you enter next to the password prompt at login time to permit only authorized acc... |
228 |
| The secret word you enter next to the password prompt at login time to permit only authorized acc... |
228 |
| See also user account. |
228 |
| path |
228 |
| path |
228 |
| The hardware address of a device that is attached to the I/O system of your workstation. |
228 |
| The hardware address of a device that is attached to the I/O system of your workstation. |
228 |
| pathname |
228 |
| pathname |
228 |
| A slash/separated series of zero or more directory names followed by a filename, that together de... |
228 |
| A slash/separated series of zero or more directory names followed by a filename, that together de... |
228 |
| See also name, object. |
228 |
| permissions |
228 |
| permissions |
228 |
| A set of rights (read, write, execute) associated with an object in the file system. Determines w... |
228 |
| A set of rights (read, write, execute) associated with an object in the file system. Determines w... |
228 |
| PID |
228 |
| PID |
228 |
| Process Identifier. Also referred to as a process ID |
228 |
| Process Identifier. Also referred to as a process ID |
228 |
| See also process ID. |
228 |
| PIM. |
228 |
| PIM. |
228 |
| Processor Internal Memory. The pim command is a command used by the Boot Console Interface for de... |
228 |
| Processor Internal Memory. The pim command is a command used by the Boot Console Interface for de... |
228 |
| See also processor internal memory. |
228 |
| pointer |
228 |
| pointer |
228 |
| Sometimes called the “mouse pointer,” the pointer’s location on the display corresponds to the mo... |
228 |
| Sometimes called the “mouse pointer,” the pointer’s location on the display corresponds to the mo... |
228 |
| process |
228 |
| process |
228 |
| A computing environment in which you may execute programs; a program currently running in the sys... |
228 |
| A computing environment in which you may execute programs; a program currently running in the sys... |
228 |
| process ID |
229 |
| process ID |
229 |
| A unique identification number assigned to all processes by the operating system. Also referred t... |
229 |
| A unique identification number assigned to all processes by the operating system. Also referred t... |
229 |
| See also PID. |
229 |
| processor internal memory. |
229 |
| processor internal memory. |
229 |
| A storage area in a processor (for example, EEPROM) that is set at the time of a high-priority ma... |
229 |
| A storage area in a processor (for example, EEPROM) that is set at the time of a high-priority ma... |
229 |
| program. |
229 |
| program. |
229 |
| A unit of executable code, in source-code or binary form. Most HP-UX commands and routines consis... |
229 |
| A unit of executable code, in source-code or binary form. Most HP-UX commands and routines consis... |
229 |
| prompt |
229 |
| prompt |
229 |
| A message or symbol displayed by the system to let you know that it is ready for your input. |
229 |
| A message or symbol displayed by the system to let you know that it is ready for your input. |
229 |
| push button |
229 |
| push button |
229 |
| A graphic control that simulates a real-life push button. Use the pointer and mouse to push the b... |
229 |
| A graphic control that simulates a real-life push button. Use the pointer and mouse to push the b... |
229 |
| R-S |
229 |
| R-S |
229 |
| RAM |
229 |
| RAM |
229 |
| Random-access memory. |
229 |
| Random-access memory. |
229 |
| ROM |
229 |
| ROM |
229 |
| Read-only memory. |
229 |
| Read-only memory. |
229 |
| root |
229 |
| root |
229 |
| See superuser. |
229 |
| scroll bar |
229 |
| scroll bar |
229 |
| A vertical or horizontal bar located on the side or bottom of a window that allows the user to vi... |
229 |
| A vertical or horizontal bar located on the side or bottom of a window that allows the user to vi... |
229 |
| SCSI |
229 |
| SCSI |
229 |
| See Small Computer System Interface. |
229 |
| SCSI ID. |
229 |
| SCSI ID. |
229 |
| The address of a peripheral device connected to a SCSI bus. |
229 |
| The address of a peripheral device connected to a SCSI bus. |
229 |
| server |
229 |
| server |
229 |
| A program that controls all access to input and output devices. |
229 |
| A program that controls all access to input and output devices. |
229 |
| session |
229 |
| session |
229 |
| The time between when you log in and when you log out. Also called a “work session” or a “login s... |
229 |
| The time between when you log in and when you log out. Also called a “work session” or a “login s... |
229 |
| See also current session. |
229 |
| shell |
229 |
| shell |
229 |
| A command-line interpreter program used to invoke programs. Some examples of HP-UX shells are the... |
229 |
| A command-line interpreter program used to invoke programs. Some examples of HP-UX shells are the... |
229 |
| See also command interpreter. |
229 |
| shell command |
230 |
| shell command |
230 |
| An instruction you give the system to execute a utility program or shell script |
230 |
| An instruction you give the system to execute a utility program or shell script |
230 |
| See also shell script, utility program. |
230 |
| shell script |
230 |
| shell script |
230 |
| A file that contains commands that the system can interpret and run in a shell. |
230 |
| A file that contains commands that the system can interpret and run in a shell. |
230 |
| shutdown |
230 |
| shutdown |
230 |
| The process of taking the system from multi-user state to system administration state. |
230 |
| The process of taking the system from multi-user state to system administration state. |
230 |
| slider |
230 |
| slider |
230 |
| One of the components of a scroll bar. The slider is the object that is dragged along the scroll ... |
230 |
| One of the components of a scroll bar. The slider is the object that is dragged along the scroll ... |
230 |
| Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) |
230 |
| Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) |
230 |
| An IEEE standard for interfacing a computer to multiple, disparate high-speed peripherals such as... |
230 |
| An IEEE standard for interfacing a computer to multiple, disparate high-speed peripherals such as... |
230 |
| See also Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI, Fast Narrow Single-Ended SCSI. |
230 |
| SPA. |
230 |
| SPA. |
230 |
| Soft Physical Address. |
230 |
| Soft Physical Address. |
230 |
| See also soft physical address. |
230 |
| soft physical address. |
230 |
| soft physical address. |
230 |
| This is a location in system memory associated with the DIMM cards. |
230 |
| This is a location in system memory associated with the DIMM cards. |
230 |
| standalone |
230 |
| standalone |
230 |
| A workstation that is not part of a cluster |
230 |
| A workstation that is not part of a cluster |
230 |
| See also cluster. |
230 |
| Style Manager |
230 |
| Style Manager |
230 |
| The HP CDE application that provides the ability to customize various user-interface aspects of y... |
230 |
| The HP CDE application that provides the ability to customize various user-interface aspects of y... |
230 |
| subdirectory |
230 |
| subdirectory |
230 |
| A directory that is located in, or anywhere on a path below, another directory. The directory abo... |
230 |
| A directory that is located in, or anywhere on a path below, another directory. The directory abo... |
230 |
| See also parent directory. |
230 |
| superuser |
230 |
| superuser |
230 |
| A user with permission to enter any directory and make changes to files and programs that typical... |
230 |
| A user with permission to enter any directory and make changes to files and programs that typical... |
230 |
| system administrator |
231 |
| system administrator |
231 |
| The person responsible for system and network installation, updating, maintenance, and security a... |
231 |
| The person responsible for system and network installation, updating, maintenance, and security a... |
231 |
| system call |
231 |
| system call |
231 |
| Invocation of a kernel process by a user program. |
231 |
| Invocation of a kernel process by a user program. |
231 |
| system name |
231 |
| system name |
231 |
| See internet protocol address. |
231 |
| T-U |
231 |
| T-U |
231 |
| terminal window |
231 |
| terminal window |
231 |
| A terminal window is a type of HP CDE window that emulates a complete display terminal. Terminal ... |
231 |
| A terminal window is a type of HP CDE window that emulates a complete display terminal. Terminal ... |
231 |
| See also HP Common Desktop Environment. |
231 |
| title bar |
231 |
| title bar |
231 |
| The rectangular area, between the top of the window and the window frame, that contains the title... |
231 |
| The rectangular area, between the top of the window and the window frame, that contains the title... |
231 |
| TOC. |
231 |
| TOC. |
231 |
| See transfer of control. |
231 |
| transceiver |
231 |
| transceiver |
231 |
| A device that transmits and receives signals. |
231 |
| A device that transmits and receives signals. |
231 |
| transfer of control. |
231 |
| transfer of control. |
231 |
| Saves the state of the processor in Processor Internal Memory (PIM) and pending I/O operations ar... |
231 |
| Saves the state of the processor in Processor Internal Memory (PIM) and pending I/O operations ar... |
231 |
| Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI |
231 |
| Ultra2 Wide Low-Voltage Differential SCSI |
231 |
| A 16-bit-wide bus with low-power receivers and drivers, which allows a cable length of up to 12 m... |
231 |
| A 16-bit-wide bus with low-power receivers and drivers, which allows a cable length of up to 12 m... |
231 |
| See also Fast Narrow Single-Ended SCSI, Small Computer System Interface. |
231 |
| user account |
231 |
| user account |
231 |
| The system administrator defines a user account for every person authorized to use the system. Ea... |
231 |
| The system administrator defines a user account for every person authorized to use the system. Ea... |
231 |
| See also user ID, password. |
232 |
| user ID |
232 |
| user ID |
232 |
| The name the computer uses to identify you. Your system administrator assigns you a user ID. Ente... |
232 |
| The name the computer uses to identify you. Your system administrator assigns you a user ID. Ente... |
232 |
| See also user account. |
232 |
| username |
232 |
| username |
232 |
| The name that the system recognizes as uniquely yours. Also known as your “login name.” The usern... |
232 |
| The name that the system recognizes as uniquely yours. Also known as your “login name.” The usern... |
232 |
| utility |
232 |
| utility |
232 |
| See utility program. |
232 |
| utility program |
232 |
| utility program |
232 |
| A program provided with the operating system to perform a frequently required task, such as print... |
232 |
| A program provided with the operating system to perform a frequently required task, such as print... |
232 |
| See also command, shell command. |
232 |
| W |
232 |
| W |
232 |
| window |
232 |
| window |
232 |
| A rectangular area of the screen for viewing information. HP CDE allows you to create several typ... |
232 |
| A rectangular area of the screen for viewing information. HP CDE allows you to create several typ... |
232 |
| See also Workspace Manager. |
232 |
| Window Manager |
232 |
| Window Manager |
232 |
| The HP CDE program that controls the size, placement, and operation of windows. |
232 |
| The HP CDE program that controls the size, placement, and operation of windows. |
232 |
| working directory |
232 |
| working directory |
232 |
| See current working directory. |
232 |
| Workspace |
232 |
| Workspace |
232 |
| What the screen becomes when you start HP CDE. Although you can hide the workspace under terminal... |
232 |
| What the screen becomes when you start HP CDE. Although you can hide the workspace under terminal... |
232 |
| See also HP Common Desktop Environment, terminal window. |
232 |
| Workspace Manager |
232 |
| Workspace Manager |
232 |
| The program that controls the size, placement, and operation of windows on the HP CDE Workspace. ... |
232 |
| The program that controls the size, placement, and operation of windows on the HP CDE Workspace. ... |
232 |
| See also Window Manager. |
232 |
| workstation |
232 |
| workstation |
232 |
| A compact, graphics-oriented computer having high speed and high memory capacity. A workstation u... |
232 |
| A compact, graphics-oriented computer having high speed and high memory capacity. A workstation u... |
232 |
| See also node, disked workstation, diskless workstation. |
233 |
| Symbols |
235 |
| A |
235 |
| B |
235 |
| C |
235 |
| D |
236 |
| E |
236 |
| F |
236 |
| H |
237 |
| I |
237 |
| K |
237 |
| L |
237 |
| M |
237 |
| N |
237 |
| O |
238 |
| P |
238 |
| R |
238 |
| S |
238 |
| T |
239 |

 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95 96
96 97
97 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144 145
145 146
146 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150 151
151 152
152 153
153 154
154 155
155 156
156 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162 163
163 164
164 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168 169
169 170
170 171
171 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182 183
183 184
184 185
185 186
186 187
187 188
188 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192 193
193 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202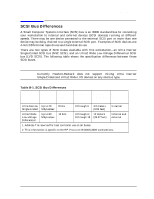 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208 209
209 210
210 211
211 212
212 213
213 214
214 215
215 216
216 217
217 218
218 219
219 220
220 221
221 222
222 223
223 224
224 225
225 226
226 227
227 228
228 229
229 230
230 231
231 232
232 233
233 234
234 235
235 236
236 237
237 238
238 239
239