HP t5630 Microsoft Windows Embedded Standard 2009 (WES) and Windows XP Embedde - Page 47
DOS Command-line Tool Boot Commands, Using Boot Commands, HP RAMDisk
 |
View all HP t5630 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 47 highlights
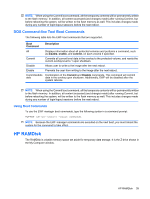
NOTE: When using the Commit boot command, all the temporary contents will be permanently written to the flash memory. In addition, all content accessed (and changes made) after running Commit, but before rebooting the system, will be written to the flash memory as well. This includes changes made during any number of login/logout sessions before the next reboot. DOS Command-line Tool Boot Commands The following table lists the EWF boot commands that are supported. Boot Command Description All Displays information about all protected volumes and performs a command, such as disable, enable, and commit, on each volume if specified. Commit Commits all current level data in the overlay to the protected volume, and resets the current overlay level to 1 upon shutdown. Disable Allows user to write to the image after the next reboot. Enable Prevents the user from writing to the image after the next reboot. Commitanddis Combination of the Commit and Disable commands. This command will commit able data in the overlay upon shutdown. Additionally, EWF will be disabled after the system reboots. NOTE: When using the Commit boot command, all the temporary contents will be permanently written to the flash memory. In addition, all content accessed (and changes made) after running Commit, but before rebooting the system, will be written to the flash memory as well. This includes changes made during any number of login/logout sessions before the next reboot. Using Boot Commands To use the EWF manager boot commands, type the following syntax in a command prompt: EWFMGR -[boot command]. NOTE: Because the EWF manager commands are executed on the next boot, you must reboot the system for the command to take effect. HP RAMDisk The RAMDisk is volatile memory space set aside for temporary data storage. It is the Z drive shown in the My Computer window. HP RAMDisk 39