Intel D425KT Product Specification - Page 57
Power Consumption, 2.7.1 Minimum Load Configuration - idle power consumption
 |
View all Intel D425KT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 57 highlights
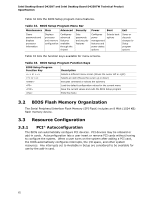
Technical Reference 2.7 Power Consumption Power measurements were performed to determine bare minimum and likely maximum power requirements from the board, as well as attached devices, in order to facilitate power supply rating estimates for specific system configurations. 2.7.1 Minimum Load Configuration Minimum load refers to the power demand placed on the power supply when using a bare system configuration with minimal power requirement conditions. Minimum load configuration test results are shown in Table 29. The test configuration was defined as follows: • 2 GB DDR3/800 MHz SO-DIMM • USB keyboard and mouse • LAN linked at 100 Mb/s • DOS booted via network (PXE); system at idle • All on board peripherals enabled (serial, parallel, audio, ...) Table 29. Minimum Load Configuration Current and Power Results Output Voltage 3.3 V 5 V 12 V1 12 V2 -12 V 5 VSB Minimum Load 0.46 A 2.3 A 0.37 A 0.062A 0.025A 0.13A 2.7.2 Maximum Load Configuration Maximum load refers to the incremental power demands placed on the power supply, augmenting the minimum load configuration into a fully-featured system that stresses power consumption from all subsystems. Maximum load configuration test results are shown in Table 30. The test configuration was defined as follows: • 4 GB DDR3/800 MHz SO-DIMM • 14.1-inch LCD via LVDS (D425KTW only) • SATA DVD-R/W ⎯ Load: DVD playback • 3.5-inch SATA hard disk drive, running Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic ⎯ Load: continuous read/write benchmark • 2.5-inch SATA hard disk drive ⎯ Load: continuous read/write benchmark • Intel Z-U130 USB Solid-State Drive or compatible device on the USB flash drive header (D425KTW only) ⎯ Load: continuous read/write benchmark • Wireless card on PCI Express x1 Mini Card slot (D425KTW only), connected via 802.11n protocol ⎯ Load: continuous read/write benchmark on remote share 57