Kenmore 4102 Use and Care Guide - Page 13
Cooking, Before, Setting, Oven Controls - slide in
 |
View all Kenmore 4102 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
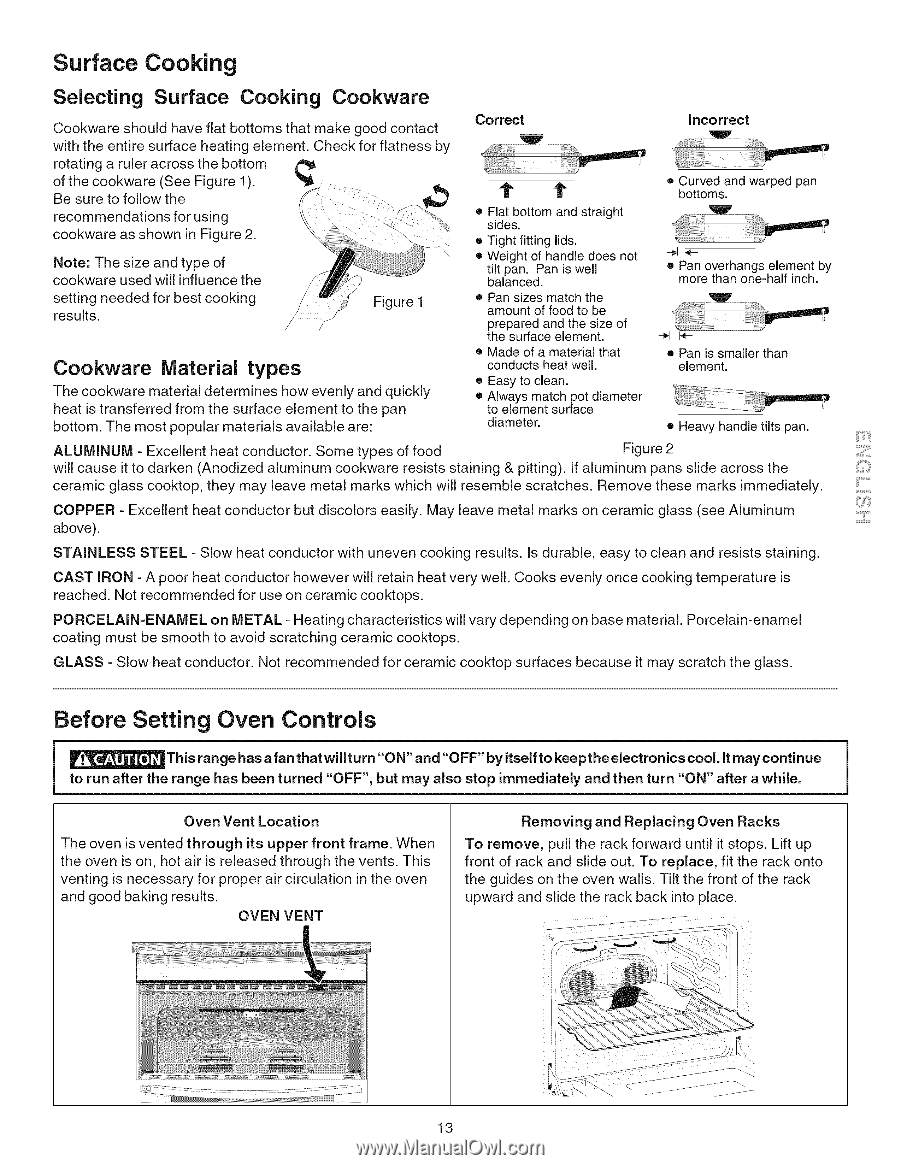
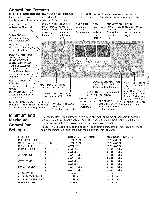
Surface Cooking Selecting Surface Cooking Cookware Cookware should have flat bottoms that make good contact with the entire surface heating element. Check for flatness by rotating a ruler across the bottom of the cookware (See Figure 1). Be sure to follow the recommendations for using cookware as shown in Figure 2. Note: The size and type of cookware used will influence the setting needed for best cooking results. Figure 1 Cookware Material types The cookware material determines how evenly and quickly heat is transferred from the surface element to the pan bottom. The most popular materials available are: Correct incorrect t 1" • Flat bottom and straight sides. • Tight fitting lids. • Weight of handle does not tilt pan. Pan is well balanced. • Pan sizes match the amount of food to be prepared and the size of the surface element. • Made of a material that conducts heat well. • Easy to clean. • Always match pot diameter to element surface diameter. o Curved and warped pan bottoms. ® Pan overhangs element by more than one-half inch. ÷1 I_ • Pan is smaller than element. • Heavy handle tilts pan. ALUMINUM - Excellent heat conductor. Some types of food Figure 2 will cause it to darken (Anodized aluminum cookware resists staining & pitting). If aluminum pans slide across the ceramic glass cooktop, they may leave metal marks which will resemble scratches. Remove these marks immediately. COPPER - Excellent heat conductor but discolors easily. May leave metal marks on ceramic glass (see Aluminum above). STAINLESS STEEL - Slow heat conductor with uneven cooking results. Is durable, easy to clean and resists staining. CAST IRON - A poor heat conductor however will retain heat very well. Cooks evenly once cooking temperature is reached. Not recommended for use on ceramic cooktops. PORCELAIN-ENAMEL on METAL - Heating characteristics will vary depending on base material. Porcelain-enamel coating must be smooth to avoid scratching ceramic cooktops. GLASS - Slow heat conductor. Not recommended for ceramic cooktop surfaces because it may scratch the glass. iii;:¸S':ili ...ii.i...... Before Setting Oven Controls _This range has afan that willturn "ON" and "OFF" by itself to keepthe electronics cool. It may continue to run after the range has been turned "OFF", but may also stop immediately and then turn "ON" after a while. Oven Vent Location The oven is vented through its upper front frame. When the oven is on, hot air is released through the vents. This venting is necessary for proper air circulation in the oven and good baking results. OVEN VENT Removing and Replacing Oven Racks To remove, pull the rack forward until it stops. Lift up front of rack and slide out. To replace, fit the rack onto the guides on the oven walls. Tilt the front of the rack upward and slide the rack back into place. 13