Lexmark X792 Lexmark Document Distributor - Page 65
Tuning the load balancer for unequal servers, Assigning servers to only run LMC or process jobs
 |
View all Lexmark X792 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 65 highlights
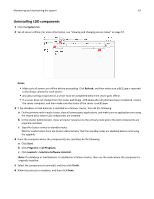
Monitoring and maintaining the system 65 Tuning the load balancer for unequal servers When all servers in the system are approximately equal, server loads should be optimal without manually tuning the load balancer. However, when servers are unequal, the least powerful machine determines the overall throughput unless you compensate by manually assigning a load balancing factor to each server. Since more powerful machines can run more concurrent jobs and complete each job in less time, routing more traffic to them increases the overall job capacity of the system. The LDD load balancer component is composed of three different Tomcat load balancing workers that separately manage Lexmark Management Console (LMC) sessions, job submissions from e‑Task 2 and e‑Task 3 printers, and job submissions from e‑Task printers. The adjustment shown here affects the e‑Task 2, e‑Task 3, and e‑Task load balancers, but not the LMC load balancer. Each load balancer distributes jobs to servers in proportion to the load balancing factors assigned to each server. For example, in a system with three servers with load balancing factors of 10,10, and 20, the first two servers each receive 25% of jobs, and the third receives 50%. The ideal job distribution depends on the hardware, network environment, and the solution being run. The optimal proportions for load balancing factors can be found by running performance tests on each server. However, some factors such as memory, number of processors, or CPU speed may suggest an initial value for the load balancing factor to add more system capacity. Note, however, that performance improvements are not linear functions of numerical improvements in hardware. Perform the following steps on each server after initial values are determined for load balancing factors: 1 From the System Health dashboard, select the address of the server from the list in the Server Health section. 2 Adjust the Load Factor slider to the desired load balancing factor for the server. Note: These settings are not saved during an upgrade. If you upgrade your LDD system, then you must repeat these steps. Assigning servers to only run LMC or process jobs When using more than one server in a system, you can assign some servers to only run LMC and other servers to only process jobs. When all servers are separated in this manner, it is usually adequate to assign only one server to run LMC. When using a configuration 1‑N, X‑N, or X‑Y‑N system with the recommended hardware, it is recommend to do the following: • Install the server component on the RAID 1 array where the operating system is installed on the load balancer computer, and configure it to only run LMC. • Configure servers installed on dedicated computers to only process jobs. 1 Launch JK Status Manager from your Web browser using the URL http://loadbalancer:9780/status/? opt=454, where loadbalancer is the computer where your load balancer is installed. Server information and the worker status for each of the three load balancing workers appear. Each server in the system is listed as a worker in each Balancer Members list. 2 For each server that should only process jobs, stop the associated worker on the adminloadbalancer load balancing worker, which balances requests to LMC: a In the "Worker Status for adminloadbalancer" section, click E beside the server name. b For Activation, select the Stopped option. c Click Update Worker.