Netgear FM114P FR114W Reference Manual - Page 140
Wireless Channel Selection, ISM Industrial, Scientific
 |
UPC - 606449024029
View all Netgear FM114P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 140 highlights
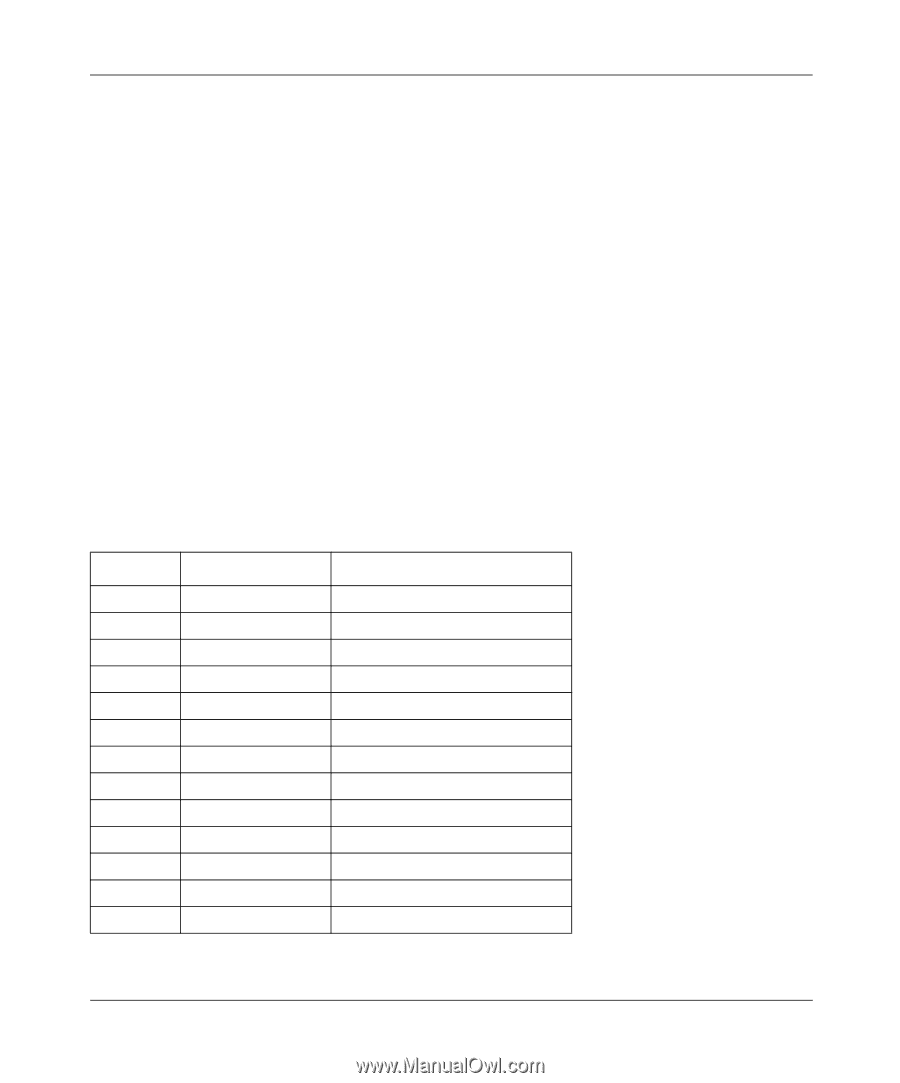
Reference Manual for the Model FR114P, FR114W and FM114P Cable/DSL ProSafe Firewall Family The 128-bit WEP data encryption method consists of 104 user-configurable bits. Similar to the forty-bit WEP data encryption method, the remaining 24 bits are factory set and not user configurable. Some vendors allow passphrases to be entered instead of the cryptic hexadecimal characters to ease encryption key entry. Wireless Channel Selection IEEE 802.11 wireless nodes communicate with each other using radio frequency signals in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band between 2.4Ghz and 2.5Ghz. Neighboring channels are 5Mhz apart. However, due to spread spectrum effect of the signals, a node sending signals using a particular channel will utilize frequency spectrum12.5Mhz above and below the center channel frequency. As a result, two separate wireless networks using neighboring channels (for example, channel 1 and channel 2) in the same general vicinity will interfere with each other. Applying two channels that allow the maximum channel separation will decrease the amount of channel cross-talk, and provide a noticeable performance increase over networks with minimal channel separation. The radio frequency channels used are listed in Table B-3: Table B-3. 802.11 Radio Frequency Channels Channel 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Center Frequency 2412Mhz 2417Mhz 2422Mhz 2427Mhz 2432Mhz 2437Mhz 2442Mhz 2447Mhz 2452Mhz 2457Mhz 2462Mhz 2467Mhz 2472Mhz Frequency Spread 2399.5Mhz - 2424.5Mhz 2404.5Mhz - 2429.5Mhz 2409.5Mhz - 2434.5Mhz 2414.5Mhz - 2439.5Mhz 2419.5Mhz - 2444.5Mhz 2424.5Mhz - 2449.5Mhz 2429.5Mhz - 2454.5Mhz 2434.5Mhz - 2459.5Mhz 2439.5Mhz - 2464.5Mhz 2444.5Mhz - 2469.5Mhz 2449.5Mhz - 2474.5Mhz 2454.5Mhz - 2479.5Mhz 2459.5Mhz - 2484.5Mhz B-14 Networks, Routing, and Firewall Basics