Optoma ZK750 ZK1050_UM - Page 30
R / G / B / C / Y / M Saturation / Hue / Gain, Color Settings
 |
View all Optoma ZK750 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
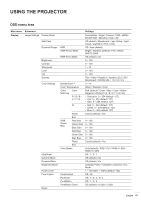
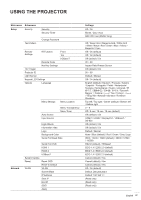
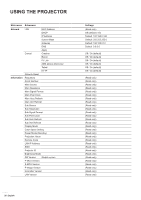
USING THE PROJECTOR Brightness Adjust the luminous brightness of the projected image to adapt to different ambient light. Contrast Adjust the contrast ratio of the projected image. The contrast controls the degree of difference between the lightest and darkest parts of the image. Sharpness Adjust the clarity of details in the projected image to make the image clearer and sharper. Color Transform video images from black and white to fully saturated color. Tint Adjust the color balance of red and green in video images. Gamma Select an appropriate gamma value to optimize the image conformance to different input sources. ‡‡ Film: Best for home theater setting. ‡‡ Video: Best for video or TV sources. ‡‡ Graphics: Best for projecting photos from PC input. ‡‡ Standard (2.2): Standard gamma value. ‡‡ 3D: Best for playing 3D videos. ‡‡ Blackboard: Best for projecting on to a blackboard. ‡‡ DICOM SIM.: Best for projecting monochrome medical images, such as X-ray diagram. ‡‡ 1.8 / 2.0 / 2.4: Select a preset gamma value to adjust the image performance. In general, the smaller the value, the brighter the dark areas of the image will become. Color Settings Configure the color settings of the projected image to improve the color performance. ‡‡ Brilliant Color™: Advanced image processing algorithm that enables the usage of more colors on the color wheel, resulting in higher brightness while providing truer and more vibrant colors in the projected image. ‡‡ Color Temperature: Adjust the color temperature of the projected image. The available options are Warm, Standard, and Cool. ‡‡ Color Matching: Change the color of a projected image by adjusting each color component in the image. The adjustable color includes Red, Green, Blue, Cyan, Yellow, Magenta, and White (R / G / B / C / Y / M / W). ±± Color: Select a color for further adjustment. ±± (R / G / B / C / Y / M) Saturation / Hue / Gain: Change the value of hue, saturation, and gain to adjust the red, green, blue, cyan, yellow, or magenta in the projected image. ±± Saturation: Adjust the saturation of the selected color. The value indicates the color shifts from or towards the white in the center of the chromaticity diagram. ±± Hue: Adjust the hue of the selected color. The value reflect the number of degrees of rotation around the chromaticity diagram from the original color. Increasing value indicates counterclockwise rotation, and decreasing value, clockwise rotation. ±± Gain: Adjust the gain of the selected color. Increase the value to brighten the image (add white to a color) or decrease the value to darken the image (add black to a color). 30 English