Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD/Constellation ES Constellation ES (.1) SAS - Page 32
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
 |
View all Seagate Enterprise Capacity 3.5 HDD/Constellation ES manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
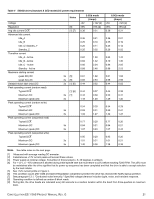
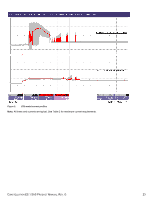
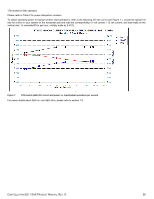
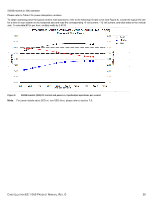
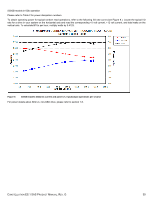
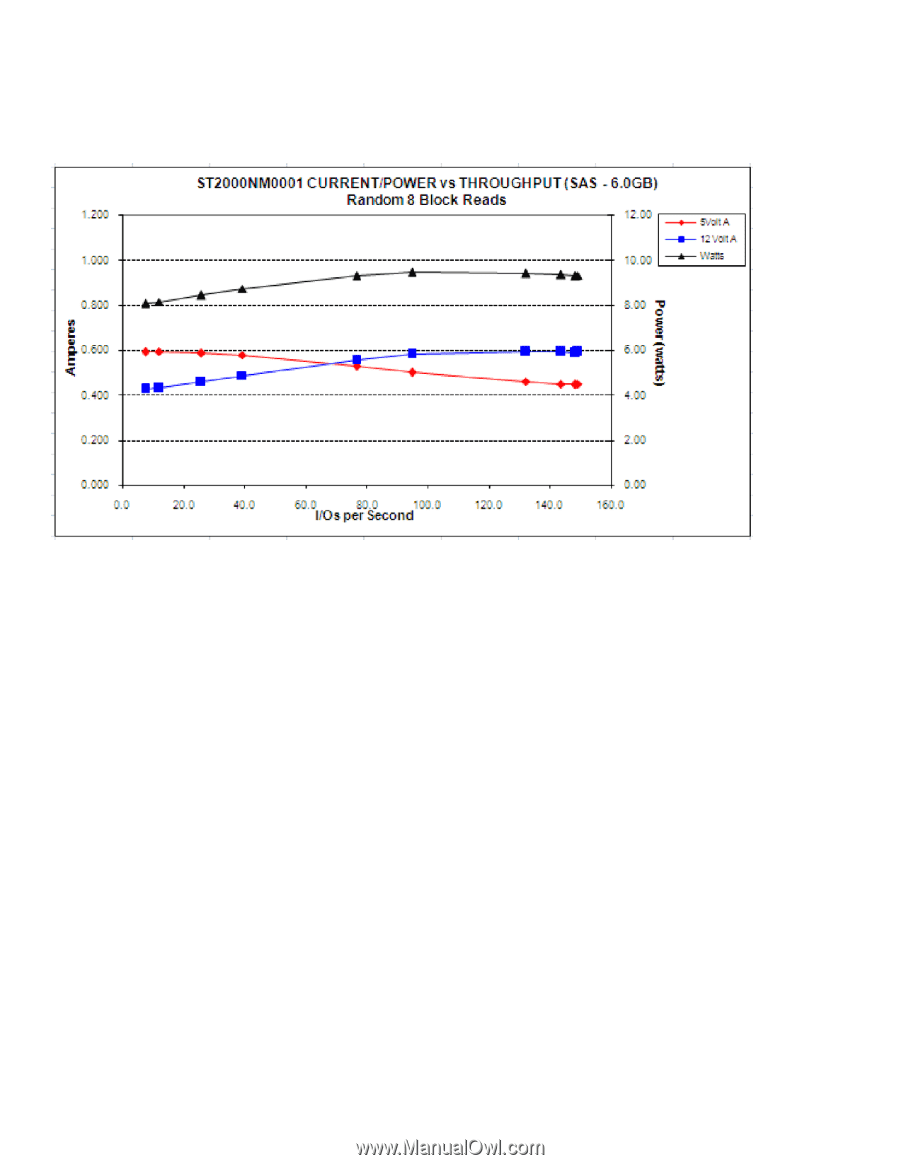
2TB models in 6Gb operation Please refer to Table 2 for power dissipation numbers. To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 5.). Locate the typical I/O rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123. Figure 5. 2TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second For power details about SED vs. non-SED drive, please refer to section 7.8. CONSTELLATION ES.1 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. G 26
C
ONSTELLATION
ES.1 SAS P
RODUCT
M
ANUAL
, R
EV
. G
26
2TB models in 6Gb operation
Please refer to Table 2 for power dissipation numbers.
To obtain operating power for typical random read operations, refer to the following I/O rate curve (see Figure 5.). Locate the typical I/O
rate for a drive in your system on the horizontal axis and read the corresponding +5 volt current, +12 volt current, and total watts on the
vertical axis. To calculate BTUs per hour, multiply watts by 3.4123.
Figure 5.
2TB models (6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second
For power details about SED vs. non-SED drive, please refer to section 7.8.