TP-Link TD-W8961NB TD-W8961NB User Guide - Page 50
Vlan - emulator
 |
View all TP-Link TD-W8961NB manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 50 highlights
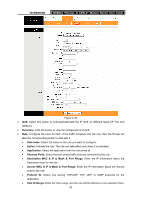
TD-W8961NB 300Mbps Wireless N ADSL2+ Modem Router User Guide • IPP/DS Field: Select the type of the action to assign the priority. When you select IPP/TOS, you can assign the priority via IP information. IP QoS function is intended to deliver guaranteed as well as differentiated Internet services by giving network resource and usage control to the Network operator. • IP Precedence Range: Enter the IP precedence range that the Router takes to differentiate the traffic. • Type of Service: Select the type of service that the Router takes to deal with the traffic. • 802.1p: Select the priority range for the rule. When you select DSCP, you can assign the priority via DHCP (the header of IP group). It maps the IP group into corresponding service class. • DSCP Range: Enter the DSCP range to differentiate the traffic. • 802.1p: Select the priority range for the rule. ¾ Action: Configure the action that the Router takes to deal with the traffic which accord with the rule. • IPP/DS Field: Select the type for the action. • IP Precedence Remarking: Select the number to remark the priority for IP precedence. • Type of Service Remarking: Select the type to remark the service. • DSCP Remarking: Enter the number to remark the DSCP priority. • 802.1p Remarking: Select the type to remark the 802.1p priority. • Queue: Select the priority type for the action. 4.4.5 VLAN Choose "Advanced Setup→VLAN", you can activate the VLAN function in the next screen. Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a group of devices on one or more LANs that are configured so that they can communicate as if they were attached to the same LAN, when in fact they are located on a number of different LAN segments. Because VLANs are based on logical instead of physical connections, it is very flexible for user/host management, bandwidth allocation and resource optimization. There are two types of VLAN as follows: Port-Based VLAN: Each physical switch port is configured with an access list specifying membership in a set of VLANs. ATM VLAN: Using LAN Emulation (LANE) protocol to map Ethernet packets into ATM cells and deliver them to their destination by converting an Ethernet MAC address into an ATM address. 44