TP-Link TL-ER604W TL-ER604W V1 User Guide 1910010844 - Page 104
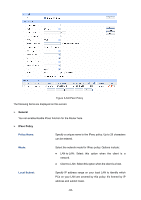
Security Protocol, AH Authentication, ESP Encryption, List of IPsec Proposal
 |
View all TP-Link TL-ER604W manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
Security Protocol: Select the security protocol to be used. Options include: AH: AH (Authentication Header) provides data origin authentication, data integrity and anti-replay services. ESP: ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) provides data encryption in addition to origin authentication, data integrity, and anti-replay services. AH Authentication: Select the algorithm used to verify the integrity of the data for AH authentication. Options include: MD5: MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm) takes a message of arbitrary length and generates a 128-bit message digest. SHA: SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) takes a message less than the 64th power of 2 in bits and generates a 160-bit message digest. ESP Authentication: Select the algorithm used to verify the integrity of the data for ESP authentication. Options include: MD5: MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm) takes a message of arbitrary length and generates a 128-bit message digest. SHA: SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) takes a message less than the 64th power of 2 in bits and generates a 160-bit message digest. ESP Encryption: Select the algorithm used to encrypt the data for ESP encryption. Options include: NONE: Performs no encryption. DES: DES (Data Encryption Standard) encrypts a 64-bit block of plain text with a 56-bit key. The key should be 8 characters. 3DES: Triple DES, encrypts a plain text with 168-bit key. The key should be 24 characters. AES128: Uses the AES algorithm and 128-bit key for encryption. The key should be 16 characters. List of IPsec Proposal In this table, you can view the information of IPsec Proposals and edit them by the action buttons. -99-