Yamaha PSR-1500 Owner's Manual - Page 93
EQ Equalizer, Select a Preset EQ type
 |
View all Yamaha PSR-1500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
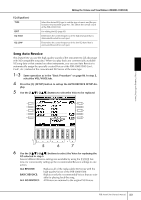
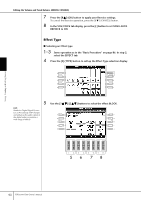
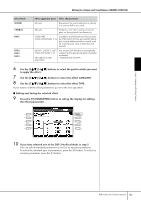
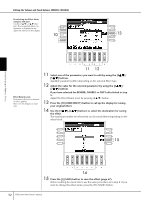
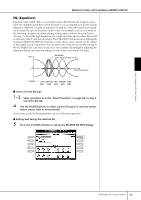
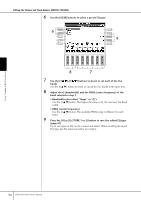
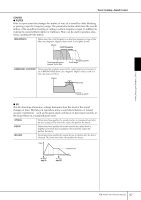
Editing the Volume and Tonal Balance (MIXING CONSOLE) EQ (Equalizer) Equalizer (also called "EQ") is a sound processor that divides the frequency spectrum into multiple bands that can be boosted or cut as required to tailor the overall frequency response. Usually an equalizer is used to correct the sound from speakers to match the special character of the room. For example, you can cut some of the low range frequencies when playing in large spaces where the sound is too "boomy," or boost the high frequencies in rooms and close spaces where the sound is relatively "dead" and free of echoes. The PSR-3000/1500 possesses a high-grade five-band digital EQ. With this function, a final effect-tone control can be added to the output of your instrument. You can select one of the five preset EQ settings in the EQ display. You can even create your own custom EQ settings by adjusting the frequency bands, and save the settings to one of two User Master EQ types. Gain Bandwidth (also called "Shape" or "Q") 0 Freq (Frequency) 5 bands → LOW LOW MID MID HIG MID HIGH EQ1 EQ2 EQ3 EQ4 EQ5 ■ Select a Preset EQ type 1-3 Same operation as in the "Basic Procedure" on page 86. In step 2, select the EQ tab. 4 Use the [A]/[B] buttons to select a preset EQ type to suit your perfor- mance (music style or environment). If you want to edit the EQ parameters, go on to the next operation. ■ Editing and Saving the selected EQ 5 Press the [F] (EDIT) button to call up the MASTER EQ EDIT display. Using, Creating and Editing Voices PSR-3000/1500 Owner's Manual 93