ZyXEL G-1000 User Guide - Page 56
Requirements for Roaming, Roaming Example
 |
View all ZyXEL G-1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 56 highlights
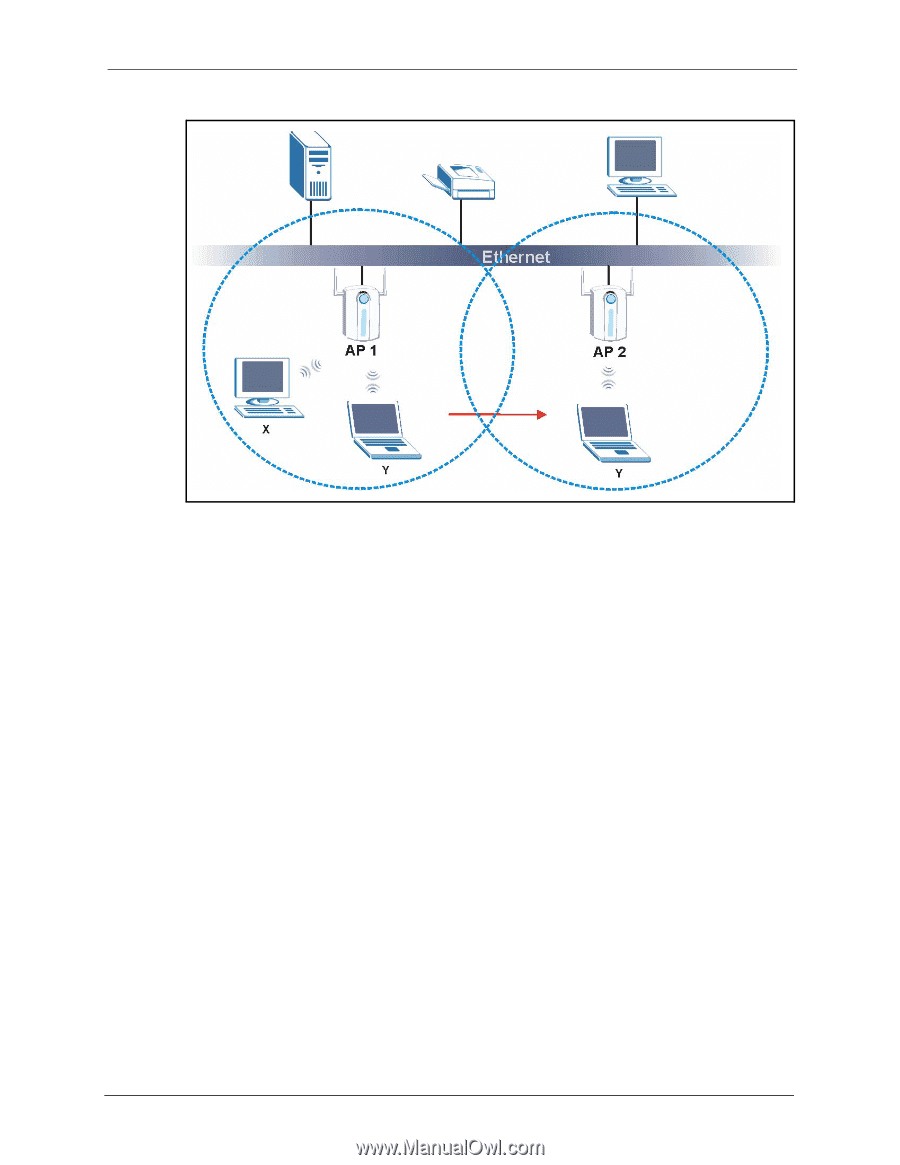
G-1000 User's Guide Figure 15 Roaming Example The steps below describe the roaming process. 1 As wireless station Y moves from the coverage area of access point AP 1 to that of access point 2 AP 2, it scans and uses the signal of access point AP 2. 3 Access point AP 2 acknowledges the presence of wireless station Y and relays this information to access point AP 1 through the wired LAN. 4 Access point AP 1 updates the new position of wireless station. 5 Wireless station Y sends a request to access point AP 2 for reauthentication. 6.4.1 Requirements for Roaming The following requirements must be met in order for wireless stations to roam between the coverage areas. 1 All the access points must be on the same subnet and configured with the same ESSID. 2 If IEEE 802.1x user authentication is enabled and to be done locally on the access point, the new access point must have the user profile for the wireless station. 3 The adjacent access points should use different radio channels when their coverage areas overlap. 4 All access points must use the same port number to relay roaming information. 5 The access points must be connected to the Ethernet and be able to get IP addresses from a DHCP server if using dynamic IP address assignment. 56 Chapter 6 Wireless LAN