2014 Ford F250 Super Duty Super Cab Diesel Supplement Printing 1 - Page 31
2014 Ford F250 Super Duty Super Cab Manual
Page 31 highlights
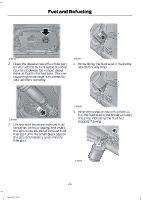
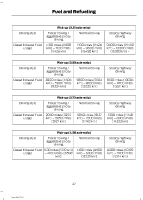
Fuel and Refueling Chassis cab (non-Power Take Off) Driving style Trailer towing / aggressive or city driving 1700 miles (2736 km) - 4700 miles (7564 km) Normal driving Steady highway driving 7800 miles (12553 km) - 9300 miles (14967 km) Diesel Exhaust Fluid usage 4700 miles (7564 km) - 7800 miles (12553 km) Chassis cab (with Power Take Off) PTO usage Diesel Exhaust Fluid usage Cont. PTO usage - Min. PTO usage 0 miles (0 km) - 7800 miles (12553 km) REFUELING Fueling Tips WARNING Do not use starting fluid such as ether or gasoline in the diesel air intake system. Such fluids can cause immediate explosive damage to the engine and possible personal injury. Truck stops have pumps and nozzles designed for larger, heavy-duty trucks. When refueling at truck stops: if the nozzle shuts off repeatedly when refueling, wait 5-10 seconds; then use a slower rate of flow (don't depress the nozzle trigger as far). If air is allowed to enter the fuel system (during fuel filter change or if you run out of fuel) the engine will purge the trapped air as it runs. To purge the air sooner: prior to engine start, prime the system by turning the key to on for 30 seconds then to off. Repeat this several times. The engine may run rough and produce white smoke while air is in the system. This is normal. An engine that suddenly becomes noisy or operates poorly after a fuel fill could be using substandard fuel (for example, high water content, low cetane rating or gasoline in the fuel). You should purchase diesel fuel from a reputable station that sells a large amount of diesel fuel. Use only clean, approved containers that will prevent the entry of dirt or water whenever you store diesel fuel. Diesel fuel must not be stored in a galvanized container. The fuel will dissolve the zinc in the galvanized container. The zinc will then remain in the fuel. If you run the contaminated fuel through the engine, the zinc will deposit in the fuel injectors causing expensive-to-repair damage. 28 Super Duty (TFA)