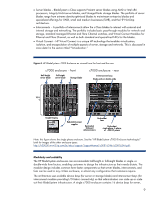
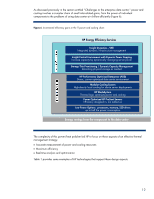
HP BL260c Delivering an Adaptive Infrastructure with the HP BladeSystem c-Clas - Page 13
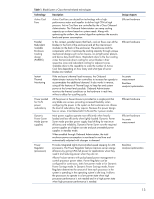
Power Savings mode. In Dynamic Power Savings mode, Power, Table 1., Technology, Description
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
Table 1. BladeSystem c-Class thermal-related technologies Technology Description Active Cool Fans Active Cool fans use ducted fan technology with a highperformance motor and impeller to deliver high CFM at high pressure. Active Cool fans are controlled by the c-Class Onboard Administrator. The Onboard Administrator can ramp cooling capacity up or down based on system needs. Along with optimizing the airflow, the control algorithm optimizes the acoustic levels and power consumption. Parallel Redundant Scalable Enclosure Cooling design (PARSEC) In this context, parallel means that fresh, cool air flows over all the blades (in the front of the enclosure) and all the interconnect modules (in the back of the enclosure). The enclosure and the components within it optimize the cooling capacity through unique mechanical designs such as fan louvers, an airtight center plenum, and device bay shutoff doors. Redundant refers to the four cooling zones that provide direct cooling for server blades in their respective zone and redundant cooling for adjacent zones. Scalable refers to the capability to scale the number of Active Cool fans depending on how many and what type of server blades are installed. Instant Thermal Monitoring If the enclosure's thermal load increases, the Onboard Administrator instructs the fan controllers to increase fan speeds to accommodate the additional demand. It also works in reverse, using all the features of Thermal Logic to keep fan and system power at the lowest level possible. Onboard Administrator monitors the thermal conditions on the hardware in real time, without a delay for a polling cycle. Power pooled for N+N power redundancy All the power in the enclosure is provided as a single pool that any blade can access, providing increased flexibility when configuring the power in the system so that customers can choose the level of redundancy they require. Because this power design has no zones, it facilitates both N+N and N+1 power modes. Dynamic Power Saver Mode (power supplies) Most power supplies operate more efficiently when heavily loaded and less efficiently when lightly loaded. Dynamic Power Saver mode provides power supply load shifting for maximum efficiency and reliability. Dynamic Power Saver runs the required power supplies at a higher use rate and puts unneeded power supplies in standby mode. When enabled through Onboard Administrator, the total enclosure power consumption is monitored in real time and automatically adjusted with changes in demand. Power Regulator (processors) Provides Integrated Lights-Out-controlled speed stepping for x86 processors. The Power Regulator feature improves server energy efficiency by giving CPUs full power for applications when they need it and reducing power when they do not. Allows ProLiant servers with policy-based power management to control processor power states. Power Regulator can be configured for continuous, static low power mode or for Dynamic Power Savings mode. In Dynamic Power Savings mode, Power Regulator determines the amount of time each processor in the system is spending in the operating system's idle loop. It allows the processors to operate in a low power state when high processor performance is not needed and in a high power state when high processor performance is needed. Design Aspects Efficient hardware Efficient hardware Accurate measurement Real-time analysis/optimization Efficient hardware Efficient hardware Accurate measurement Real-time analysis/optimization 13