HP BL260c Delivering an Adaptive Infrastructure with the HP BladeSystem c-Clas - Page 16
Flex-10 technology, Managing virtual and physical resources
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
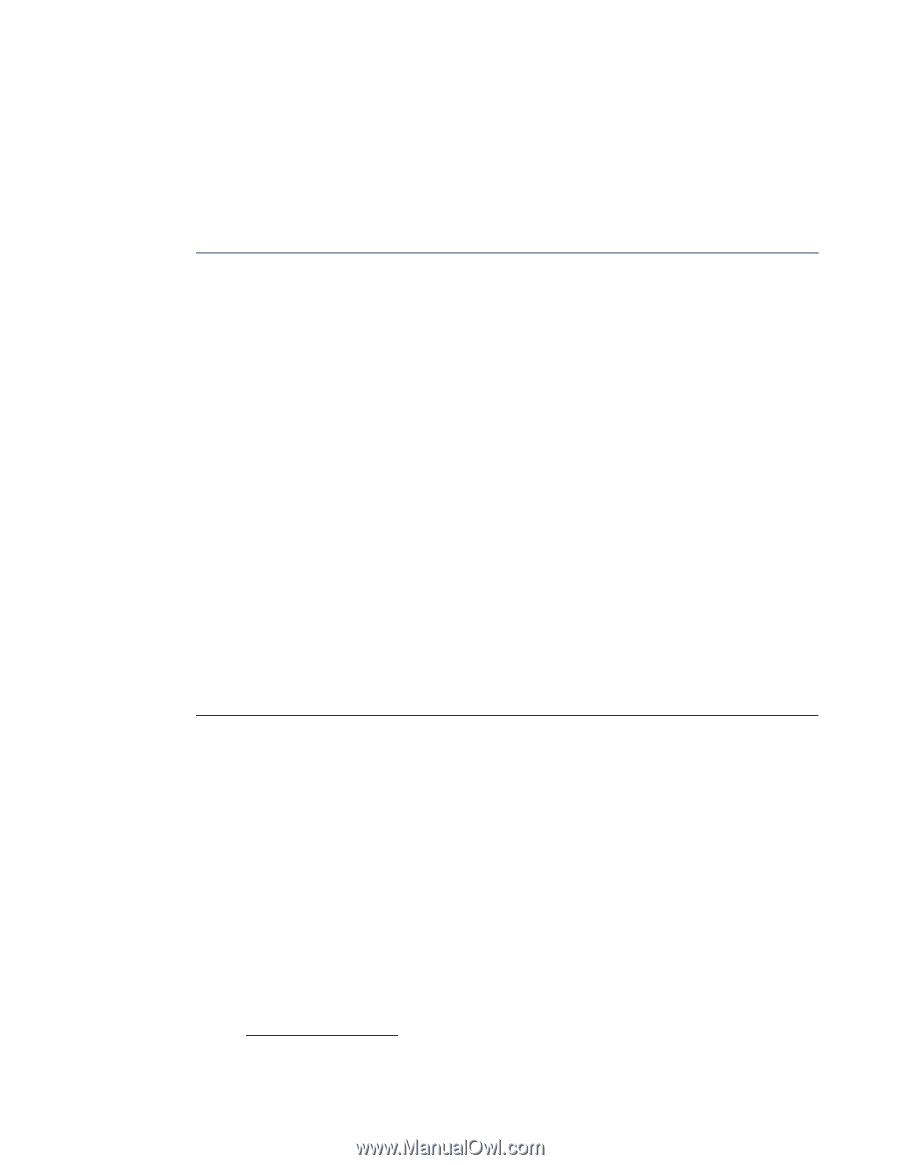
default World Wide Names (WWNs) for all host bus adapters (HBAs), the Virtual Connect Manager creates bay-specific server profiles, assigns unique MAC addresses and WWNs to these profiles, and administers them locally. Virtual Connect securely manages the MACs and WWNs by accessing the physical NICs and HBAs through the enclosure's Onboard Administrator and the iLO interfaces on the individual server blades. It allows these profiles to be modified and migrated without disturbing the data center network administrator's view of the servers - to the external network, a c-Class BladeSystem appears to be a collection of servers with static MAC and WWN assignments. For more information about Virtual Connect technology, see the technology brief titled "HP Virtual Connect technology implementation for the HP BladeSystem c-Class": http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00814156/c00814156.pdf. Flex-10 technology The most recent technology introduced as part of Virtual Connect is Flex-10 technology, which lets customers partition a 10 Gb Ethernet connection and to regulate the size and data speed of each partition. Administrators can configure a single 10 Gb network port to represent up to four physical NIC devices, or FlexNICs, for a total bandwidth of 10 Gbps. Each dual-port Flex-10 device supports up to eight FlexNICs, four on each physical port, and each Flex-10 Interconnect Module can support up to 64 FlexNICs. These FlexNICs appear to the operating system (OS) as discrete NICs, each with its own driver. While the FlexNICs share the same physical port, traffic flow for each one is isolated with its own MAC address and virtual local area network (VLAN) tags between the FlexNIC and VC Flex-10 interconnect module. Significant infrastructure savings are also realized since additional server NIC mezzanine cards and associated interconnect modules may not be needed, especially in a virtual machine environment where multiple NICS are needed. The ability to fine-tune each network connection dynamically from 100 Mb to 10 Gb in 100 Mb increments helps eliminate bottlenecks. Because it has native 10 Gb, administrators can perform ultrafast virtual server moves and recoveries within a BladeSystem enclosure and between blades; administrators can also precisely control the virtual server network traffic across backup, virtual machine migration, management console, and production application channels. For more information about Flex-10 technology, see the technology brief "HP Flex-10 technology" at http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01608922/c01608922.pdf. Managing virtual and physical resources The Virtual Connect solution includes the optional Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager (VCEM) software that provides a central console to manage multiple Virtual Connect domains and efficiently manage LAN and SAN connections across the domain. VCEM allows group-based configuration management. It lets administrators assign, move, and perform failover of server-to-network connections and their workloads for up to 150 BladeSystem enclosures (2400 servers). VCEM provides a central pool of Virtual Connect LAN and SAN addresses, allowing customers to physically or logically link multiple enclosures, and pre-provision the server-to-network connections in bulk. Virtual Connect also enables the physical layer abstraction of servers in a resource pool, so that administrators can use the concept of a logical server to describe either a virtual machine (virtual machine-logical server, VM-LS) or a physical machine (physical machine-logical servers, PM-LS). HP has developed tools such as HP Insight Dynamics - VSE and HP Insight Orchestration software to manage both virtual and physical machines in a resource pool using the same methods (described in more detail in the following sections). For more information about Virtual Connect Enterprise Manager refer to www.hp.com/go/vcem. 16