HP BL260c Delivering an Adaptive Infrastructure with the HP BladeSystem c-Clas - Page 8
BladeSystem c-Class and Adaptive Infrastructure, Standardized IT infrastructure
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
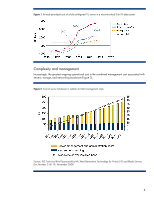
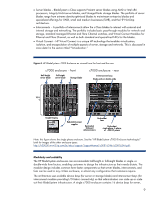
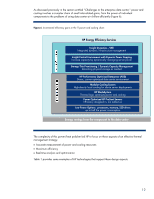
moves the architecture away from infrastructure silos or "IT islands" to pools of IT resources. These pools allow administrators to realign IT structures to meet specific business goals. An Adaptive Infrastructure environment is based on standard building blocks, automated using modular software, and delivered through comprehensive services. For more details about the HP Adaptive Infrastructure, see www.hp.com/go/ai. Figure 3 represents the key aspects of the HP Adaptive Infrastructure architecture. Figure 3. Key enablers for HP Adaptive Infrastructure vision High-cost IT islands Low-cost pooled IT assets Scalable IT Systems Power & Cooling •Modularity •Scalability •Resilience •Availability •Energy efficient Management Security Virtualization Automation •Discovery & State information •Virtual & Physical •Isolation & encapsulation •Analyze & Optimize •Virtual & Physical •Isolation & encapsulation •Analyze & Optimize •Analyze & Optimize BladeSystem c-Class and Adaptive Infrastructure The following sections discuss some of the ways that the BladeSystem meets the goals of the Adaptive infrastructure. Standardized IT infrastructure The core technologies of the Adaptive Infrastructure are based on cost-efficient, open industry standards. Like all HP ProLiant servers, the BladeSystem c-Class architecture is based on innovation within a framework of industry standards. Furthermore, BladeSystem c-Class architecture was designed as a general-purpose, flexible infrastructure to be extremely modular and scalable. The HP BladeSystem c-Class consolidates power, cooling, connectivity, redundancy, and security into a modular, self-tuning system with intelligence built in. The following sections outline the general architecture of the BladeSystem c-class and give examples of its modularity, scalability, resiliency, and availability. These are only examples and not an exhaustive list. For more information about current products, see www.hp.com/go/bladesystem. Understanding the Blade c-Class architecture The BladeSystem consists of several core components (Figure 4): • The enclosure - An HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure accommodates server blades, storage blades, I/O option blades, interconnect modules (switches and pass-thru modules), a NonStop passive signal midplane, a passive power backplane, shared power and cooling infrastructure (power supplies and fans), and Onboard Administrator modules for local management. 8