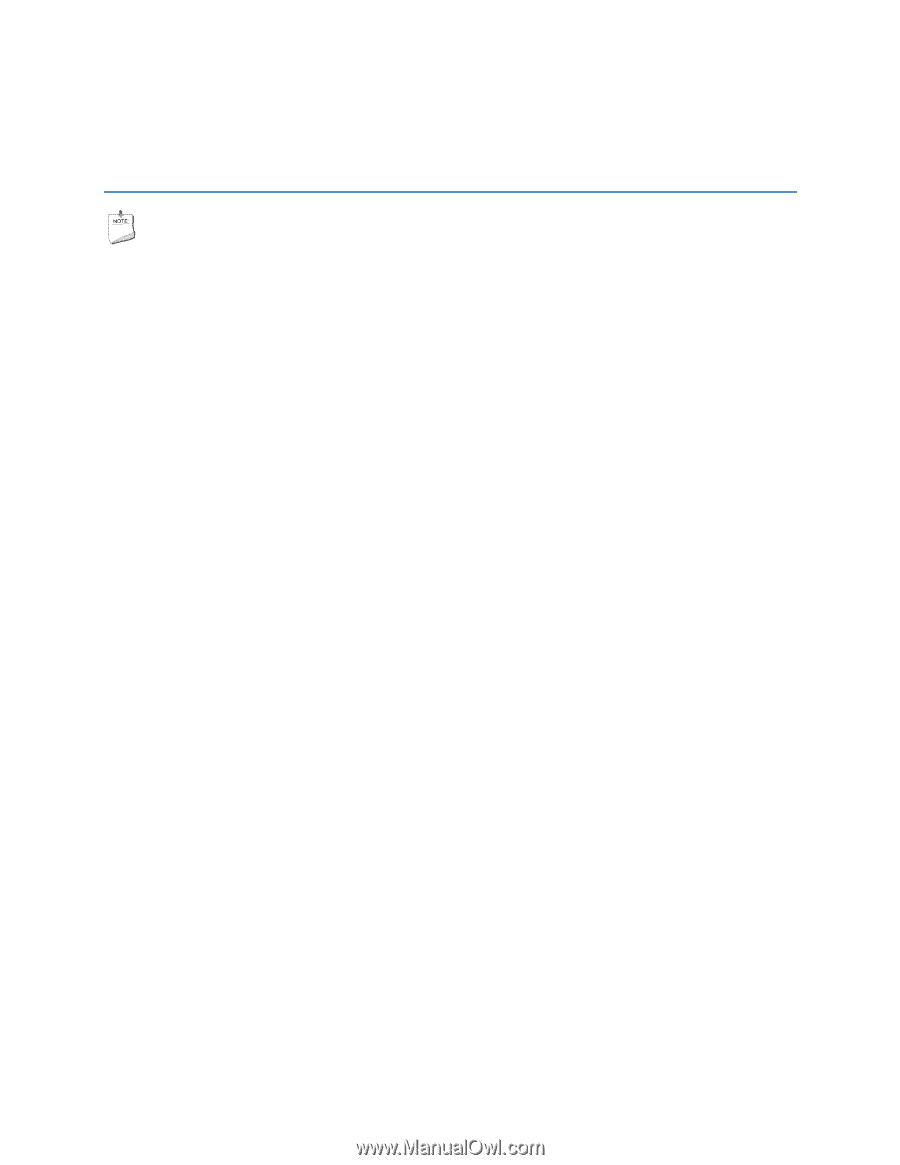Intel DG965WH Product Guide - Page 69
Intel® Quick Resume Technology Driver (Intel® QRTD), Overview - audio driver windows 7
 |
View all Intel DG965WH manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 69 highlights
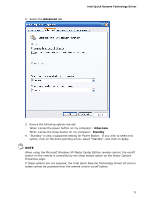
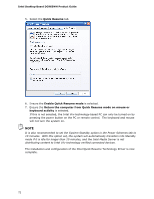
5 Intel® Quick Resume Technology Driver (Intel® QRTD) NOTE This feature is not supported by Microsoft Windows Vista. Skip this chapter if you are using that operating system. Similar functionality is implemented by the Microsoft Windows Vista Away mode. Overview The Intel® Quick Resume Technology Driver manages the on and off functions for an Intel® Viiv™ technology-based PC and has the following features: • Instantly turns the Intel Viiv technology-based PC when the user presses the power button on the PC or the remote control. • Instantly turns the Intel Viiv technology-based PC on when the user moves the mouse, presses a key on the keyboard, or presses the on/off button on the remote control or computer. • In the Intel Quick Resume Technology Driver off state, the: ― Video output stops sending data to the display and audio is muted (Quick Resume mode) if the Intel Viiv Media Server is distributing content to Intel Viiv verified connected devices. ― System goes into Standby (S3 state) or Hibernate (S4 state) when the system is idle and the Intel Viiv Media Server is not distributing content to Intel Viiv technology verified connected devices. Intel Quick Resume Technology Power Modes The following is a brief description of the system's behavior in each Power Mode option: • In Quick Resume mode, video output is turned off and audio is muted. However, power continues to vital components in the system (processor, fans, etc) and tasks that do not require user input can continue in the background. • In Standby mode, power to most components except memory is turned off. Standby will resume the system quicker than Hibernate, but consumes more power. • In Hibernate mode, all contents of the system memory is saved to the hard drive and power to all components is turned off. Resume time from Hibernate is longer than from Standby. 69