Ryobi BT3KIT English Manual - Page 18
Blade Information, Choice Of Blade And Speed, Using Variable Speed
 |
View all Ryobi BT3KIT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
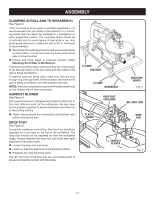
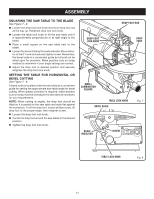
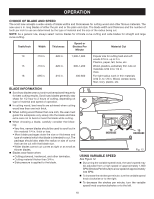
OPERATION CHOICE OF BLADE AND SPEED The scroll saw accepts a wide variety of blade widths and thicknesses for cutting wood and other fibrous materials. The saw uses 5 in. long blades of either the pin end or the plain end style. The blade width and thickness and the number of teeth per inch to use are determined by the type of material and the size of the radius being cut. NOTE: As a general rule, always select narrow blades for intricate curve cutting and wide blades for straight and large curve cutting. Teeth/Inch Width Thickness Speed or Strokes Per Minute Material Cut 10 .110 in. .020 in. 1,200-1,600 Popular size for cutting hard and soft (2.8 mm) (0.5 mm) woods 3/16 in. up to 2 in. Plastics, paper, felt, bone, etc. 15 .110 in. .020 in. 600-1,200 Wood, plastics, extremely thin cuts on (2.8 mm) (0.5 mm) materials 3/32 in.to 1/2 in. thick. 18 .095 in. .010 in. 400-600 For tight radius work in thin materials (2.4 mm) (0.3 mm) 3/32 in. to 1/8 in. Wood, veneer, bone, fiber, ivory, plastic, etc. BLADE INFORMATION Scroll saw blades wear out and must be replaced frequently for best cutting results. Scroll saw blades generally stay sharp for 1/2 hour to 2 hours of cutting, depending on type of material and speed of operation. In cutting wood, best results are achieved when cutting wood less than one inch thick. When cutting wood thicker than one inch, the user must guide the workpiece very slowly into the blade and take extra care not to bend or twist the blade while cutting. 0 When choosing a blade, carefully consider the following: • Very fine, narrow blades should be used to scroll cut in thin material 1/4 in. thick or less. • Most blade packages state the size or thickness and type of material which that blade is intended to cut. The package should also state the radius or size of curve that can be cut with that blade size. • Wider blades cannot cut curves as tight or as small as thinner blades. Blades wear faster when: • Cutting plywood, hardwood, and other laminates. • Cutting material thicker than 3/4 in. • Side pressure is applied to the blade. ON OF F 15 30 45 TO INCREASE TO DECREASE Fig. 12 USING VARIABLE SPEED See Figure 12. By turning the variable speed knob, the saw's speed may be adjusted from a high speed of approximately 1,600 SPM (Strokes Per Minute) to a low speed of approximately 400 SPM. To increase the strokes per minute, turn the variable speed knob clockwise or to the right. To decrease the strokes per minute, turn the variable speed knob counterclockwise or to the left. 18