ATI Xpert 98 User Manual - Page 111
Partition and Format the Logical Drive, Migration
 |
UPC - 727419404952
View all ATI Xpert 98 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 111 highlights
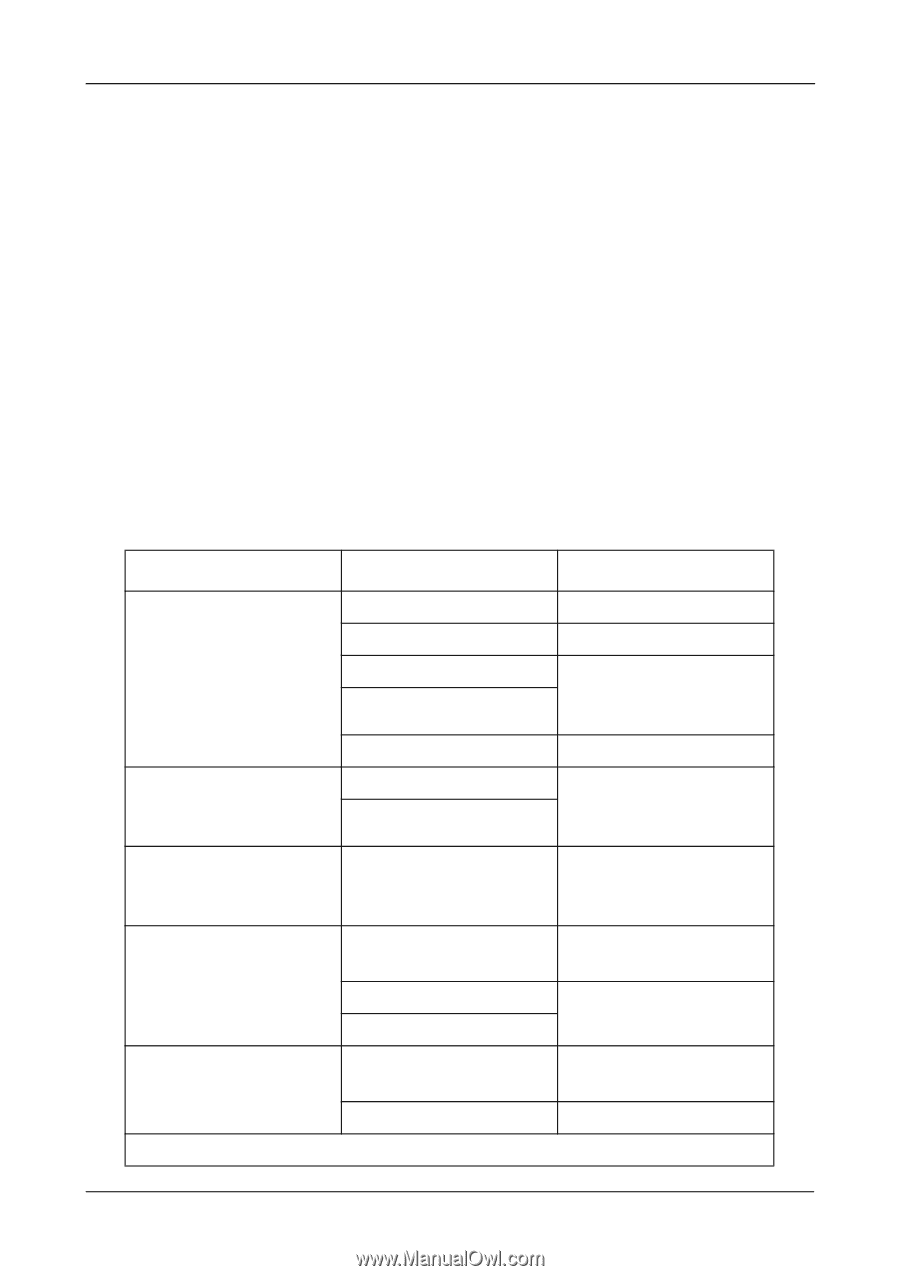
Chapter 6: Technology Background Partition and Format the Logical Drive Like any other type of fixed disk media in your system, a RAID logical drive must also be partitioned and formatted before use. Use the same method of partitioning and formatting on a logical drive as you would any other fixed disk. See "Appendix B: Partition and Format" on page 111. Migration Migration is the process of: • Changing the RAID level of an existing logical drive • Adding more physical drives to a logical drive while keeping the same RAID level See "Migrating a Logical Drive" on page 71 for instructions. You can change the RAID level of a logical drive with certain combinations of RAID level and number of physical drives, as described in the table below. From To Result RAID Ready: 1 drive RAID 0: 2 to 6 drives RAID 1: 2 drives Increases capacity Adds redundancy RAID 5: 3 to 6 drives* RAID 10: 4 drives Increases performance and capacity, adds redundancy RAID 0: 2 drives RAID 0: 3 drives JBOD: 2 to 6 drives RAID 5: 3 to 6 drives* RAID 10: 4 drives RAID 5: 4 drives* Increases capacity Increases performance and capacity, adds redundancy Increases performance and capacity, adds redundancy RAID 1: 2 drives RAID 10: 4 drives RAID 0: 2 drives RAID 5: 3 to 6 drives* RAID 10: 4 drives RAID 0: 4 drives Increases capacity, loses redundancy Increases performance and capacity Increases capacity, loses redundancy RAID 5: 4 to 6 drives* Increases capacity * Only with AMD Chipset SATA Controllers that support RAID 5. 105