Asus SP97 User Manual - Page 25
Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards
 |
View all Asus SP97 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
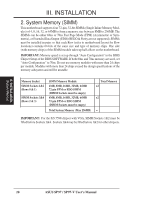
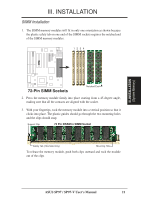
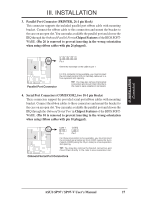
III. INSTALLATION (DMA Channels) III. INSTALLATION Both ISA and PCI expansion cards may require to use IRQs. System IRQs are available to cards installed in the ISA expansion bus first, then any remaining IRQs are available to PCI cards. Currently, there are two types of ISA cards. The original ISA expansion card design, now referred to as legacy ISA cards, requires that you configure the card's jumpers manually and then install it in any available slot on the ISA bus. You may use Microsoft Diagnostics (MSD.EXE) utility located in the Windows directory to see a map of your used and free IRQs. If you use Windows 95, the Resources tab under Device Manager displays the resource settings being used by a particular device (to access, double-click the System icon under the Control Panel program). Ensure that no two devices share the same IRQs or your computer will experience problems when those two devices are in use at the same time. To simplify this process, the motherboard complies with the Plug and Play (PnP) specification, which was developed to allow automatic system configuration whenever a PnP-compliant card is added to the system. For PnP cards, IRQs are assigned automatically from those available. If the system has both legacy and PnP ISA cards installed, IRQs are assigned to PnP cards from those not used by legacy cards. The PCI and PNP configuration section of the BIOS setup utility can be used to assign which IRQs are being used by legacy cards. For older legacy cards that do not work with the BIOS, you may contact your vendor for an ISA Configuration Utility. An IRQ number is automatically assigned to PCI expansion cards after those used by legacy and PnP ISA cards. In the PCI bus design, the BIOS automatically assigns an IRQ to a PCI slot that contains a card requiring an IRQ. Leave all PCI INT assignments on "A." PCI slot 1 automatically assigns an INT letter starting from AB-C-D, PCI slot 2 assigns B-C-D-A, slot 3 assigns C-D-A-B, and slot 4 assigns DA-B-C in these orders, therefore manual offsetting is not necessary. Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards Some ISA cards, both legacy and PnP, may also need to use a DMA (Direct Memory Access) channel. DMA assignments for this motherboard are handled the same way as the IRQ assignment process described earlier. You can select a DMA channel in the PCI and PnP configuration section of the BIOS Setup utility. IMPORTANT: To avoid conflicts, reserve the necessary IRQs and DMAs for legacy ISA cards (under PNP AND PCI SETUP of the BIOS SOFTWARE, choose Yes in IRQ xx Used By ISA and DMA x Used By ISA for those IRQs and DMAs you want to reserve). ASUS SP97 / SP97-V User's Manual 25