Celestron CPC Deluxe 800 HD Computerized Telescope CPC Deluxe HD Manual - Page 36
Appendix B - Glossary Of Terms
 |
View all Celestron CPC Deluxe 800 HD Computerized Telescope manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
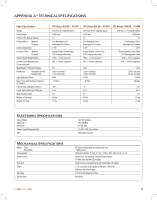
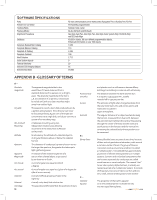
Software Specifications Ports Period Error Correction Tracking Rates Tracking Modes Alignment Procedures Database Complete Revised NGC Catalog Complete Messier Catalog Complete IC Catalog Complete Caldwell Abell Galaxies Solar System objects Famous Asterisms Selected CCD Imaging Objects Selected SAO Stars RS-232 communication port on hand control, Autoguider Port, 2 Auxiliary Port, PC Port Permanently programmable Sidereal, Solar, Lunar Alt-Az, EQ North and EQ South Sky Align, Auto Two-Star Align, Two-Star Align, Solar System Align, EQ North Align and EQ South Align 40,000+ objects, 99 user defined programmable objects. Enhanced information on over 200 objects 7,840 110 5,386 109 2,712 9 20 25 29,500 APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY OF TERMS A - Absolute magnitude Airy disk Alt-Azimuth Mounting Altitude Aperture Apparent Magnitude Arc minute Arc second Asterism Asteroid Astrology 34 The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were observed from a standard distance of 10 parsecs, or 32.6 light- years. The absolute magnitude of the Sun is 4.8. at a distance of 10 parsecs, it would just be visible on Earth on a clear moonless night away from surface light. The apparent size of a star's disk produced even by a perfect optical system. Since the star can never be focused perfectly, 84 per cent of the light will concentrate into a single disk, and 16 per cent into a system of surrounding rings. A telescope mounting using two independent rotation axes allowing movement of the instrument in Altitude and Azimuth. In astronomy, the altitude of a celestial object is its Angular Distance above or below the celestial horizon. The diameter of a telescope's primary lens or mirror; the larger the aperture, the greater the telescope's light-gathering power. A measure of the relative brightness of a star or other celestial object as perceived by an observer on Earth. A unit of angular size equal to 1/60 of a degree. A unit of angular size equal to 1/3,600 of a degree (or 1/60 of an arc minute). A small unofficial grouping of stars in the night sky. A small, rocky body that orbits a star. The pseudoscientific belief that the positions of stars Astronomical unit (AU) Aurora Azimuth B - Binary Stars C - Celestial Equator and planets exert an influence on human affairs; astrology has nothing in common with astronomy. The distance between the Earth and the Sun. It is equal to 149,597,900 km., usually rounded off to 150,000,000 km. The emission of light when charged particles from the solar wind slams into and excites atoms and molecules in a planet's upper atmosphere. The angular distance of an object eastwards along the horizon, measured from due north, between the astronomical meridian (the vertical line passing through the center of the sky and the north and south points on the horizon) and the vertical line containing the celestial body whose position is to be measured. Binary (Double) stars are pairs of stars that, because of their mutual gravitational attraction, orbit around a common center of mass. If a group of three or more stars revolve around one another, it is called a multiple system. It is believed that approximately 50 percent of all stars belong to binary or multiple systems. Systems with individual components that can be seen separately by a telescope are called visual binaries or visual multiples. The nearest "star" to our solar system, Alpha Centauri, is actually our nearest example of a multiple star system. It consists of three stars, two very similar to our Sun and one dim, small, red star orbiting around one another. The projection of the Earth's equator on to the celestial sphere. It divides the sky into two equal hemispheres. >> www.celestron.com