Cisco CISCO876-SEC-I-K9 Configuration Guide - Page 59
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
 |
UPC - 882658021800
View all Cisco CISCO876-SEC-I-K9 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 59 highlights
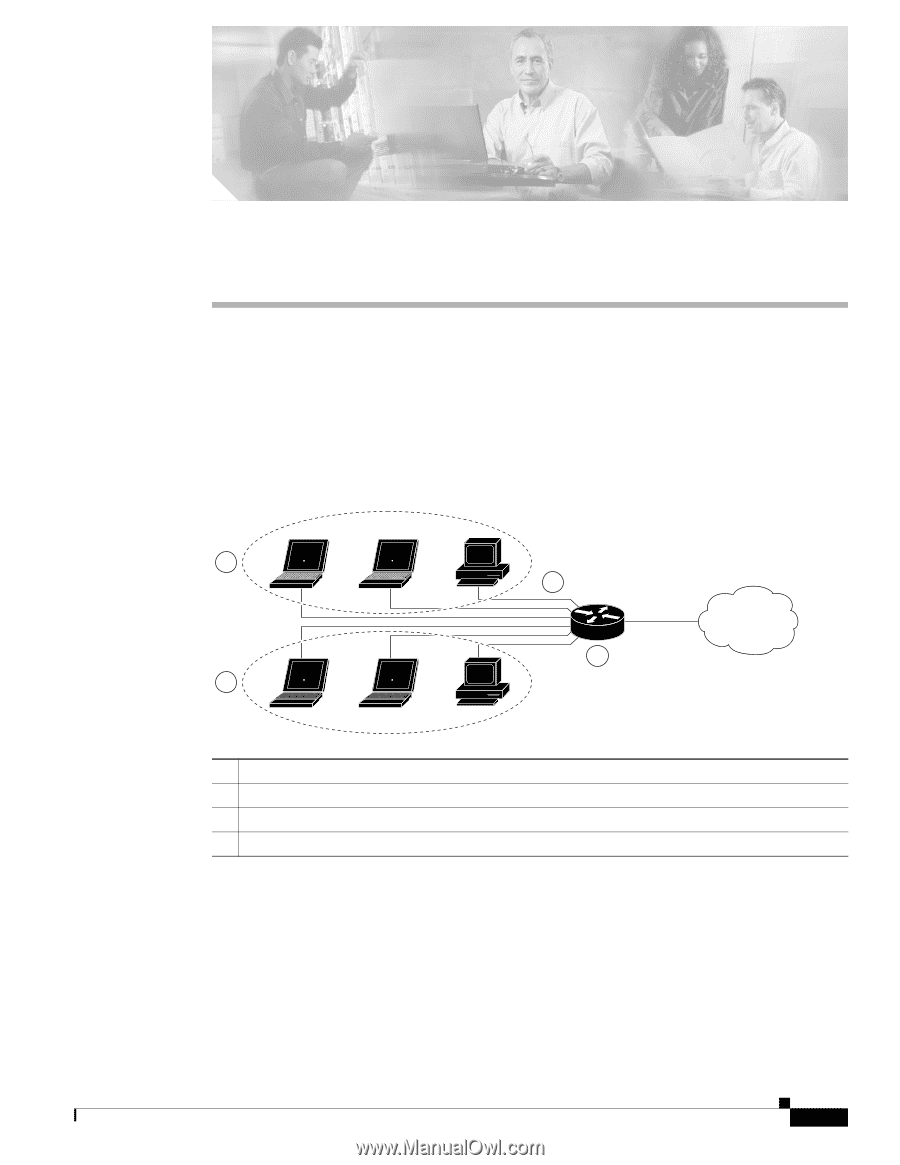
CH A P T E R 5 Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs The Cisco 870 series routers support clients on both physical LANs and virtual LANs (VLANs). The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable automatic assignment of IP configurations for nodes on these networks. Figure 5-1 shows a typical deployment scenario with two physical LANs connected by the router and two VLANs. Figure 5-1 Physical and Virtual LANs with DHCP Configured on the Cisco Router 3 1 2 4 92339 1 Fast Ethernet LAN (with multiple networked devices) 2 Router and DHCP server-Cisco 870 series access router-connected to the Internet 3 VLAN 1 4 VLAN 2 DHCP DHCP, which is described in RFC 2131, uses a client/server model for address allocation. As an administrator, you can configure your Cisco 800 series router to act as a DHCP server, providing IP address assignment and other TCP/IP-oriented configuration information to your workstations. DHCP frees you from having to manually assign an IP address to each client. OL-5332-01 Cisco 850 Series and Cisco 870 Series Access Routers Software Configuration Guide 5-1