D-Link DGS-3620-28SC-EI Hardware Installation Guide - Page 37
Password Protection, Assigning IP Addresses, SNMP Settings
 |
View all D-Link DGS-3620-28SC-EI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
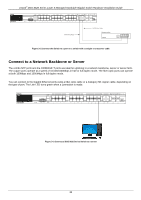
xStack® DGS-3620 Series Layer 3 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch Hardware Installation Guide Password Protection The DGS-3620 Series Switches do not have a default user name and password. One of the first tasks when settings up the Switch is to create user accounts. Logging in using a predefined administrator-level user name will give the user privileged access to the Switch's management software. After the initial login, define new passwords for both default user names to prevent unauthorized access to the Switch, and record the passwords for future reference. To create an administrator-level account for the Switch, do the following: 1. At the CLI login prompt, enter create account admin followed by the and press the Enter key. 2. The Switch will then prompt the user to provide a password. Type the administrator and press the Enter key. 3. Once entered, the Switch will again ask the user to insert the same password again to verify it. Type the same password and press the Enter key. 4. A new administrative account is created once the "Success" prompt appears. Note: Passwords are case sensitive. User names and passwords can be up to 15 characters in length. Assigning IP Addresses The Switch's default IP address is 10.90.90.90. A user may change this default IP address to meet their criteria. IP addresses are primarily used to communicate with an SNMP manager, or other TCP/IP appications like BOOTP or TFTP. The Switch is also assigned a unique MAC address by the factory. This MAC address cannot be changed, and can be found by entering the command "show switch" into the command line interface. The Switch's MAC address also appears in the Device Information and System Information windows of the Webbased management interface. The IP address for the Switch must be set before using the Web-based manager. The Switch IP address can be automatically set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, in which case the actual address assigned to the Switch must be known. SNMP Settings Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure system features for proper operation, monitor performance and detect potential problems in the Switch, switch group or network. Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the device. A defined set of variables (managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage the device. These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard presentation of the information controlled by the on-board SNMP agent. SNMP defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the network. The Switch supports SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. The administrator may specify which SNMP version to use to monitor and control the Switch. The three SNMP versions vary in the level of security provided between the management station and the network device. 37