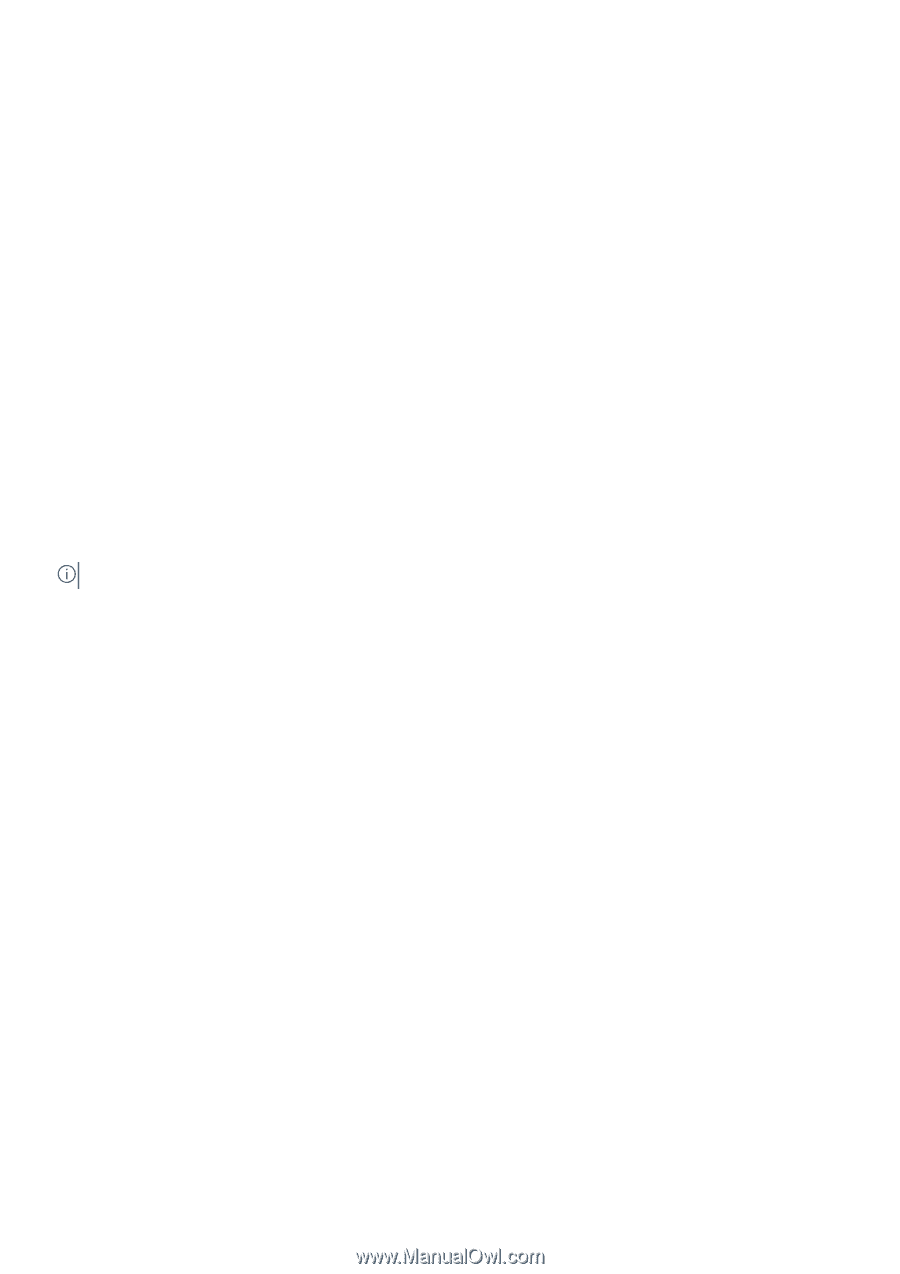Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS EqualLogic Auto-Snapshot Manager/Microsoft Edition Ve - Page 83
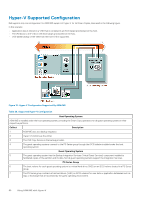
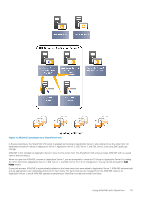
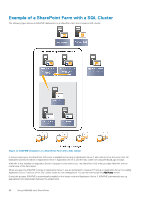
Cluster Shared Volumes, CSVs in a Windows Server 2012 Environment
 |
View all Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 83 highlights
If the snapshot reserve space is low, a warning is displayed. 2. Click Next if the snapshot reserve space is low. Otherwise, go step 3. The Select Virtual Machines dialog box opens. 3. Select one or more virtual machines and click Next. The Select Mount Location dialog box opens. 4. Perform one of the following steps: • Click the Next button to select the path in the Mount folder root field. • Click the Browse button next to the Mount folder root field to navigate to a different path. 5. Select the mount folder or a drive letter in the Mount To field. Click Next. 6. Type a name for the new virtual machine, or accept the default name provided. Specify the memory (in MB) or accept the default. Click Restore. ASM/ME lists the sequence of restore operations it performs. 7. Click Close when the operations are complete. The new VM displays under the Applications node in the tree panel. Cluster Shared Volumes Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) are a feature of Windows failover clustering for use with Hyper-V. CSVs greatly simplify a typical failover cluster configuration because each cluster node can access CSVs to manage files and perform read and write operations on them. Multiple nodes can host or run VMs residing on the same CSV. In a CSV configuration, a coordination node performs backups and restores of the VMs stored on the CSV. The coordination node can easily and frequently be changed from one node to another. The coordination node becomes the temporary owner of the CSV and the VMs that reside on it. The remaining nodes in the cluster can still access the CSV. NOTE: Moving the coordination node is not necessary to perform a backup of a CSV in Windows Server 2012 or later. While a backup operation is in progress, I/O from all the other cluster nodes is temporarily redirected through the coordination node. The redirected I/O state can be viewed from the Windows Failover Cluster Manager. CSVs in a Windows Server 2012 Environment On Windows Server 2012 or later, you can manage CSVs from any node, regardless of which one owns it. All nodes display the CSV with a blue icon. Creating Smart Copies in a CSV-Enabled Cluster Smart Copy operations in CSV-enabled clusters provide the following benefits: • Significant performance improvements and ease of use-Only one schedule is needed to capture every VM residing on a CSV. You do not need to create a single schedule for each VM on the CSV, which could slow down performance. • Conservation of storage space-Because you only need one schedule to capture every VM residing on a CSV, less snapshot reserve space is consumed. • File System Consistency-Windows Server 2012 or later Smart Copies are application-consistent because the operation uses the Hyper-V VSS writer. The Smart Copies contain all virtual machines that reside on the CSV, including those that are running on other cluster nodes. When CSV is enabled in a cluster, you can create: • Smart Copies of VMs residing on CSVs-The supported Smart Copy types depend on Windows Server 2012 or later, with snapshots and clones supported. • Smart Copies of CSVs-A single Smart Copy of a CSV copy every VM that resides on the CSV. • CSV collections and then create Smart Copies of those collections. • Schedules for the preceding Smart Copy operations. Using ASM/ME with Hyper-V 83