Dell PowerEdge M1000e Technical Guide - Page 31
Power Supply Specifications, Heat Dissipation
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge M1000e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
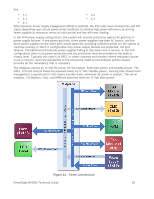
Dell Figure 24. PMBus Communication Channels All VMware® products include consuming the "current power consumption" and "current power cap/limit" retrieval via Dell specific IPMI commands using iDRAC. They are using this to report the total power consumed by the server and also using this as part of their calculations to determine/approximate the VM-level power. The Power Management chapter in the Dell Chassis Management Controller (CMC) User Guide provides extensive information on power management. 5.2 Power Supply Specifications Each power supply offers: • 91%+ AC/DC Conversion Efficiency • Dynamic Power Supply Engagement which automatically engages the minimum number of supplies required to power a given configuration, maximizing power supply efficiency The following are the PowerEdge M-1000e chassis power supply capabilities: • 2360 watts maximum for each PSU • 220 VAC (Volts Alternate Current) input (a single PSU runs between 180V and 260V AC) • 50Hz or 60Hz input • 14A maximum input • 192A (Amps) @ + 12 Volts DC ( Direct Current) output Operational • 4.5A @ +12 Volt output Standby • 3 or 6 PSU configurations available • PSUs are hot-swappable 5.3 Heat Dissipation The cooling strategy for the M1000e supports a low‐impedance, high‐efficiency design philosophy. Driving lower airflow impedance allows the M1000e to draw air through the system at a lower operating pressure and reduces the system fan power consumed to meet the airflow requirements of the system. The low impedance design is coupled with a high‐efficiency air-moving device designed explicitly for the PowerEdge M1000e chassis. The efficiency of an air-moving device is defined as the work output PowerEdge M1000e Technical Guide 30