Dell S5148F-ON EMC Networking OS10 Enterprise Edition Switch Configuration Gui - Page 12
Topology options
 |
View all Dell S5148F-ON manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
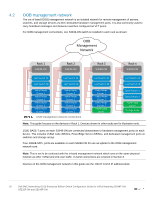
3 Topology options VxRail may be deployed using a single or dual switch topology. Using a single switch provides the lowest initial cost but creates a single point of failure. A dual switch configuration helps ensure high availability by eliminating this single point of failure. A dual switch configuration may be used with or without VLT. Dell EMC recommends a dual switch configuration with VLT. The sections that follow explain the different options. 3.1 Dual switch In a dual switch topology, each VxRail node has one or more connections to each of the two leaf switches providing redundancy at the NIC and switch levels. If VLT is used, the switches are connected with a VLT interconnect (VLTi). If VLT is not used, the switches are connected with a standard LACP port channel. 3.1.1 Dual switch with VLT Dell EMC recommends using a dual switch configuration with VLT as shown in Figure 9. S5148F-Leaf1A S5148F-Leaf1B VLTi 12 VxRail node 1 12 VxRail node 2 100GbE VLTi connections 25GbE connections 12 VxRail node n Rack 1 Dual switch topology with VLT VLT synchronizes ARP, MAC tables, and IPv6 neighbors between the VLT peers and makes the switch pair appear as one logical unit to connected devices. VLT provides the following benefits: • Provides a loop-free topology and eliminates STP-blocked ports • Optimizes the use of all available uplink bandwidth • Guarantees fast convergence if either a link or a device fails 12 Dell EMC Networking OS10 Enterprise Edition Switch Configuration Guide for VxRail featuring S5248F-ON, S5232F-ON and S5148F-ON