HP Indigo W7250 Strain Gauge Second Transfer Measurement Service and Troublesh - Page 6
Principles of Operation, Wheatstone bridge, Wheatstone bridge diagram, Strain Gauge - How It Works
 |
View all HP Indigo W7250 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
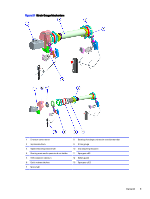
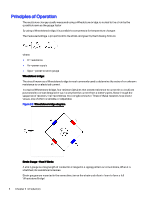
Principles of Operation The resistance change, usually measured using a Wheatstone bridge, is related to the strain by the quantity known as the gauge factor By using a Wheatstone bridge, it is possible to compensate for temperature changes The measured voltage is proportional to the strain, and given by the following formula where: ● R = resistance ● Vs = power supply ● Vgsa - power to strain gauge Wheatstone bridge: The circuit known as a Wheatstone bridge is most commonly used to determine the value of an unknown resistance to an electrical current. In a typical Wheatstone bridge, four resistors (devices that create resistance to current in a circuit) are positioned in a circuit designed in such a way that the current from a battery splits, flows through the sequence of resistors, then recombines into a single conductor, Three of these resistors have known values, one of which is variable, or adjustable. Figure 2-2 Wheatstone bridge diagram Strain Gauge - How It Works A strain gauge is a long length of conductor arranged in a zigzag pattern on a membrane, When it is stretched, its resistance increases. Strain gauges are mounted in the same direction as the strain and often in fours to form a full 'Wheatstone Bridge' 4 Chapter 2 Introduction