HP ML150 Optimizing facility operation in high density data center environment - Page 10
Methods for calculating power supply requirements, Power protection and management - proliant power switch
 |
UPC - 884420743644
View all HP ML150 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
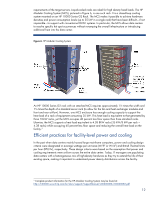
It provides the height, weight, power, and thermal requirements for each system to be racked as well as the requirements for the fully configured rack. These specifications are crucial for data center managers who must know whether these specifications fall within acceptable parameters for their existing facility infrastructures, or for those managers who require planning data to support IT equipment upgrades. Methods for calculating power supply requirements Requirements for uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) can be calculated using sizers from the equipment maker. Using a UPS sizer is important to prevent over provisioning of power resources. A sizer for HP UPSes is available at: www.upssizer.com. Power protection and management UPS management modules can enable the administrator to monitor and manage power environments through comprehensive control of UPSes. Such modules can support either a single or multiple UPS configurations providing redundancy and no-single-point-of-failure. The management module can be configured to send alert traps to networked remote management programs or be used as a stand-alone management system. Rack based power distribution The ability to monitor and manage power distribution units (PDU) is key to optimizing rack-based power distribution. PDUs can provide power displays for local monitoring and serial ports for remote monitoring. This can be augmented with a management module enabling the administrator to monitor power environments through comprehensive control of individual PDUs. Embedded network capabilities can also allow these modules to be tied into comprehensive remote management suites. To learn more about HP examples of both UPS and PDU hardware and management tools, see the technology brief titled "Critical factors in intra-rack power distribution planning for high-density systems" in the "For more information" section at the end of this document. High-efficiency power supplies All ProLiant servers are equipped with high-efficiency switch-mode power supplies, when compared to typical power supplies in the industry. For example, a typical white-box server power supply has an efficiency rating between 65 percent and 70 percent. ProLiant servers operate with efficiencies of 85 percent or greater when connected to a high-line voltage source. ProLiant server power supplies operate at maximum efficiency when connected to high-line input power (200 to 240 VAC). As with typical power supplies in the industry, operating at low line power (100 to 120 VAC) causes the power supply to operate at a lower efficiency and to draw more current for the same power output. Understanding Internal airflow HP rack-mounted equipment is designed for front-to-back cooling. This means that the following conditions must exist: • At least 65 percent of each of the front and rear rack surfaces must be open • Airflow must be configured to force all air through the front and allow it to exhaust easily through the rear. This is promoted by using gaskets, blanking panels, and efficient cable management. Even with the designation for cabinet doors that are 65 percent open to incoming airflow. There is still a 35 percent restriction to air discharged by the equipment in the rack. Servers will intake air from the path of least resistance. Therefore, they will access the higher-pressure discharge air flowing inside the cabinet mare easily than they will access cooling air coming through the front of the cabinet. Some configurations, such as those with extreme cable or server density, may create a backpressure situation forcing heated exhaust air around the side of a server and back into its inlet. 10