HP Workstation x2100 hp workstation x2100 - Linux getting started guide and wa - Page 46
booting single user mode directly
 |
View all HP Workstation x2100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
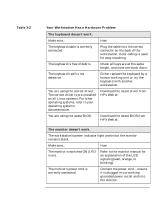
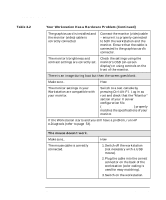
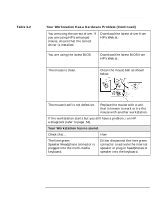
Linux system setup and recovery recovering your Linux system Table 2-1 Linux Commands (Continued) gunzip mke2fs probe zcat NOTE The man command is not available in rescue mode. Make sure you know how to use all the above commands before you use rescue mode. If your root file system is undamaged, you can mount it and then run any standard Linux utility. For example, suppose your root file system is in /dev/hda5. Here is how to mount this partition: mount -t ext2 /dev/hda5 /foo Where /foo is a directory that you have created. Now you can run man and other utilities. At this point, you are running Linux in single-user mode. If you do not know the names of your Linux partitions, you can guess; mounting non-existent partitions will do no harm. booting single user mode directly You may be able to boot single-user mode directly. If your system boots, but does not allow you to login when it has completed booting, try rebooting and specifying one of these options at the LILO boot prompt: LILO boot: linux single LILO boot: linux emergency In single-user mode, you computer boots to run level 1. Your local file systems will be mounted but your network will not be activated. You get a usable system maintenance shell. In emergency mode, you are booted into the most minimal environment possible. The root file system will be mounted read-only and almost nothing will be set up. The main advantage of this over Linux single user is that your init files are not loaded. If init is corrupted or not working, you can still mount file systems to recover data that could be lost during a re-installation. 46 Chapter 2
-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72
 |
 |

