Hitachi NR90GC Service Manual - Page 18
the Pushing Lever [64], When pressing the Pushing Lever [64] after
 |
UPC - 717709008533
View all Hitachi NR90GC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
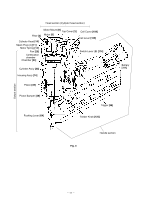
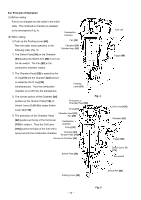
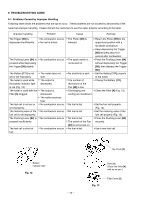
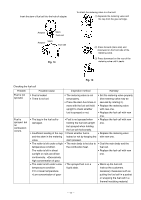
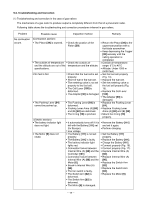
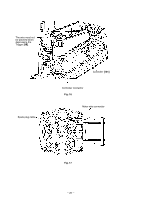
(5) Full sequential action mechanism Press the Pushing Lever [64] against the workpiece and move the Chamber [24] to the uppermost position. Then the nailer operates only when the Trigger [98] is depressed. The nailer does not operate if the pressing amount of the Pushing Lever [64] is insufficient or if the Pushing Lever [64] is pressed after depressing the Trigger [98]. Tension Plate [113] Convex portion of the Chamber [24] When depressing the Trigger [98] after pressing the Pushing Lever [64] The convex portion of the Chamber [24] pushes up the Tension Plate [113] and rotates when the Chamber [24] reaches the uppermost position. Therefore, the end of Switch Lever (B) [114] is moved toward the Trigger [98] (Fig. 9). The Lever Stopper [116] at the side of the Trigger [98] does not prevent Switch Lever (B) [114] from Pushing Lever [64] rotating (Fig. 10). The switch is turned on and nails are driven by depressing the Trigger [98]. Fig. 9 Switch Lever (B) [114] A A A Trigger [98] When pressing the Pushing Lever [64] after depressing the Trigger [98] When depressing the Trigger [98], the Lever Stopper [116] is deformed by the Trigger [98] and the end of the Lever Stopper [116] is positioned toward Switch Lever (B) [114] (Fig. 11). Lever Stopper [116] Then the convex portion of the Chamber [24] pushes up the Tension Plate [113] when the Pushing Lever [64] is pressed. However, the Lever Stopper [116] prevents Switch Lever (B) [114] from rotating. Thus the switch of the Trigger [98] is not turned on. Switch Lever (B) [114] Trigger [98] Fig. 10 (A --- A) Switch Lever (B) [114] Lever Stopper [116] Trigger [98] Fig. 11 (A --- A) --- 15 ---