Stihl HT 101 Instruction Manual - Page 14
To Avoid Pull-in - pruner
 |
View all Stihl HT 101 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
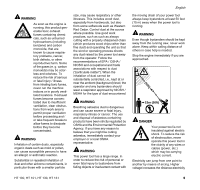
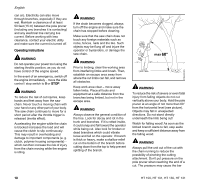
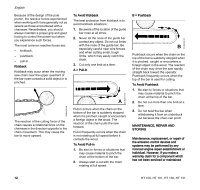
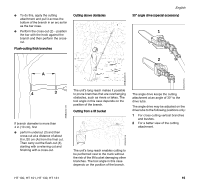
002BA230 KN 001BA037 KN 001BA038 KN English Because of the design of the pole pruner, the reactive forces experienced when working with it are generally not as severe as those encountered with a chainsaw. Nevertheless, you should always maintain a proper grip and good footing to control the power tool when you experience such forces. The most common reactive forces are: - kickback, - pushback, - pull-in. Kickback Kickback may occur when the moving saw chain near the upper quadrant of the bar nose contacts a solid object or is pinched. The reaction of the cutting force of the chain causes a rotational force on the chainsaw in the direction opposite to the chain movement. This may cause the bar to move upward. To Avoid Kickback The best protection from kickback is to avoid kickback situations: 1. Be aware of the location of the guide bar nose at all times. 2. Never let the nose of the guide bar contact any object. Do not cut limbs with the nose of the guide bar. Be especially careful near wire fences and when cutting small, tough limbs, which may easily catch the chain. 3. Cut only one limb at a time. A = Pull-in A Pull-in occurs when the chain on the bottom of the bar is suddenly stopped when it is pinched, caught or encounters a foreign object in the wood. The reaction of the chain pulls the saw forward. Pull-in frequently occurs when the chain is not rotating at full speed before it contacts the wood. To Avoid Pull-in 1. Be alert to forces or situations that may cause material to pinch the chain at the bottom of the bar. 2. Always start a cut with the chain rotating at full speed. B = Pushback B Pushback occurs when the chain on the top of the bar is suddenly stopped when it is pinched, caught or encounters a foreign object in the wood. The reaction of the chain may drive the saw rapidly straight back toward the operator. Pushback frequently occurs when the top of the bar is used for cutting. To Avoid Pushback 1. Be alert to forces or situations that may cause material to pinch the chain at the top of the bar. 2. Do not cut more than one limb at a time. 3. Do not twist the bar when withdrawing it from an underbuck cut because the chain can pinch. MAINTENANCE, REPAIR AND STORING Maintenance, replacement, or repair of the emission control devices and systems may be performed by any nonroad engine repair establishment or individual. However, if you make a warranty claim for a component which has not been serviced or maintained 12 HT 100, HT 101, HT 130, HT 131