Dell PowerConnect W-IAP3WN Dell Instant 6.2.0.0-3.2.0.0 User Guide - Page 144
Understanding WPA and WPA2, Recommended Authentication and Encryption Combinations, Personal
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W-IAP3WN manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 144 highlights
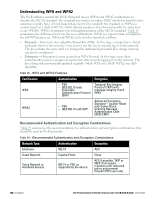
Understanding WPA and WPA2 The Wi-Fi Alliance created the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and WPA2 certifications to describe the 802.11i standard. The standard was written to replace WEP, which was found to have numerous security flaws. It took longer than expected to complete the standard, so WPA was created based on a draft of 802.11i, which allowed people to move forward quickly to create more secure WLANs. WPA2 encompasses the full implementation of the 802.11i standard. Table 18 summarizes the differences between the two certifications. WPA2 is a superset that encompasses the full WPA feature set. WPA and WPA2 can be further classified as follows: l Personal - Personal is also called Pre-Shared Key (PSK). In this type, a unique key is shared with each client in the network. Users have to use this key to securely log in to the network. The key remains the same until it is changed by authorized personnel. Key change intervals can also be configured. l Enterprise - Enterprise is more secure than WPA Personal. In this type, every client automatically receives a unique encryption key after securely logging on to the network. This key is long and automatically updated regularly. While WPA uses TKIP, WPA2 uses AES algorithm. Table 18 - WPA and WPA2 Features Certification WPA Authentication l PSK l IEEE 802.1X with Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Encryption Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) with message integrity check (MIC) WPA2 l PSK l IEEE 802.1X with EAP Advanced Encryption Standard -- Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code (AESCCMP) Recommended Authentication and Encryption Combinations Table 19 summarizes the recommendations for authentication and encryption combinations that should be used in Wi-Fi networks. Table 19 - Recommended Authentication and Encryption Combinations Network Type Employee Authentication 802.1X Encryption AES Guest Network Captive Portal None Voice Network or Handheld devices 802.1X or PSK as supported by the device AES if possible, TKIP or WEP if necessary (combine with restricted policy enforcement firewall (PEF) user role). 144 | Encryption Dell PowerConnect W-Series Instant Access Point 6.2.0.0-3.2.0.0 | User Guide