HP BL260c ISS Technology Update, Volume 6 Number 7 - Newsletter - Page 11
Note that live AC circuits still exist inside the power enclosure even if both of the power enclosure AC breakers are turned off.
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
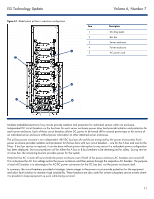
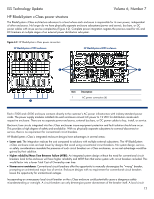
ISS Technology Update Figure 4-1. BladeSystem p-Class in maximum configuration Item 1 2 3 4 n 5 o Volume 6, Number 7 Description DC drop leads Bus bar Server enclosure Power enclosure AC power cord p r q Multiple embedded electronic fuse circuits provide isolation and protection for individual servers within an enclosure. Independent DC circuit breakers on the bus bars for each server enclosure power drop lead provide isolation and protection for each server enclosure. Each of these circuit breakers allows DC power to be turned off for unused power taps or for service of an individual server enclosure without power interruption to other attached server enclosures. The p-Class power structure's two independent -48 VDC bus bars (A and B) are energized by the power enclosure(s). Each power enclosure provides isolation and protection for the bus bars with two circuit breakers - one for the A bus and one for the B bus. If bus bar service is required, it can be done without power interruption to any server if a redundant power configuration has been deployed. Service procedures call for either the A bus or B bus breakers to be de-energized for safety. During service of a bus bar, the remaining bus bar provides power for the system. Note that live AC circuits still exist inside the power enclosure even if both of the power enclosure AC breakers are turned off. This is because the AC line voltage enters the power enclosure and then passes through the respective AC breaker. The purpose of each AC breaker is to de-energize the AC-DC power conversion for the DC bus bar, not the power enclosure itself. In summary, the circuit breakers provided at strategic interim stages in the power circuit provide protection for the equipment and allow fault isolation to maintain high availability. These breakers are also useful for certain subsystem service events where it is possible to keep equipment up even while being serviced. 11