HP BL260c ISS Technology Update, Volume 6 Number 7 - Newsletter - Page 8
How to use the data collected from the request output, Additional resources, Table 2-1., Location
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
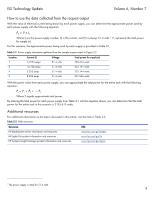
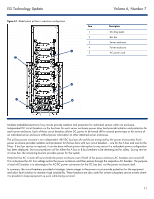
ISS Technology Update Volume 6, Number 7 How to use the data collected from the request output With the value of electrical current being drawn by each power supply, you can determine the approximate power used by each power supply with the following equation: Pn = V x In Where (n) is the power supply number, (I) is the current, and (V) is always 51.4 volts.1 Pn represents the total power for supply (n). For this scenario, the approximate power being used by each supply is provided in Table 2-1. Table 2-1. Power supply information gathered from the sample request output in Figure 2-2 Location 1 2 4 5 Current (I) 14.973 amps 12.708 amps 5.353 amps 8.904 amps Voltage 51.4 volts 51.4 volts 51.4 volts 51.4 volts Total power for supply (n) 769.612 watts 653.191 watts 275.144 watts 457.666 watts With the power value from each power supply, you can approximate the total power for the entire rack with the following equation: Pt = P1 + P2 + xxx Pn Where Pt equals approximate total power. By entering the total power for each power supply from Table 2-1 into the equation above, you can determine that the total power for the entire rack in this scenario is 2155.613 watts. Additional resources For additional information on the topics discussed in this article, visit the links in Table 2-2. Table 2-2. Web resources Resource URL HP BladeSystem server information and resources www.hp.com/go/blades HP Lights-Out product information and resources www.hp.com/go/ilo HP Systems Insight Manager product information and resources www.hp.com/go/hpsim 1 The power supply is rated for 51.4 volts. 8