HP Cisco Nexus 5000 Cisco MDS 9000 Family Release Notes for Cisco MDS NX-OS Re - Page 23
Upgrading with IVR Enabled, Current Release with, FICON Enabled, Upgrade Path
 |
View all HP Cisco Nexus 5000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
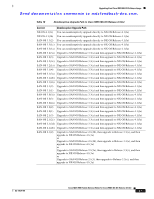
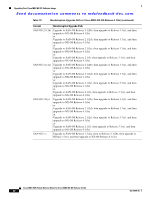
Upgrading Your Cisco MDS NX-OS Software Image Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc.com. Use Table 11 to determine your FICON nondisruptive upgrade path to Cisco MDS NX-OS Release 4.1(3a). Find the image release number you are currently using in the Current Release with FICON Enabled column of the table and use the path recommended. Table 11 FICON Nondisruptive Upgrade Path to NX-OS Release 4.1(3a) Current Release with FICON Enabled NX-OX 4.1(1c) SAN-OS 3.3(1c) SAN-OS 3.2(2c) SAN-OS 3.0(3b) SAN-OS 3.0(2) SAN-OS 3.0(1) and earlier SAN-OS 2.0(2b) SAN-OS 1.x Upgrade Path You can nondisruptively upgrade directly to NX-OS Release 4.1(3a). You can nondisruptively upgrade directly to NX-OS Release 4.1(3a). First upgrade to SAN-OS Release 3.3(1c) and then upgrade to NX-OS Release 4.1(1c). First upgrade to SAN-OS Release 3.3(1c) and then upgrade to NX-OS Release 4.1(3a). First upgrade to SAN-OS Release 3.3(1c) and then upgrade to NX-OS Release 4.1(3a). First upgrade to SAN-OS Release 3.3(1c) and then upgrade to NX-OS Release 4.1(3a). Use the interface shutdown command to administratively shut any Fibre Channel ports on Generation 1 modules that are in an operationally down state before nondisruptively upgrading from SAN-OS Release 2.0(2b) to SAN-OS Release 3.0(2) or SAN-OS Release 3.0(3b), and then upgrade to Release 3.3(1c). An operationally down state includes Link failure or not-connected, SFP not present, or Error Disabled status in the output of a show interface command. When an interface is administratively shut it will then show as Administratively down. Interfaces that are currently up or trunking do not need to be shut down. Upgrade to SAN-OS Release 3.0(2). Use the interface shutdown command to shut all the ports operationally down and administratively up on all the Generation 1 modules before nondisruptively upgrading to Release 2.0(2b) and then upgrade to 1.3(4a). Upgrading with IVR Enabled An Inter-Switch Link (ISL) flap resulting in fabric segmentation or a merge during or after an upgrade from Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.0(x) to a later image where IVR is enabled might be disruptive. Some possible scenarios include the following: • FCIP connection flapping during the upgrade process resulting in fabric segmentation or merge. • ISL flap results in fabric segmentation or merge because of hardware issues or a software bug. • ISL port becomes part of PCP results in fabric segmentation or merge because of a port flap. If this problem occurs, syslogs indicate a failure and the flapped ISL could remain in a down state because of a domain overlap. OL-17675-05 Cisco MDS 9000 Family Release Notes for Cisco MDS NX-OS Release 4.1(3a) 23