HP Jetdirect 610n HP Jetdirect Print Servers - HP Jetdirect and SSL/TLS - Page 13
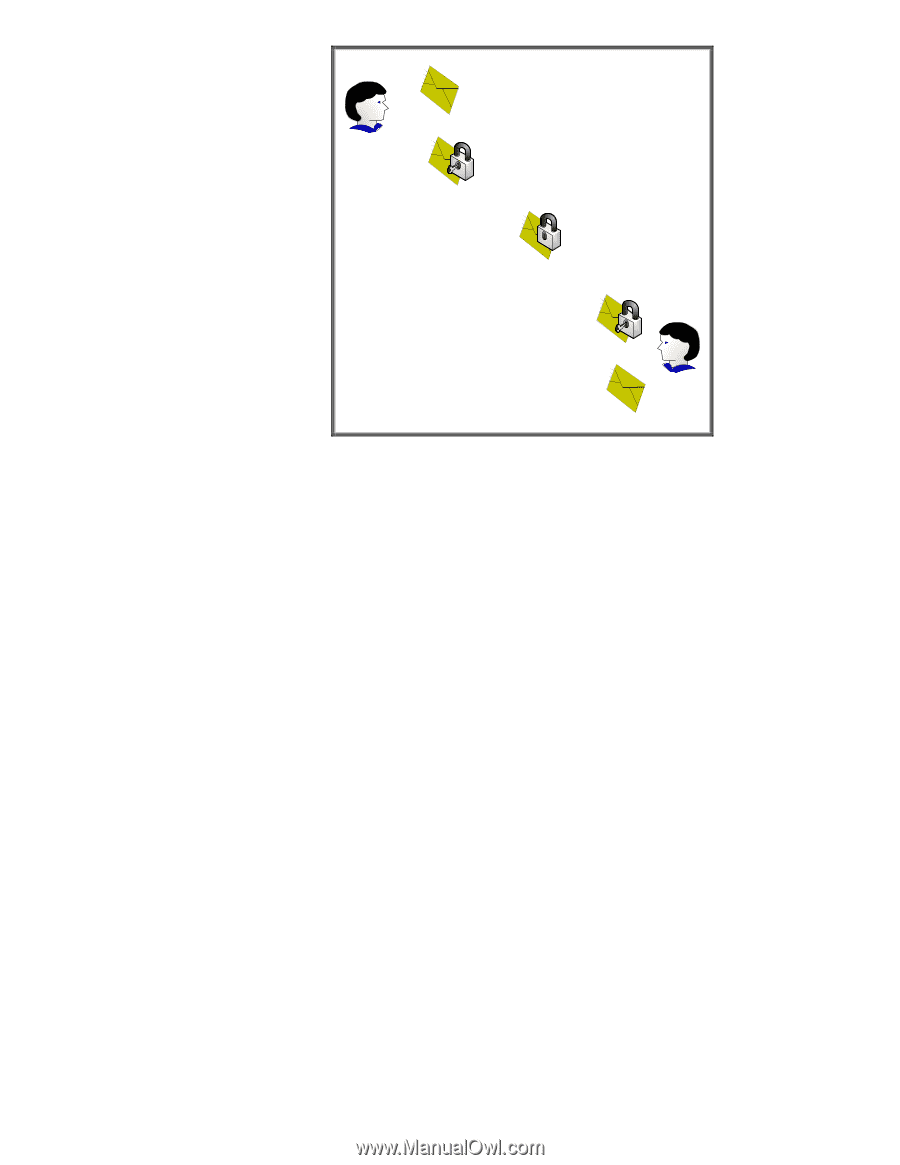
Symmetric Cryptography
 |
View all HP Jetdirect 610n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
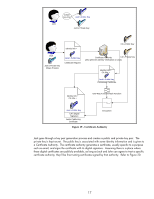
User Unencrypted Message Encryption Performed Message Delivery Decryption Performed User Unencrypted Message Figure 15 - Symmetric Cryptography In Figure 15, the confidentiality provided to the message is done via a single key. Because the same key is used for encryption and decryption, this process is known as symmetric cryptography. Symmetric cryptography commonly has two attributes associated with it: • It performs well - it is fast and easy to implement • It has a key distribution problem - how do you get the symmetric key to everyone that needs it in a secure way? Asymmetric cryptography is also available and functions very different than symmetric cryptography. It has two keys - one Public and one Private. The private key is not shared with anyone. The Public key is like a public telephone number. You can share it with everyone. Let's look at Figure 16 - Asymmetric Cryptography. 13