HP Pavilion a6000 Start Here Guide - Page 59
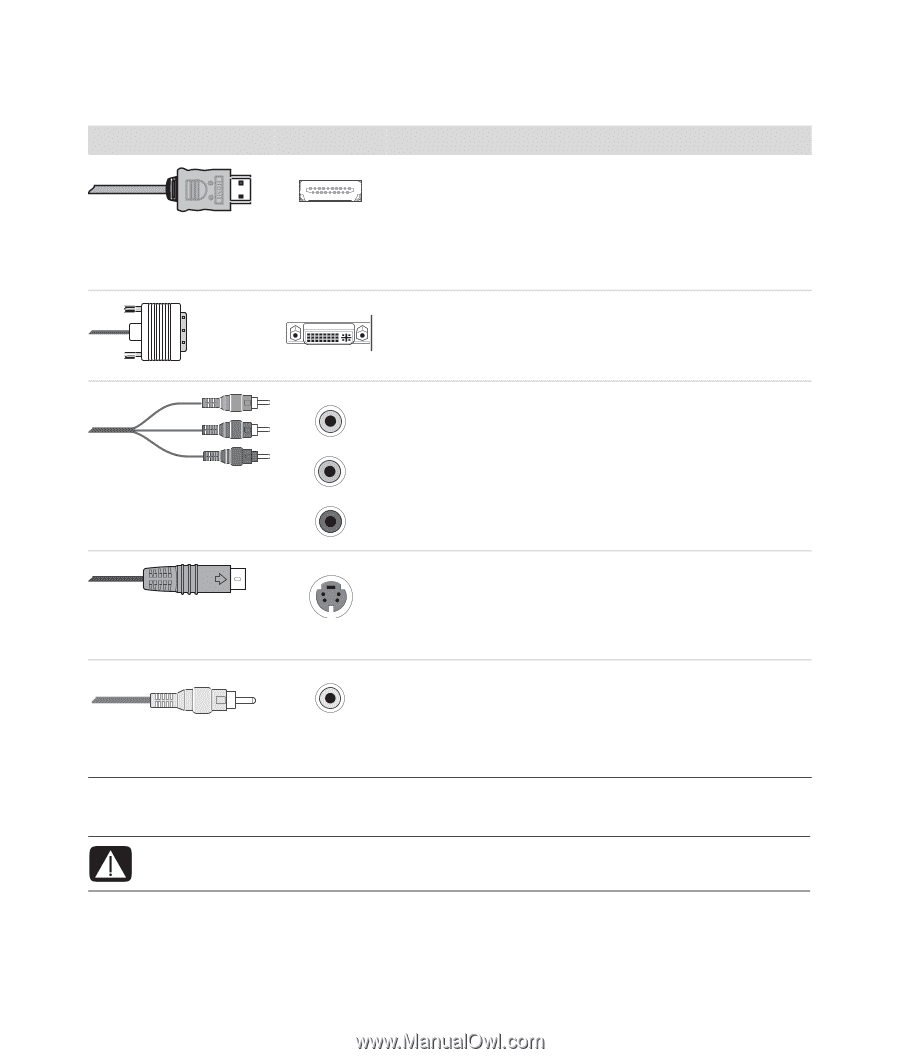
Cable, Connection description, Component video, S-video, Example: A DVD/VHS player to a TV.
 |
View all HP Pavilion a6000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 59 highlights
The following table shows the possible AV connection types, listed in order of decreasing video playback quality (from best to good). Cable Port Connection description HDMI transmits an all-digital signal and is the recommended choice for playback from a digital DVD or DVR. It is capable of transmitting both uncompressed digital audio and digital video signals, because it has video, audio and control signals. For more information, see "Connecting an HDMI device." DVI transmits an all-digital video signal for playback from a digital DVD or DVR. For more information, see "Connecting a DVI device." Component video transmits video as separate red (Pr), green (Y), and blue (Pb) signals. It is available in standarddefinition and high-definition (HD) versions. It delivers higher quality than S-video and composite video connections. Example: A TV to a DVD player. For more information, see "Connecting to component video." S-video transmits video. (The "S" stands for "separate.") It delivers a sharper image than a composite video connection. Example: A TV to a VCR. For more information, see "Connecting to S-video." Composite video transmits video as a single signal. It usually has a yellow tip. It delivers a less sharp image than component video and S-video connections. Example: A DVD/VHS player to a TV. The remainder of this chapter describes how to connect optional equipment, including the audio connections when applicable. The order follows that of the preceding table. WARNING: Before connecting optional equipment, unplug the power cord for the TV and all connected components. Ensure that the optional equipment is turned off. Connecting the Television Signal and Video Cables 53