Intel DG965WH Product Specification - Page 49
DMA Channels, PCI Interrupt Routing Map
 |
View all Intel DG965WH manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
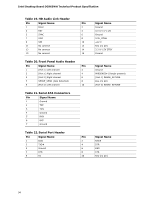
Technical Reference 2.6 DMA Channels Table 16. DMA Channels DMA Channel Number Data Width 0 8 or 16 bits 1 8 or 16 bits 2 8 or 16 bits 3 8 or 16 bits 4 8 or 16 bits 5 16 bits 6 16 bits 7 16 bits System Resource Open Parallel port Diskette drive Parallel port (for ECP or EPP) DMA controller Open Open Open 2.7 PCI Interrupt Routing Map This section describes interrupt sharing and how the interrupt signals are connected between the PCI bus connectors and onboard PCI devices. The PCI specification specifies how interrupts can be shared between devices attached to the PCI bus. In most cases, the small amount of latency added by interrupt sharing does not affect the operation or throughput of the devices. In some special cases where maximum performance is needed from a device, a PCI device should not share an interrupt with other PCI devices. Use the following information to avoid sharing an interrupt with a PCI add-in card. PCI devices are categorized as follows to specify their interrupt grouping: • INTA: By default, all add-in cards that require only one interrupt are in this category. For almost all cards that require more than one interrupt, the first interrupt on the card is also classified as INTA. • INTB: Generally, the second interrupt on add-in cards that require two or more interrupts is classified as INTB. (This is not an absolute requirement.) • INTC and INTD: Generally, a third interrupt on add-in cards is classified as INTC and a fourth interrupt is classified as INTD. The ICH8 has eight Programmable Interrupt Request (PIRQ) input signals. All PCI interrupt sources either onboard or from a PCI add-in card connect to one of these PIRQ signals. Some PCI interrupt sources are electrically tied together on the board and therefore share the same interrupt. Table 17 shows an example of how the PIRQ signals are routed. For example, using Table 17 as a reference, assume an add-in card using INTA is plugged into PCI bus connector 3. In PCI bus connector 3, INTA is connected to PIRQB, which is already connected to the ICH8 audio controller. The add-in card in PCI bus connector 3 now shares an interrupt with the onboard interrupt source. 49