LG 42PC5DC Owners Manual - Page 114
Transmission, Acknowledgemen, AcknowledgernenL
 |
UPC - 719192171688
View all LG 42PC5DC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 114 highlights
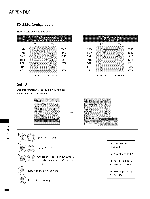
Data 05: The table above lists the binary code which must be converted to Hexadecimal before sending. For example: The binary code to tune the sub source to an NTSC cable channel is "1000 0001 ", which translates to "81" in Hex. 7th bit : For which source do you want to change the channel. 6th bit: Use a two part or one part channel. Most cases just use 0 since it's ignored when using NTSC. 5th bit: Use 0 with NTSC since it can only use the physical channel number. Normally use 1 for ATSC since most times it doesn't matter what the physical number is. 4th bit: Set to 0. 3-0 bits: Choose signal type. 22. Channel Add/Del (Command: m b) To add and delete the channels. Transmission [m] [b][] [Set ID][ ][Data] [cr] Data 00: Channel Delete Data 01 : Channel Add Acknowledgemen_ [b][ ][Set ID][ ][OKiNG] [Data] [x] 23. Key (Command: m c) To send IR remote key code. Transmission [m] [c] [ ] [Set ID] [ ] [Data] [Cr] p.106. AcknowledgernenL [c] [ ] [Set ID] [ ] [OKiNG] [Data] [x] Tune Command Examples: 1. Tune to the analog (NTSC) cable channel 35. Data 00 = Physical of 35 = 23 Data 01 & 02 = No Major = 00 00 Data 03 & 04 = No Minor = 00 00 Z C7 Data 05 = 0000 0001 in binary = 01 X Tota I = ma 0023 0000000001 2. Tune to the digital (ATSC) local channel 30-3. Data 00 = Don't know Physical = 00 Data 01 &02 = Major is 30 = 00 1E Data 03 & 04 = Minor is 3 = 0003 Data 05 = 0010 0010 in binary = 22 Tota I = ma 000000 1E0003 22 Ackno_ledg_men![a][] [Set !D][] [O K] [DataO0] [DataO] ] [Data02] [Data05] [Data04 ] [x] [a][] [Set !D NG] [DataO0] [x] 112