Linksys WRE54G Cisco WAP54GP Wireless-G Exterior Access Point User Guide - Page 7
Introduction - help
 |
UPC - 745883559046
View all Linksys WRE54G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
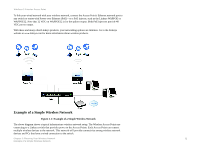
Wireless-G Exterior Access Point Chapter 1: Introduction Welcome Thank you for choosing the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point. This Access Point will allow you to network wirelessly better than ever. How does the Access Point do all of this? An access point allows for greater range and mobility within your wireless network while also allowing you to connect the wireless network to a wired environment. In fact, the Wireless-G Exterior Access Point can support communications on up to eight wireless networks, using Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) technology. The Wireless-G Exterior Access Point also offers the convenience of Power over Ethernet (PoE) capability, so it can receive data and power over a single Ethernet network cable. And with the advantage of its weatherresistant housing, you can mount the Access Point outside to extend your wireless networking range and mobility to the outdoors. You can even connect wired networks in two different buildings, by using two Access Points set to Wireless Bridge mode. But what does all of this mean? Networks are useful tools for sharing computer resources. You can access one printer from different computers and access data located on another computer's hard drive. Networks are even used for playing multiplayer video games. So, networks are not only useful in homes and offices, they can also be fun. PCs on a wired network create a LAN, or Local Area Network. They are connected with Ethernet cables, which is why the network is called "wired". PCs equipped with wireless client cards or adapters can communicate without cumbersome cables. By sharing the same wireless settings, within their transmission radius, they form a wireless network. This is sometimes called a WLAN, or Wireless Local Area Network. The Access Point bridges wireless networks of both 802.11g and 802.11b standards and wired networks. Use the instructions in this Guide to help you connect the Access Point, set it up, and configure it to bridge your different networks. These instructions should be all you need to get the most out of the Access Point. access point: a device that allows wireless-equipped computers and other devices to communicate with each other and with devices on a wired network. Also used to expand the range of a wireless network. network: a series of computers or devices connected together. lan (local area network): the computers and networking devices that make up your local network. poe (power over ethernet): a technology enabling an Ethernet network cable to deliver both data and power. ethernet: network protocol defined in IEEE 802.3 standard that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved from a common transmission medium. adapter: a device that adds network functionality to your PC. 802.11g: a wireless networking standard that specifies a maximum data transfer rate of 54Mbps, an operating frequency of 2.4GHz, and backward compatibility with 802.11b devices. 802.11b: a wireless networking standard that specifies a maximum data transfer rate of 11Mbps and an operating frequency of 2.4GHz. Chapter 1: Introduction 1 Welcome