Asus P4G8X P4G8X User Manual - Page 127
RAID 0/RAID 1 configurations
 |
View all Asus P4G8X manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 127 highlights
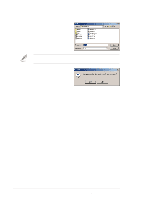
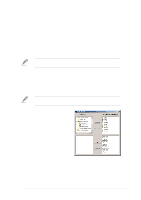
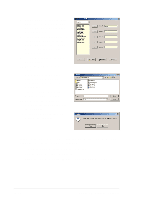
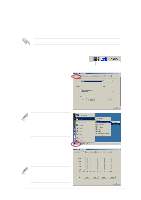
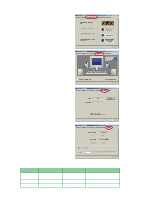
5.4 RAID 0/RAID 1 configurations The motherboard includes the Silicon Image Sil3112A controller chipset and two Serial ATA interfaces to support Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) configuration. This feature supports Serial ATA hard disks. Use the SATARaid™ utility to configure a RAID set. RAID 0 (called data striping) optimizes two identical hard disk drives to read and write data in parallel, interleaved stacks. Two hard disks perform the same work as a single drive but at a sustained data transfer rate, double that of a single disk alone, thus improving data access and storage. RAID 1 (called data mirroring) copies and maintains an identical image of data from one drive to a second drive. If one drive fails, the disk array management software directs all applications to the surviving drive as it contains a complete copy of the data in the other drive. This RAID configuration provides data protection and increases fault tolerance to the entire system. 5.4.1 Install the hard disks The Sil3112A chipset supports Serial ATA hard disk drives. For optimal performance, install identical drives of the same model and capacity when creating a RAID set. • If you are creating a RAID 0 (striping) array for perfomance, use two new drives. • If you are creating a RAID 1 (mirroring) array for protection, you can use two new drives or use an existing drive and a new drive (the new drive must be of the same size or larger than the existing drive). If you use two drives of different sizes, the smaller capacity hard disk will be the base storage size. For example, one hard disk has an 80GB storage capacity and the other hard disk has 60GB storage capacity, the maximum storage capacity for the RAID 1 set is 60GB. ASUS P4G8X series motherboard user guide 5-23